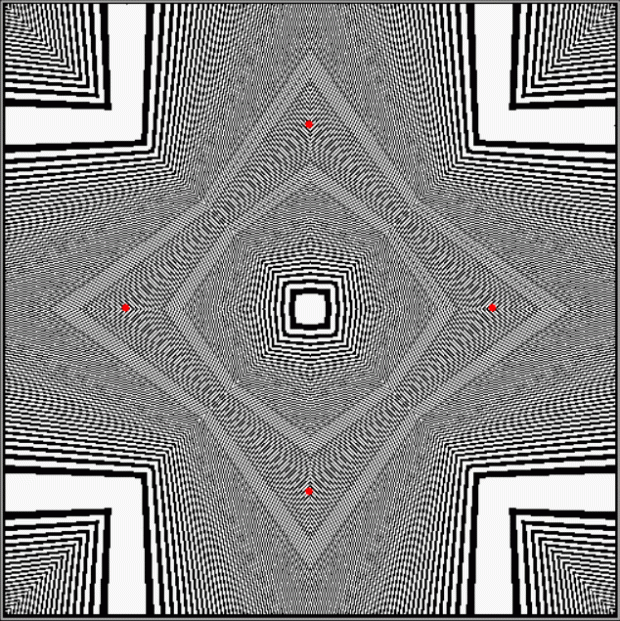
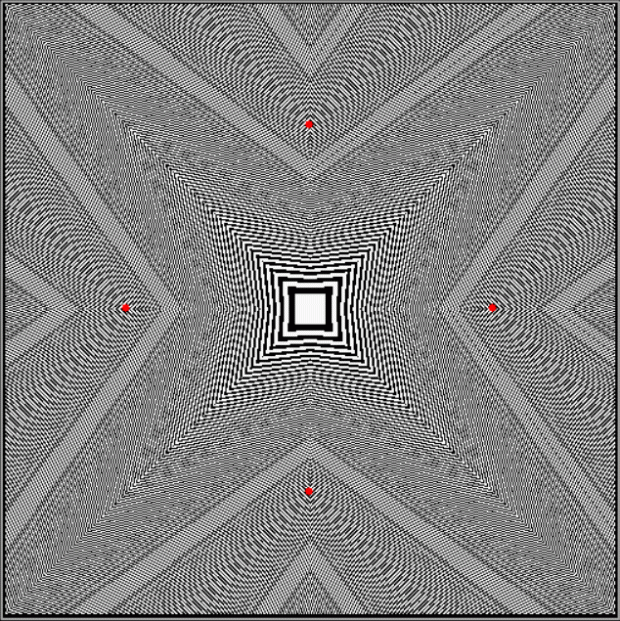
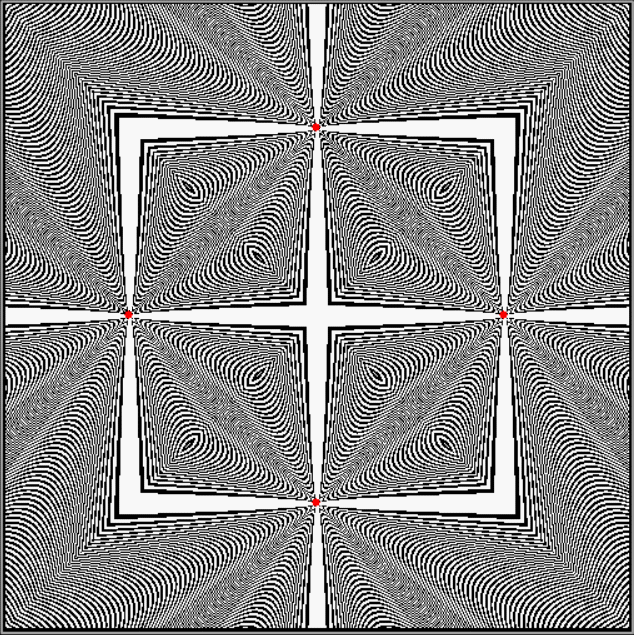
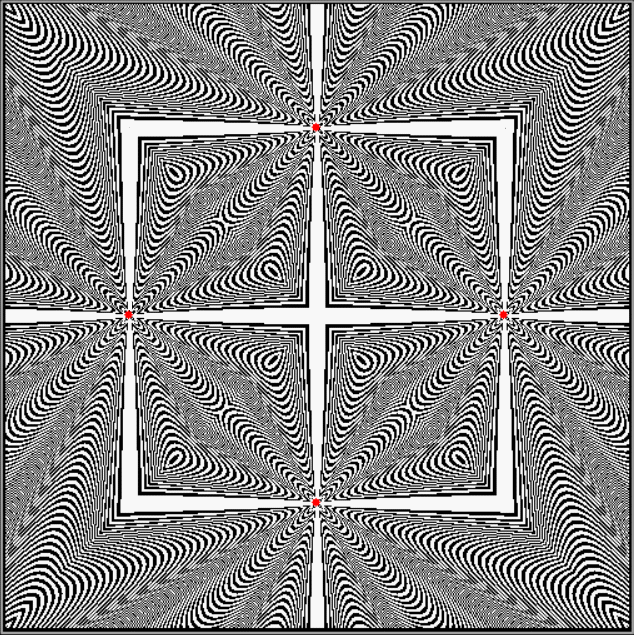
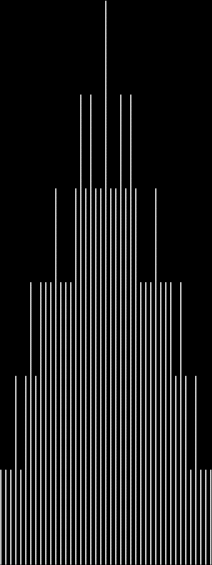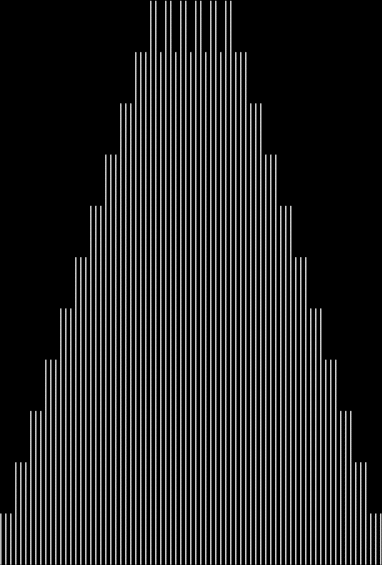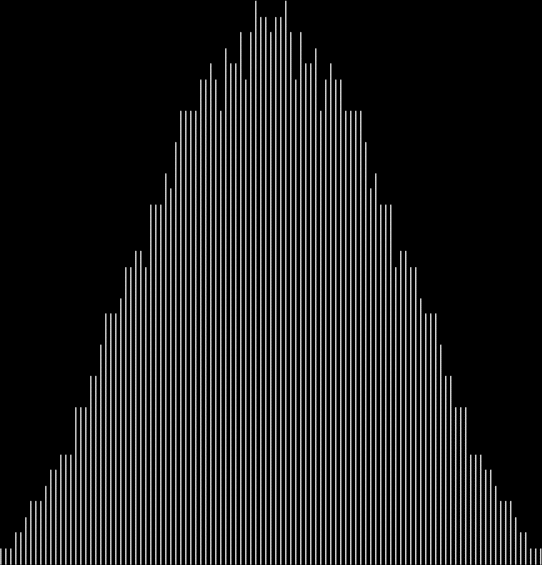Practically speaking, I’d never heard of them. Practical numbers, that is. They’re defined like this at the Online Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences:
A005153 Practical numbers: positive integers m such that every k <= sigma(m) is a sum of distinct divisors of m. Also called panarithmic numbers. […] Equivalently, positive integers m such that every number k <= m is a sum of distinct divisors of m. — A005153 at OEIS
In other words, if you take, say, divisors(12) = 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, you can find partial sums of those divisors that equal every number from 1 to 16, where 16 = 1+2+3+4+6. Here are all those sums, with c as the count of divisor-sums equalling a particular k (to simplify things, I’m excluding 12 as a divisor of 12):
1, 2, 3, 4, 6 = divisors(12)
01 = 1 (c=1)
02 = 2 (c=1)
03 = 1 + 2 = 3 (c=2)
04 = 1 + 3 = 4 (c=2)
05 = 2 + 3 = 1 + 4 (c=2)
06 = 1 + 2 + 3 = 2 + 4 = 6 (c=3)
07 = 1 + 2 + 4 = 3 + 4 = 1 + 6 (c=3)
08 = 1 + 3 + 4 = 2 + 6 (c=2)
09 = 2 + 3 + 4 = 1 + 2 + 6 = 3 + 6 (c=3)
10 = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 = 1 + 3 + 6 = 4 + 6 (c=3)
11 = 2 + 3 + 6 = 1 + 4 + 6 (c=2)
12 = 1 + 2 + 3 + 6 = 2 + 4 + 6 (c=2)
13 = 1 + 2 + 4 + 6 = 3 + 4 + 6 (c=2)
14 = 1 + 3 + 4 + 6 (c=1)
15 = 2 + 3 + 4 + 6 (c=1)
16 = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 6 (c=1)
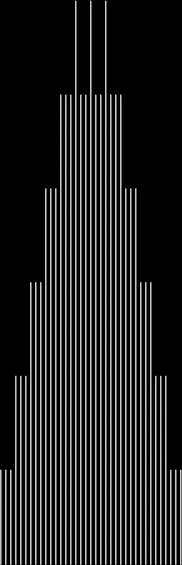
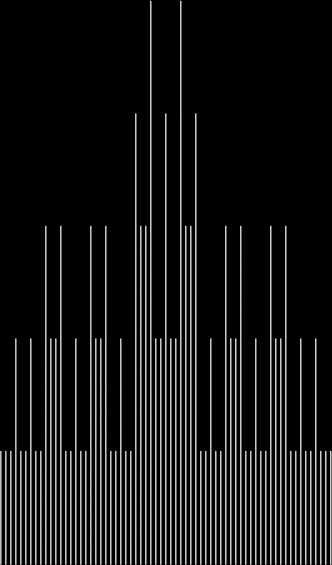
Learning about practical numbers inspired me to look at the graphs of the count of the divisor-sums for 12. If you include count(0) = 1 (there is one way of choosing divisors of 12 to equal 0, namely, by choosing none of the divisors), the graph looks like this:

counts of divisorsum(12) = k, where 12 = 2^2 * 3 → 1, 2, 3, 4, 6
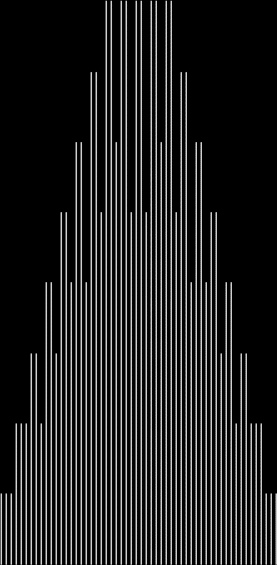
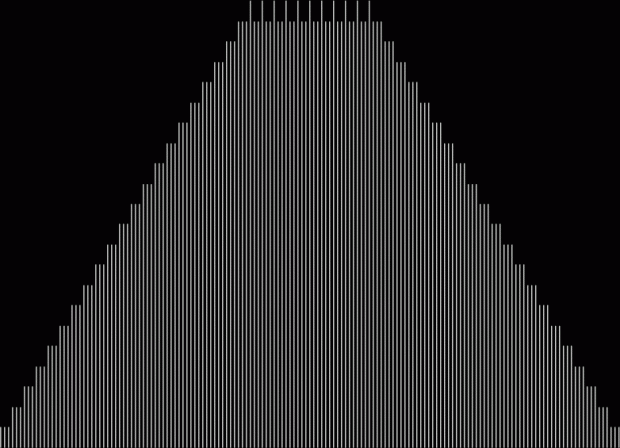
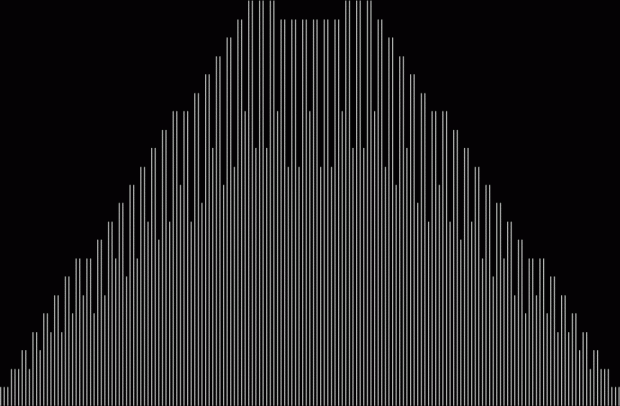
Here are some more graphs for partialsumcount(n), adjusted for a standardized y-max. They remind me variously of skyscrapers, pyramids, stupas, factories and factory façades, forts bristling with radar antennae, and the Houses of Parliament. All in an art-deco style:

18 = 2 * 3^2 → 1, 2, 3, 6, 9
24 = 2^3 * 3 → 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12
30 = 2 * 3 * 5 → 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15
36 = 2^2 * 3^2 → 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18
48 = 2^4 * 3 → 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 24
54 = 2 * 3^3 → 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18, 27
60 = 2^2 * 3 * 5 → 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, 30
72 = 2^3 * 3^2 → 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36
88 = 2^3 * 11 → 1, 2, 4, 8, 11, 22, 44, 88
96 = 2^5 * 3 → 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 24, 32, 48
100 = 2^2 * 5^2 → 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20, 25, 50
108 = 2^2 * 3^3 → 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 27, 36, 54
120 = 2^3 * 3 * 5 → 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 24, 30, 40, 60
126 = 2 * 3^2 * 7 → 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 9, 14, 18, 21, 42, 63
162 = 2 * 3^4 → 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18, 27, 54, 81
220 = 2^2 * 5 * 11 → 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 11, 20, 22, 44, 55, 110
And what about im-practical numbers, where the partial sums of divisors(m) don’t equal every number 1..sigma(m)? There are interesting fractal patterns to be uncovered there, as you can see from the graph for 190 (because all divsumcount(k) = 1, the graph looks like a bar-code):

190 = 2 * 5 * 19 → 1, 2, 5, 10, 19, 38, 95