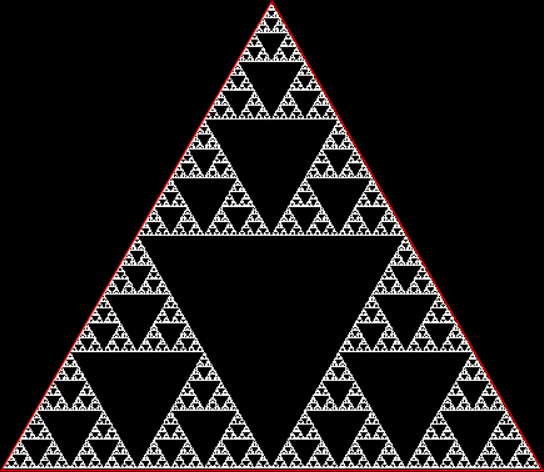
Triangles? Yes. Squares? No. If you scout the routes with a triangle, you get a beautiful fractal. If you scout the routes with a square, you don’t. Here’s what you get with a triangle:
A Sierpiński triangle
But how do you scout the routes? (That phrase works best in the American dialects where “scout” rhymes with “route”.) Simple: you mark the final positions reached when a point traces all possible ways of jumping, say, eight times 1/2-way towards the vertices of a polygon. Here’s an animation of a point scouting the routes of eight jumps towards the vertices of a triangle (it starts each time at the center):
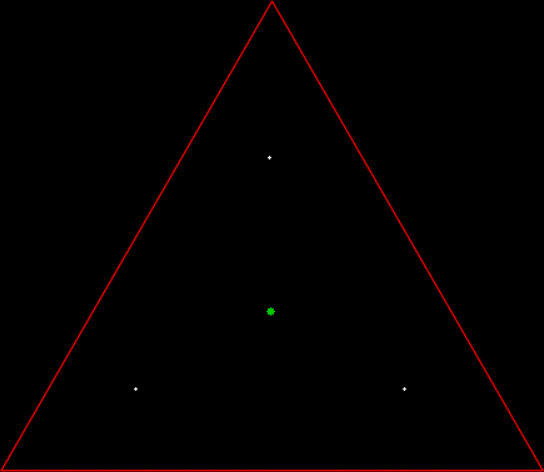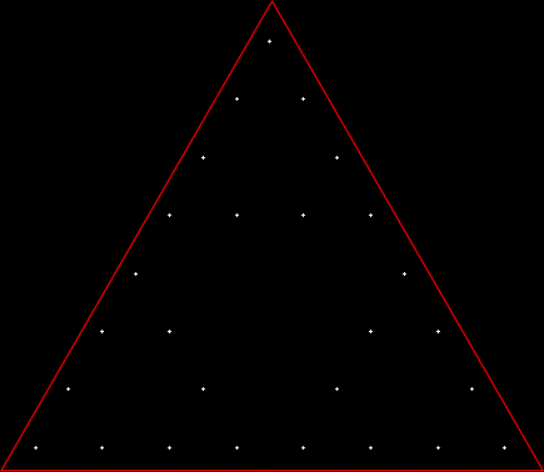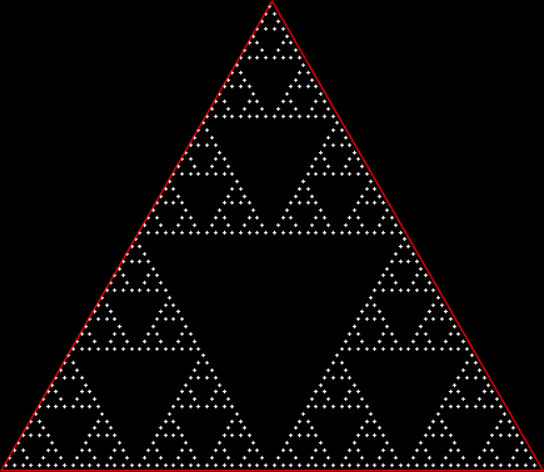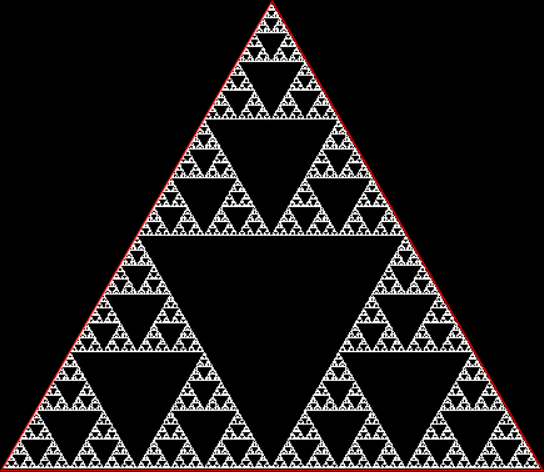
Creating a Sierpiński triangle by scouting the routes (animated at Ezgif)
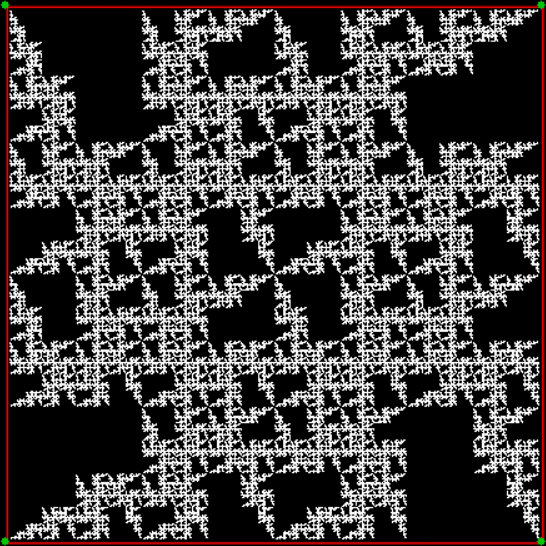
If you scout the routes with a square, you don’t get a fractal. Instead, the interior of the square fills evenly (and boringly) with the end-points of the routes:
Scouting the routes with a square (animated at Ezgif)
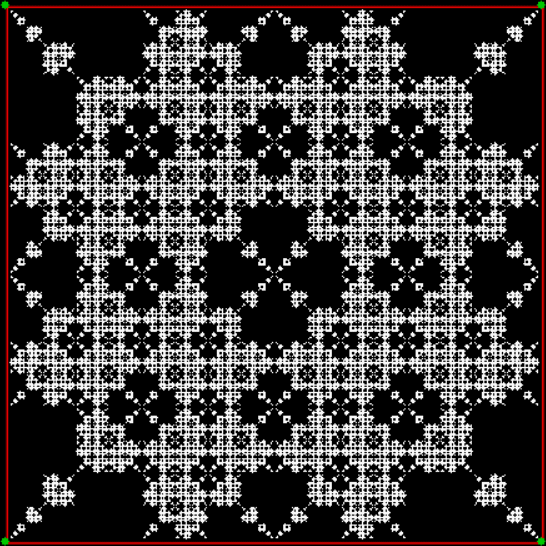
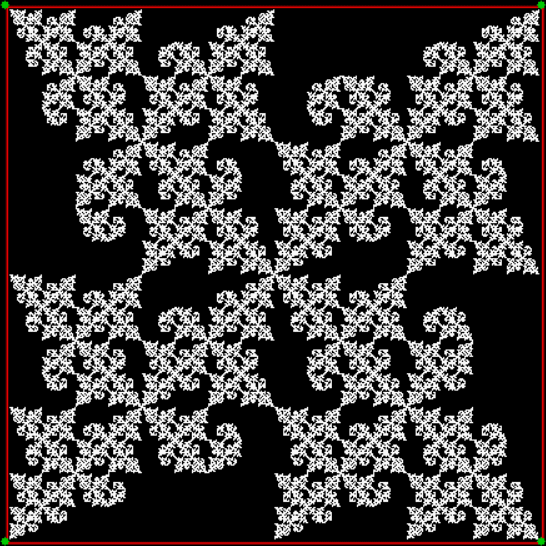
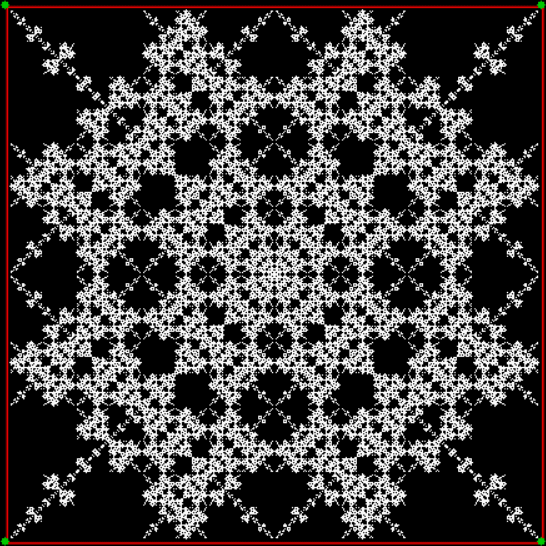
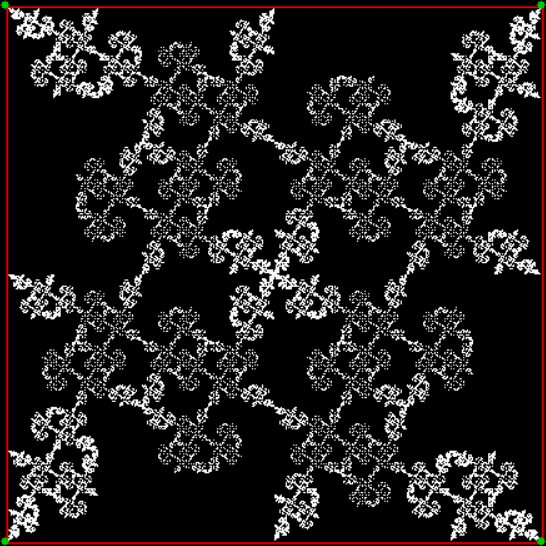
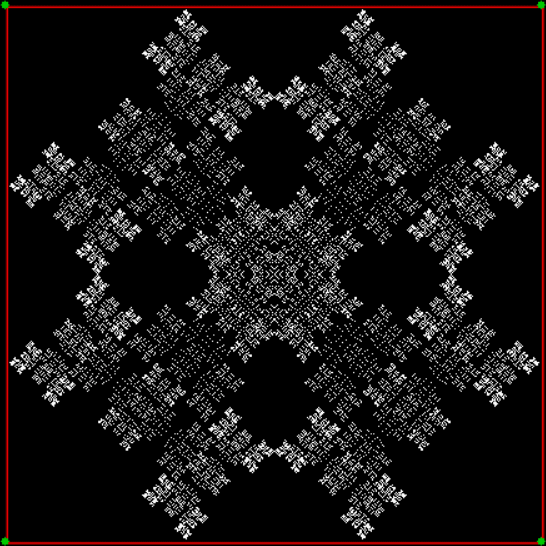
But you can create fractals with a square if you out routes as you scout routes. That is, if you exclude some routes and don’t mark their end-points. One way to do this is to compare the proposed next jump-vertex (vertex-jumped-towards) with the previous jump-vertex. For example, if the proposed jump-vertex, jv[t], is the same as the previous jump-vertex, jv[t-1], you don’t jump towards jv[t] or you jump towards it in a different way. The test is jv[t] = jv[t-1] + vi. If vi = 0 and you jump towards the clockwise neighbor of jv when the test is true, you get a fractal looking like this:
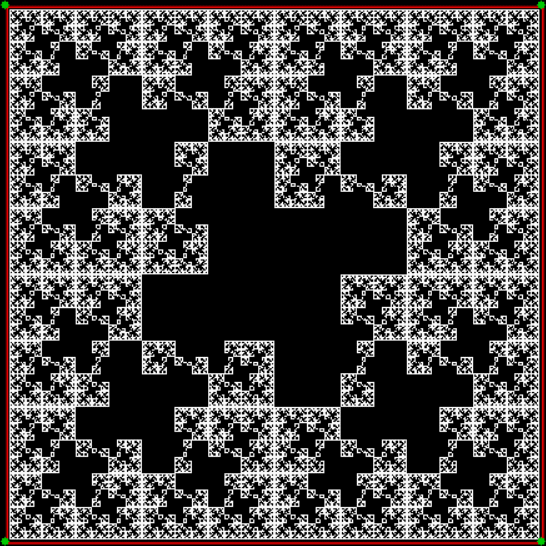
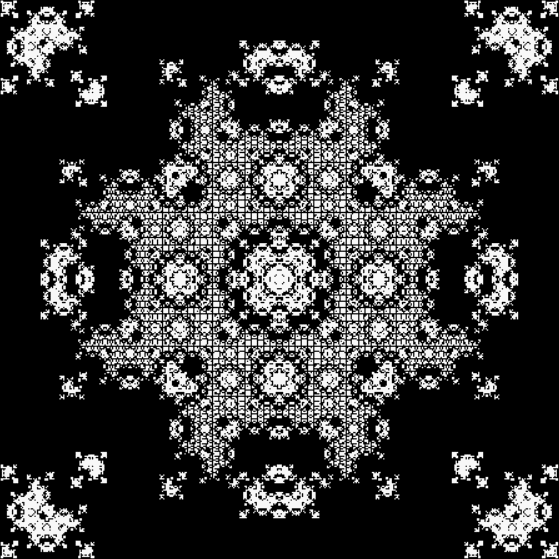
vi = 0, action = jv → jv + 1
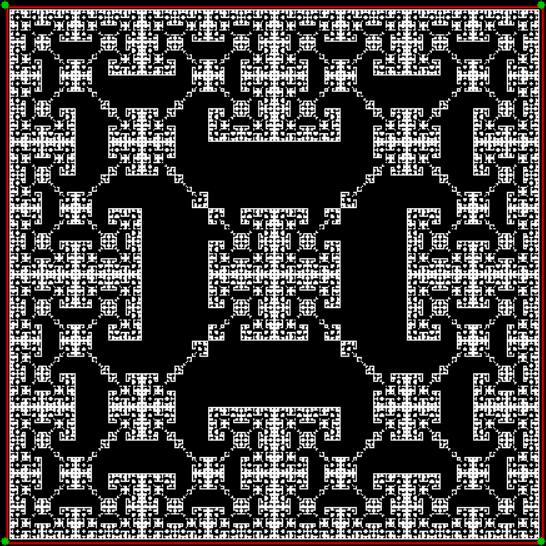
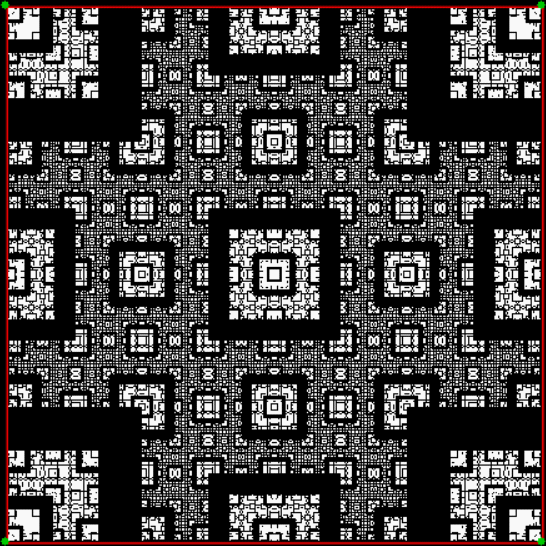
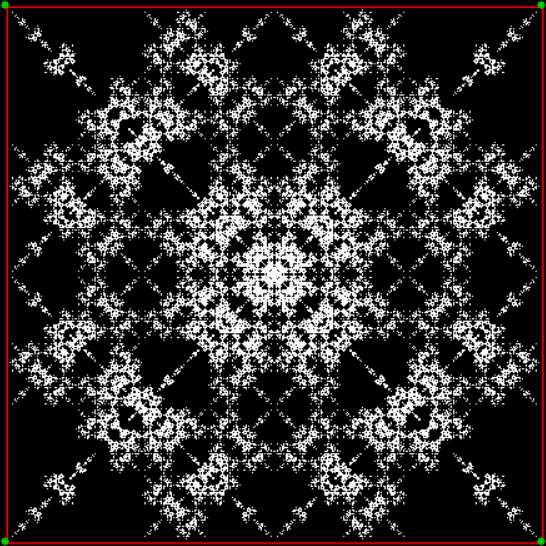
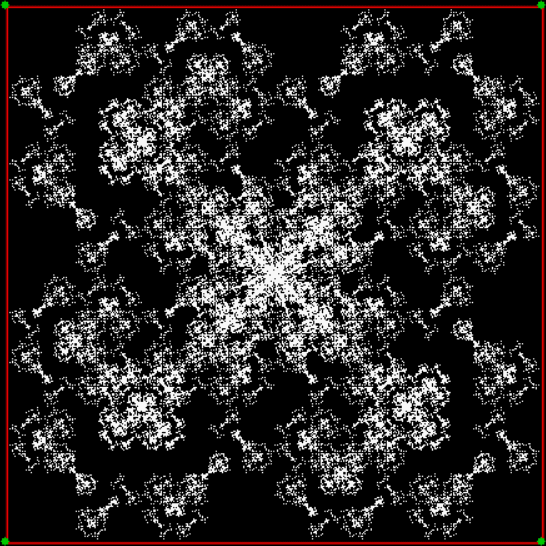
Here’s the fractal if you jump towards the clockwise-neighbor-but-one when the test is true:
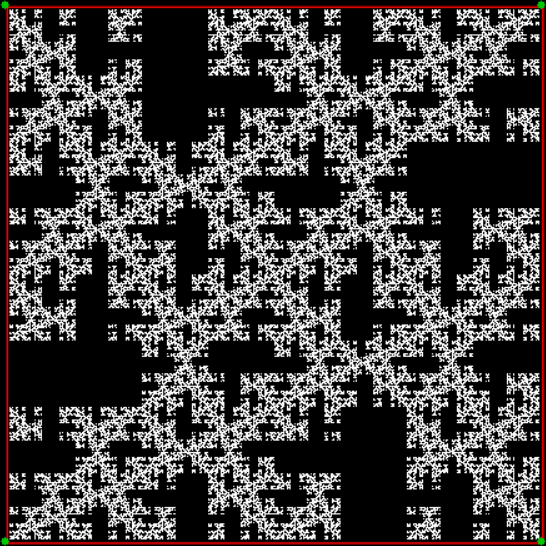
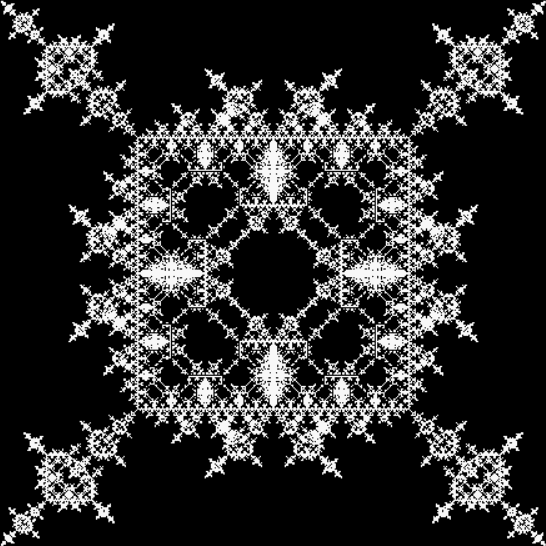
vi = 0, action = jv + 2
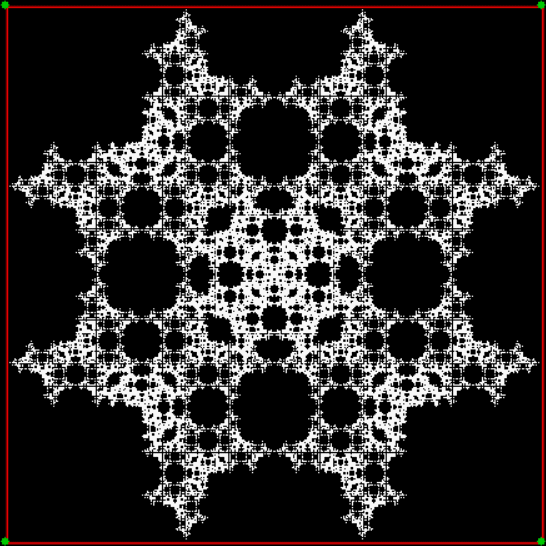
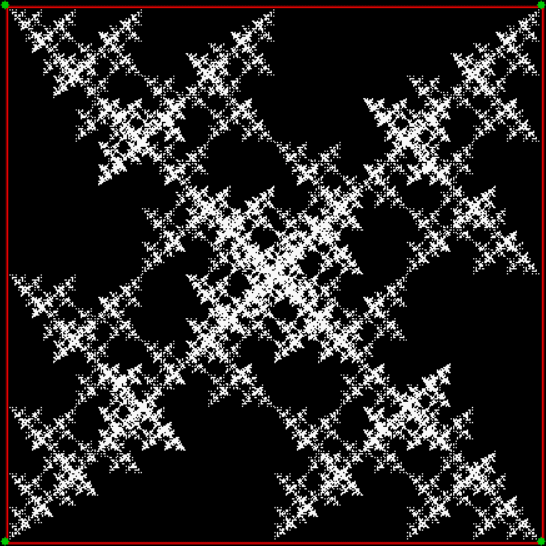
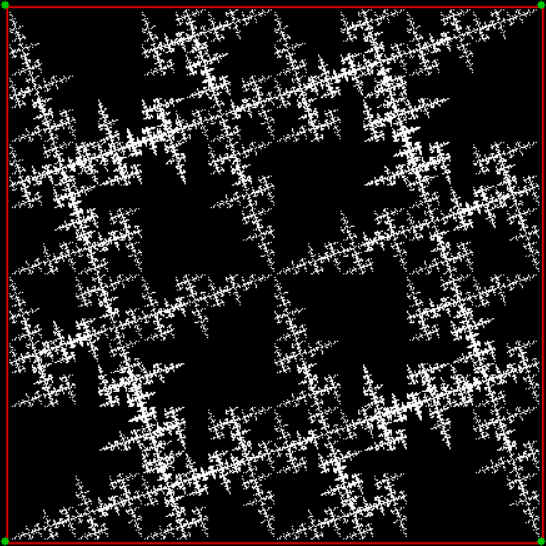
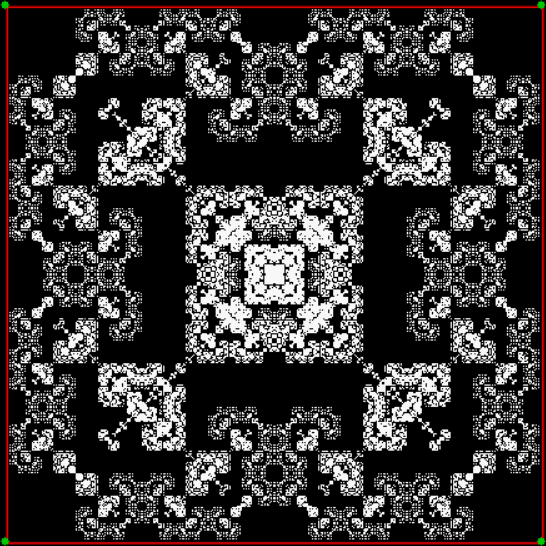
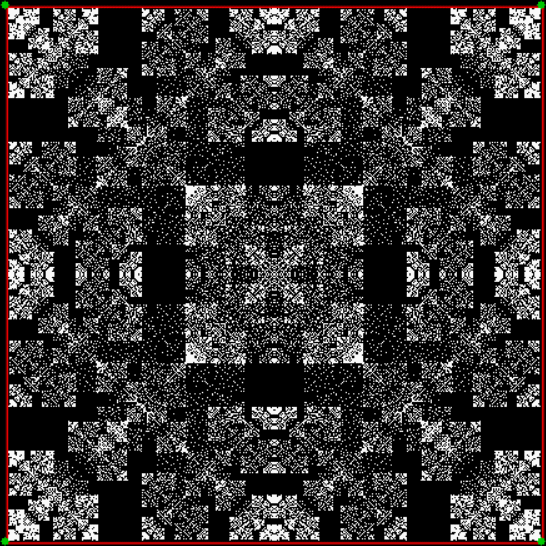
Now try varying the vi of the jv[t-1] + vi:
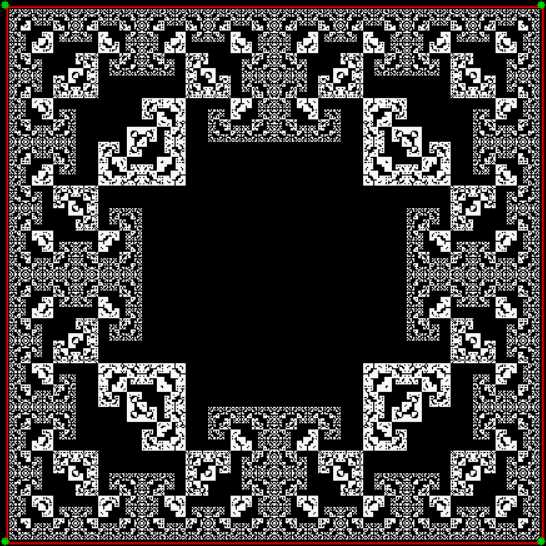
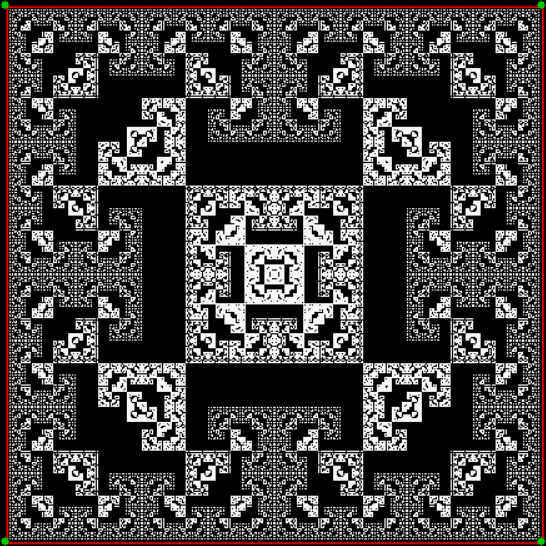
vi = 2, action = jv + 2
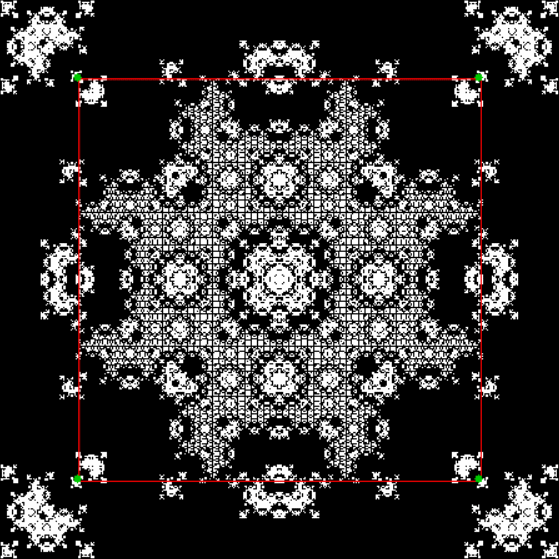
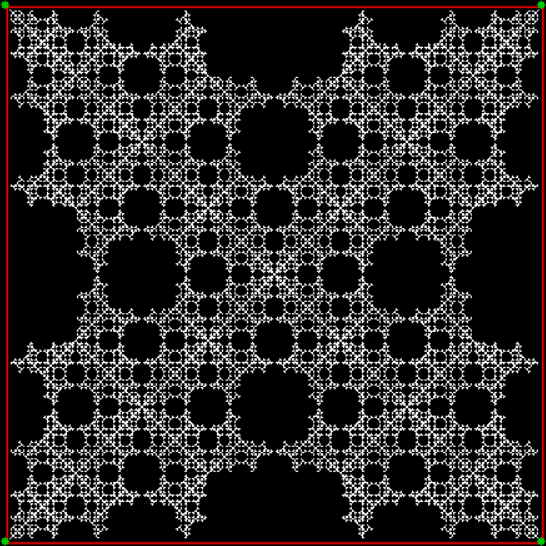
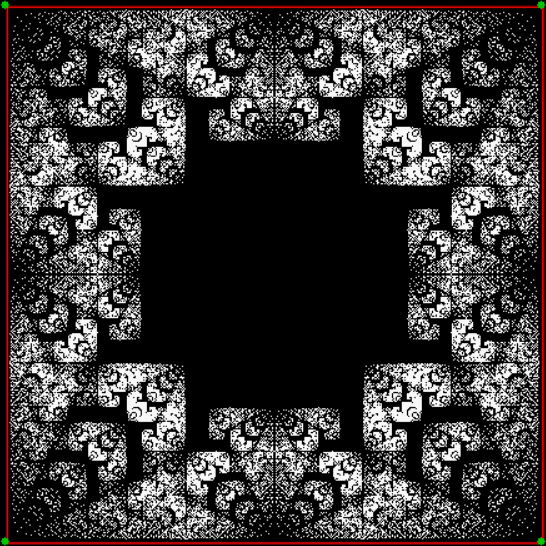
vi = 2, action = jv + 1
vi = 3, action = jv + 1
Or what about jumping in a different way towards jv when the test is true? If you jump 2/3 of the way rather 1/2, you get his fractal:
vi = 2, action = jump 2/3
And if you jump 4/3 of the way (i.e., you overshoot the vertex jv), you get this fractal:
vi = 0, action = jump 4/3rds to vertex
vi = 0, jump 4/3 (guide-square removed)
vi = 2, jump 4/3rds (guide-square removed)
And in this fractal the point jumps 2/3 of the way to the center of the square when the test is true:
vi = 2, action = jump 2/3rds of way to center of square
But why apply only one test to jv[1] and use only when one alternative jump? If jv[t] = jv[t-1] + 1 or jv[t] = jv[t-1] + 3, jv[t] becomes jv[t]+1 or jv[t]+3, respectively, you get this fractal:
vi = 1, jv + 1; vi = 3, jv + 3
Here are more fractals created by single and double tests:
vi = 1, jv + 1
vi = 0, jump 2/3
vi = 0, jump towards center 2/3rds
vi = 1, jump-center 2/3
vi = 2, jump 1/3; vi = 3, jump 1/1 (i.e, 1)
vi = 0, jv + 2; vi = 2, jump-center 1/2
vi = 0, jv + 2; vi = 2, jump-center 2/3
vi = 0, jv + 2; vi = 2, jump-center 4/3
vi = 0, jv + 1; vi = 2, jump 2/3
vi = 0, jv + 2; vi = 2, jump 2/3
vi = 0, jump 4/3; vi = 2, jv + 2
vi = 0, jump 2/3; vi = 2, jv + 1
vi = 0, jump 4/3; vi = 1, jv + 2
vi = 0, jump 2/3; vi = 2, jump 1/3
vi =0, jump 1/3; vi = 2, jump 2/3
vi = 0, jump 0/1 (i.e, 0); vi = 2, jump 1/3