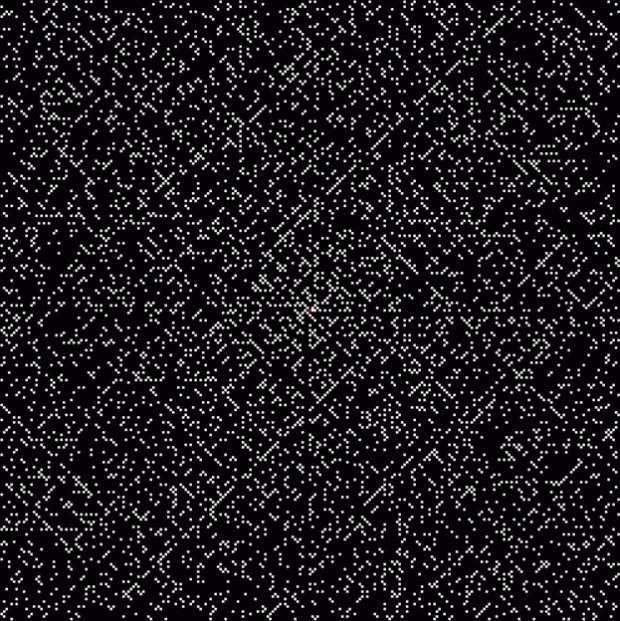
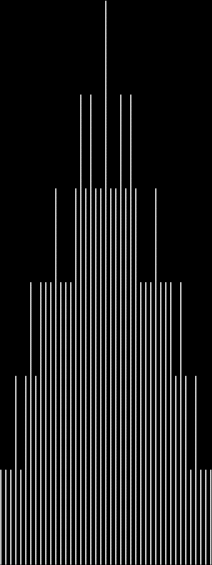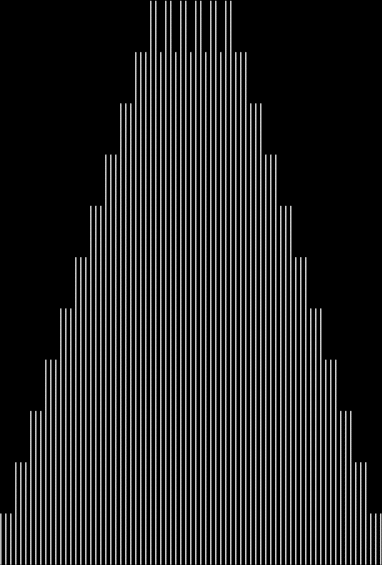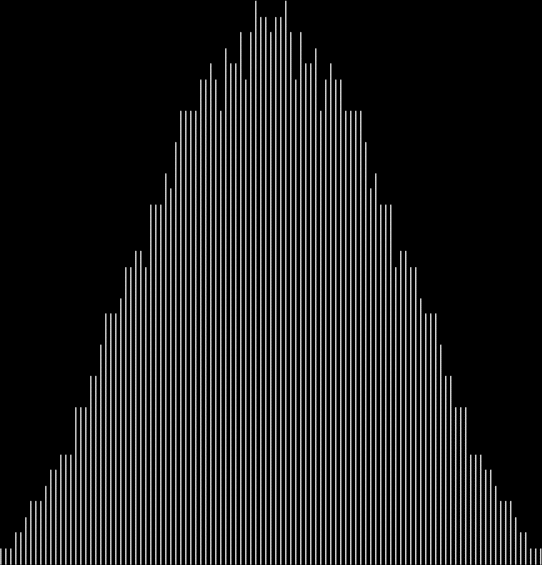This is the famous Ulam spiral, in which prime numbers are represented on filled squares on a square spiral:
The Ulam spiral
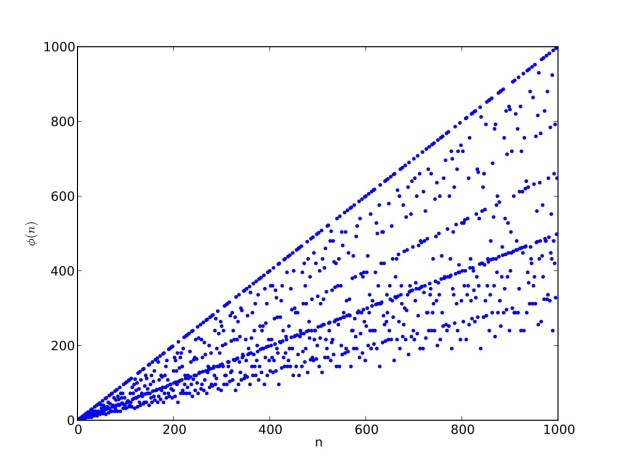
I like the way the spiral sits between chaos and calm. It’s not wholly random and it’s not wholly regular — it’s betwixt and between. You get a similar chaos-and-calm vibe from a graph for a function called Euler phi. And primes are at work there too. Here’s the graph from Wikipedia:
Graph of eulerphi(n) = φ(n) (see Euler’s totient function)
But what is the Euler phi function? For any integer n, eulerphi(n) gives you the count of numbers < n that are relatively prime to n. That is, the count of numbers < n that have no common factors with n other than one. You can see how eulerphi(n) works by considering whether you can simplify the fraction a/b, where a = 1..n-1 and b = n:
φ(6) = 2
1/6 (1)
2/6 → 1/3
3/6 → 1/2
4/6 → 2/3
5/6, ∴ φ(6) = 2
φ(7) = 6
1/7 (1)
2/7 (2)
3/7 (3)
4/7 (4)
5/7 (5)
6/7, ∴ φ(7) = 6
φ(12) = 4
1/12 (1)
2/12 → 1/6
3/12 → 1/4
4/12 → 1/3
5/12 (2)
6/12 → 1/2
7/12 (3)
8/12 → 2/3
9/12 → 3/4
10/12 → 5/6
11/12, ∴ φ(12) = 4
φ(13) = 12
1/13 (1)
2/13 (2)
3/13 (3)
4/13 (4)
5/13 (5)
6/13 (6)
7/13 (7)
8/13 (8)
9/13 (9)
10/13 (10)
11/13 (11)
12/13, ∴ φ(13) = 12
As you can see, eulerphi(n) = n-1 for primes. Now you know what the top line of the Eulerphi graph is. It’s the primes. Here’s a bigger version of the graph:
Graph of eulerphi(n) = φ(n)
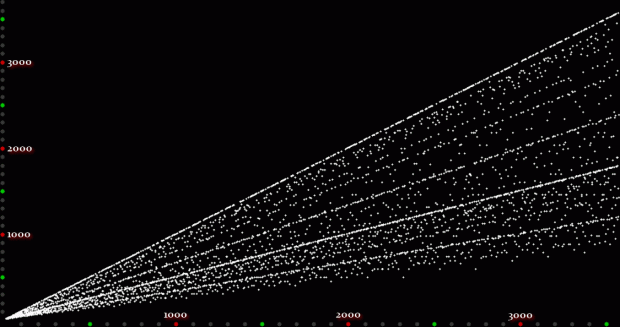
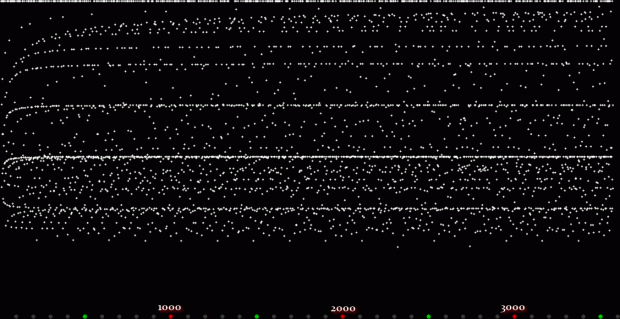
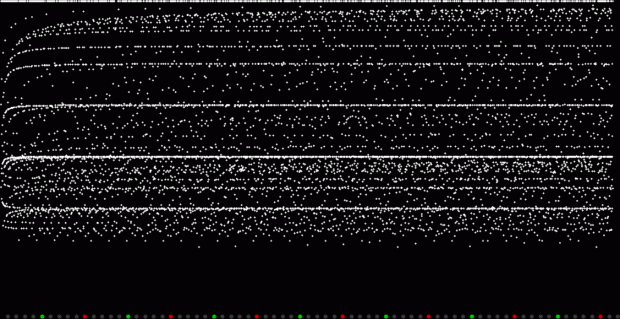
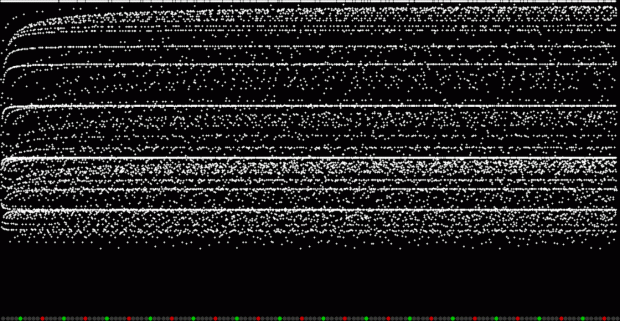
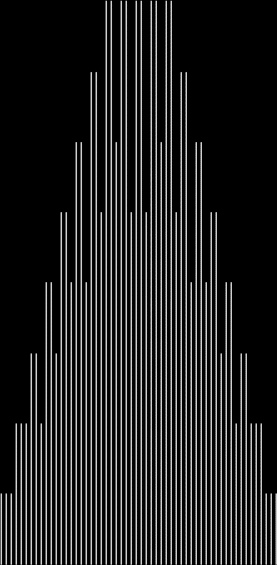
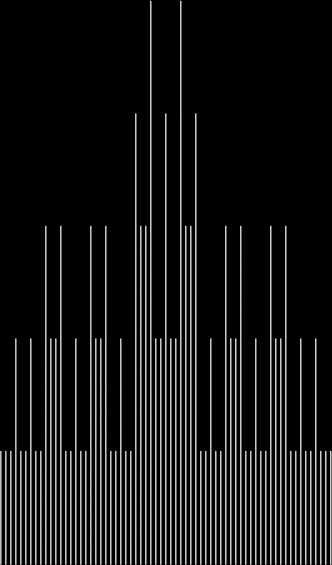
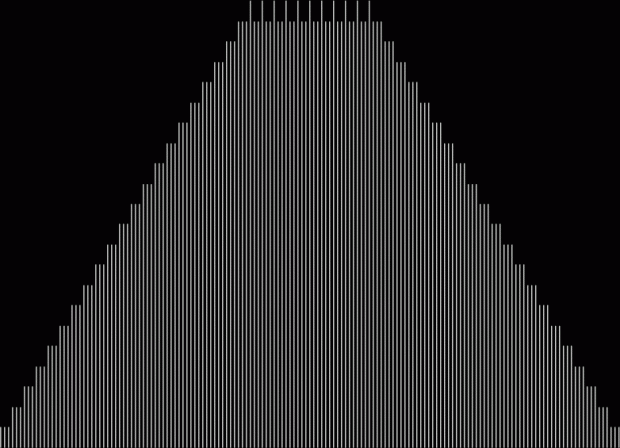
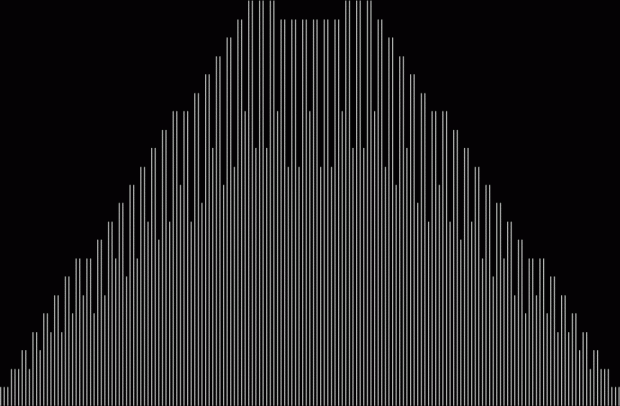
Unlike the Ulam spiral, however, the Eulerphi graph is cramped. But it’s easy to stretch it. You can represent φ(n) as a fraction between 0 and 1 like this: phifrac(n) = φ(n) / (n-1). Using phifrac(n), you can create Eulerphi bands, like this:
Eulerphi band, n <= 1781
Eulerphi band, n <= 3561
Eulerphi band, n <= 7121
Eulerphi band, n <= 14241
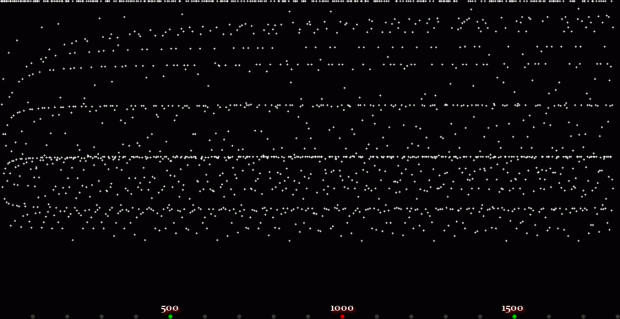
Or you can create Eulerphi discs, like this:
Eulerphi disc, n <= 1601
Eulerphi disc, n <= 3201
Eulerphi disc, n <= 6401
Eulerphi disc, n <= 12802
Eulerphi disc, n <= 25602
But what is the bottom line of the Eulerphi bands and inner ring of the Eulerphi discs, where φ(n) is smallest relative to n? Well, the top line or outer ring is the primes and the bottom line or inner ring is the primorials (and their multiples). The function primorial(n) is the multiple of the first n primes:
primorial(1) = 2
primorial(2) = 2*3 = 6
primorial(3) = 2*3*5 = 30
primorial(4) = 2*3*5*7 = 210
primorial(5) = 2*3*5*7*11 = 2310
primorial(6) = 2*3*5*7*11*13 = 30030
primorial(7) = 2*3*5*7*11*13*17 = 510510
primorial(8) = 2*3*5*7*11*13*17*19 = 9699690
primorial(9) = 2*3*5*7*11*13*17*19*23 = 223092870
primorial(10) = 2*3*5*7*11*13*17*19*23*29 = 6469693230
Here are the numbers returning record lows for φfrac(n) = φ(n) / (n-1):
φ(4) = 2 (2/3 = 0.666…)
4 = 2^2
φ(6) = 2 (2/5 = 0.4)
6 = 2.3
φ(12) = 4 (4/11 = 0.363636…)
12 = 2^2.3
[…]
φ(30) = 8 (8/29 = 0.275862…)
30 = 2.3.5
φ(60) = 16 (16/59 = 0.27118…)
60 = 2^2.3.5
[…]
φ(210) = 48 (48/209 = 0.229665…)
210 = 2.3.5.7
φ(420) = 96 (96/419 = 0.2291169…)
420 = 2^2.3.5.7
φ(630) = 144 (144/629 = 0.228934…)
630 = 2.3^2.5.7
[…]
φ(2310) = 480 (480/2309 = 0.2078822…)
2310 = 2.3.5.7.11
φ(4620) = 960 (960/4619 = 0.20783719…)
4620 = 2^2.3.5.7.11
[…]
30030 = 2.3.5.7.11.13
φ(60060) = 11520 (11520/60059 = 0.191811385…)
60060 = 2^2.3.5.7.11.13
φ(90090) = 17280 (17280/90089 = 0.1918103209…)
90090 = 2.3^2.5.7.11.13
[…]
φ(510510) = 92160 (92160/510509 = 0.18052571061…)
510510 = 2.3.5.7.11.13.17
φ(1021020) = 184320 (184320/1021019 = 0.18052553…)
1021020 = 2^2.3.5.7.11.13.17
φ(1531530) = 276480 (276480/1531529 = 0.180525474868579…)
1531530 = 2.3^2.5.7.11.13.17
φ(2042040) = 368640 (368640/2042039 = 0.18052544540040616…)
2042040 = 2^3.3.5.7.11.13.17