Here is the sequence of triangular numbers, created by summing consecutive integers from 1 (i.e., 1+2+3+4+5…):
1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, 28, 36, 45, 55, 66, 78, 91, 105, 120, 136, 153, 171, 190, 210, 231, 253, 276, 300, 325, 351, 378, 406, 435, 465, 496, 528, 561, 595, 630, 666, 703, 741, 780, 820, 861, 903, 946, 990, 1035, 1081, 1128, 1176, 1225, 1275, 1326, 1378, 1431, 1485, 1540, 1596, 1653, 1711, 1770, 1830, 1891, 1953, 2016, 2080, 2145, 2211, 2278, 2346, 2415, 2485, 2556, 2628, 2701, 2775, 2850, 2926, 3003, 3081, 3160, 3240, 3321, 3403, 3486, 3570, 3655, 3741, 3828, 3916, 4005, 4095, 4186, 4278, 4371, 4465, 4560, 4656, 4753, 4851, 4950, 5050, 5151, 5253, 5356, 5460, 5565, 5671, 5778, 5886, 5995...
And here is a sequence of truncated triangulars, created by summing consecutive integers from 15 (i.e., 15+16+17+18+19…):
15, 31, 48, 66, 85, 105, 126, 148, 171, 195, 220, 246, 273, 301, 330, 360, 391, 423, 456, 490, 525, 561, 598, 636, 675, 715, 756, 798, 841, 885, 930, 976, 1023, 1071, 1120, 1170, 1221, 1273, 1326, 1380, 1435, 1491, 1548, 1606, 1665, 1725, 1786, 1848, 1911, 1975, 2040, 2106, 2173, 2241, 2310, 2380, 2451, 2523, 2596, 2670, 2745, 2821, 2898, 2976, 3055, 3135, 3216, 3298, 3381, 3465, 3550, 3636, 3723, 3811, 3900, 3990, 4081, 4173, 4266, 4360, 4455, 4551, 4648, 4746, 4845, 4945, 5046, 5148, 5251, 5355, 5460, 5566, 5673, 5781...
It’s obvious that the sequences are different at each successive step: 1 ≠ 15, 3 ≠ 31, 6 ≠ 48, 10 ≠ 66, 21 ≠ 85, and so on. But seven numbers occur in both sequences: 15, 66, 105, 171, 561, 1326 and 5460. And that’s it — 7 is the 14-th entry in A309507 at the Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences:
0, 1, 1, 1, 3, 3, 1, 2, 5, 3, 3, 3, 3, 7, 3, 1, 5, 5, 3, 7, 7, 3, 3, 5, 5, 7, 7, 3, 7, 7, 1, 3, 7, 7, 11, 5, 3, 7, 7, 3, 7, 7, 3, 11, 11, 3, 3, 5, 8, 11, 7, 3, 7, 15, 7, 7, 7, 3, 7, 7, 3, 11, 5, 3, 15, 7, 3, 7, 15, 7, 5, 5, 3, 11, 11, 7, 15, 7, 3, 9, 9, 3, 7 — A309507
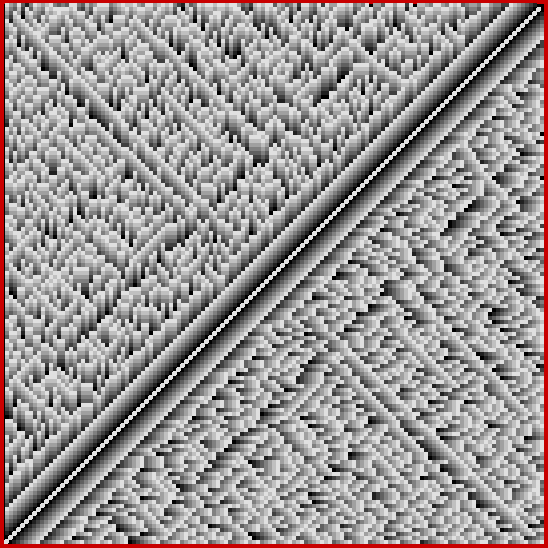
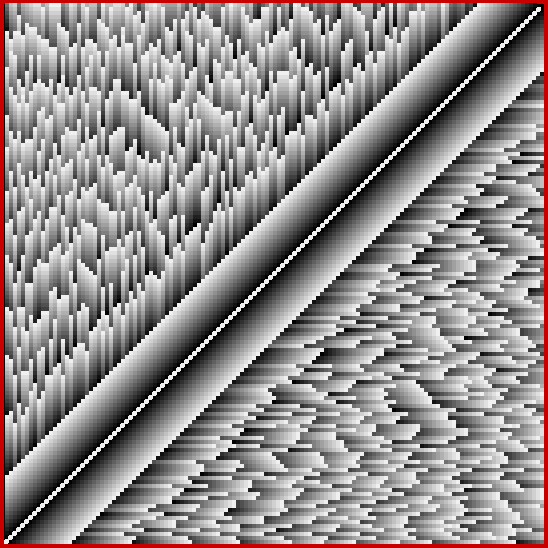
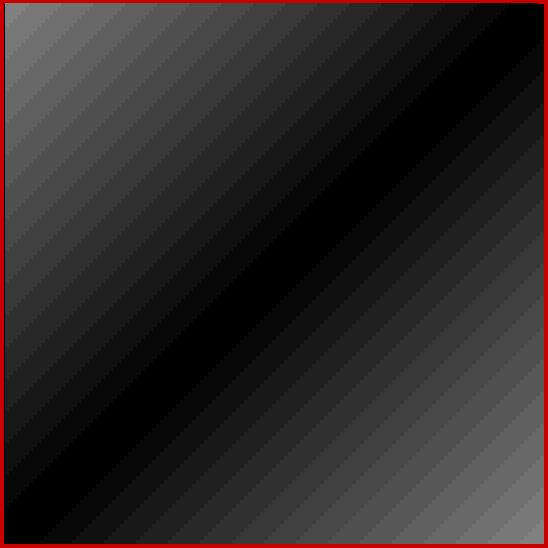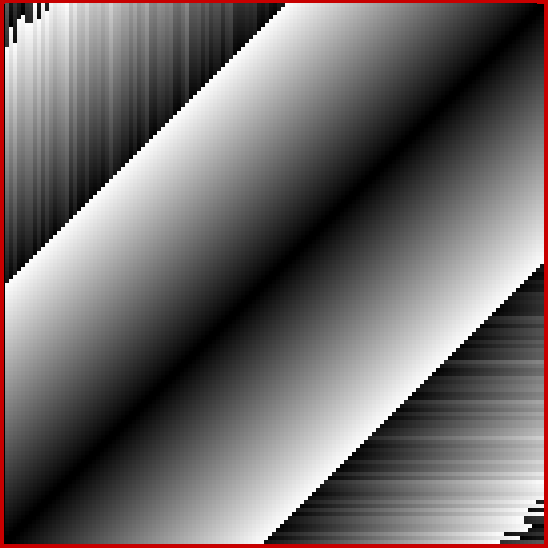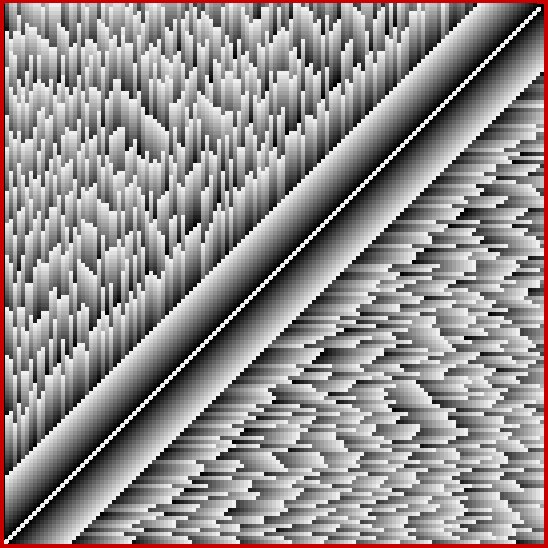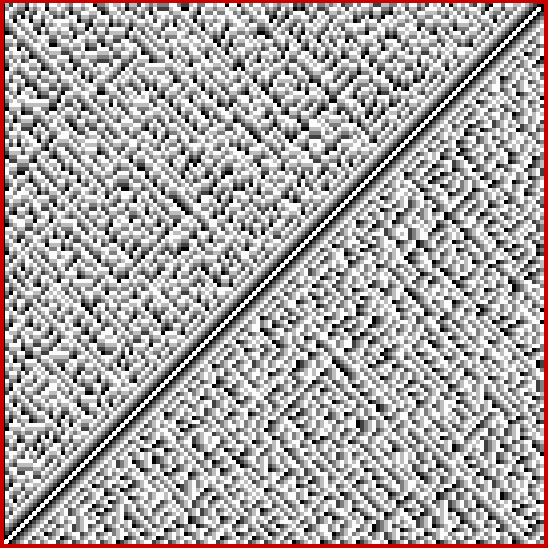
I decided to take create graphs of shared numbers in compared sequences like this. In the 135×135 grid below, the brightness of the squares corresponds to the count of shared numbers in the sequence-pair sum(x..x+n) and sum(y..y+n), where x and y are the coordinates of each individual square. I think the grid looks like a city of skyscrapers bisected by a highway:
Count of shared numbers in sequence-pairs sum(x..x+n) and sum(y..y+n)
Note that the bright white diagonal in the grid corresponds to the sequence-pairs where x = y. Because the sequences are identical in each pair, the count of shared numbers is infinite. The grid is symmetrically reflected along the diagonal because, for example, the sequence-pair for x=12, y=43, where sum(12..12+n) is compared with sum(43..43+n), corresponds to the sequence pair for x=43, y=12, where sum(43..43+n) is compared with sum(12..12+n). The scale of brightness runs from 0 (black) to 255 (full white) and increases by 32 for each shared number in the sequence. Obviously, then, the brightness can’t increase indefinitely and some maximally bright squares will represent sequence-pairs that have different counts of shared pairs.
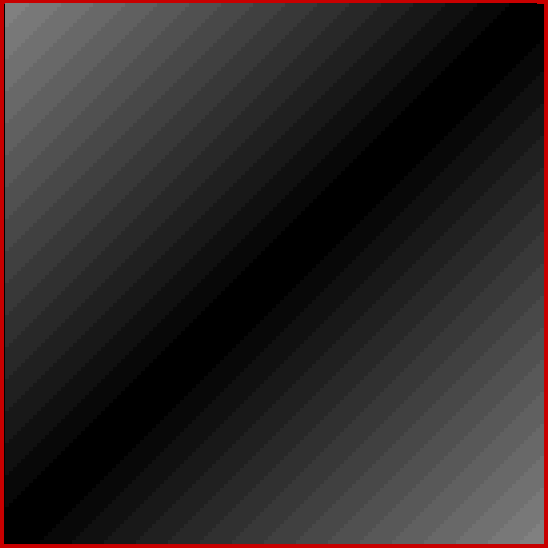
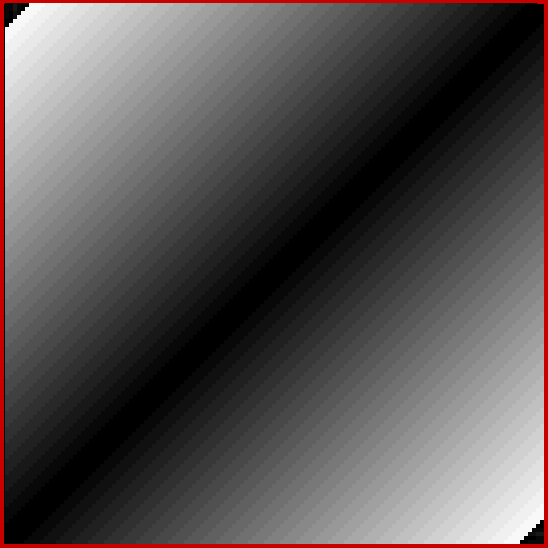
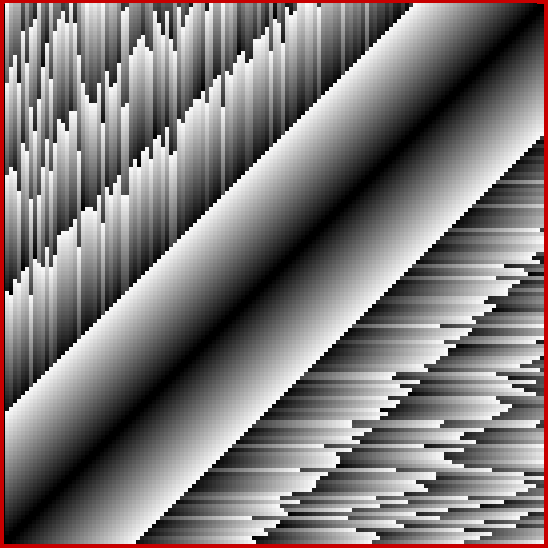
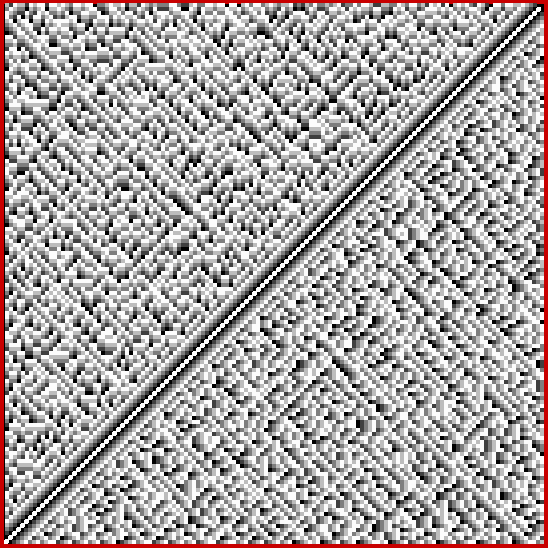
Now try altering the size of the step in brightness. You get grids in which the width of the central strip increases (smaller step) or decreases (bigger step). Here are grids for steps for 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 and 64 (I’ve removed the bright x=y diagonal for the first few grids, because it’s too prominent against duller shades):
Brightness-step = 1
Brightness-step = 2
Brightness-step = 4
Brightness-step = 8
Brightness-step = 16
Brightness-step = 32
Brightness-step = 63
Brightness-step = 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 63 (animated)