First a bit of a boredom. Then a bit of beauty. These are the triangular numbers, including 666, the Number of the Beast:
1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, 28, 36, 45, 55, 66, 78, 91, 105, 120, 136, 153, 171, 190, 210, 231, 253, 276, 300, 325, 351, 378, 406, 435, 465, 496, 528, 561, 595, 630, 666, 703, 741, 780, 820, 861, 903, 946, 990, 1035, 1081, 1128, 1176, 1225, 1275, …
You can createthem as sumbers, that is, as numbers made by summing the whole numbers:
tri(1) = 1 = 1
tri(2) = 3 = 2+1
tri(3) = 6 = 3+2+1
tri(4) = 10 = 4+3+2+1
tri(5) = 15 = 5+4+3+2+1
tri(6) = 21 = 6+5+4+3+2+1
tri(7) = 28 = 7+6+5+4+3+2+1
tri(8) = 36 = 8+7+6+5+4+3+2+1
tri(9) = 45 = 9+8+7+6+5+4+3+2+1
tri(10) = 55 = 10+9+8+7+6+5+4+3+2+1
And here are the square numbers:
1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100, 121, 144, 169, 196, 225, 256, 289, 324, 361, 400, 441, 484, 529, 576, 625, 676, 729, 784, 841, 900, 961, 1024, 1089, 1156, 1225, 1296, 1369, 1444, 1521, 1600, 1681, 1764, 1849, 1936, 2025, 2116, 2209, 2304, 2401, 2500, …
You can create square numbers in various ways. Most obviously, by multiplying each whole number by itself:
sq(1) = 1*1 = 1
sq(2) = 2*2 = 4
sq(3) = 3*3 = 9
sq(4) = 4*4 = 16
sq(5) = 5*5 = 25
sq(6) = 6*6 = 36
sq(7) = 7*7 = 49
sq(8) = 8*8 = 64
sq(9) = 9*9 = 81
sq(10) = 10*10 = 100
Less obviously, by summing consecutive odd numbers:
sq(1) = 1 = 1
sq(2) = 1+3 = 4
sq(3) = 1+3+5 = 9
sq(4) = 1+3+5+7 = 16
sq(5) = 1+3+5+7+9 = 25
sq(6) = 1+3+5+7+9+11 = 36
sq(7) = 1+3+5+7+9+11+13 = 49
sq(8) = 1+3+5+7+9+11+13+15 = 64
sq(9) = 1+3+5+7+9+11+13+15+17 = 81
sq(10) = 1+3+5+7+9+11+13+15+17+19 = 100
And by summing pairs of consecutive triangular numbers (note that tri(0) = 0):
sq(1) = tri(0) + tri(1) = 0 + 1 = 1
sq(2) = tri(1) + tri(2) = 1 + 3 = 4
sq(3) = tri(2) + tri(3) = 3 + 6 = 9
sq(4) = tri(3) + tri(4) = 6 + 10 = 16
sq(5) = tri(4) + tri(5) = 10 + 15 = 25
sq(6) = tri(5) + tri(6) = 15 + 21 = 36
sq(7) = tri(6) + tri(7) = 21 + 28 = 49
sq(8) = tri(7) + tri(8) = 28 + 36 = 64
sq(9) = tri(8) + tri(9) = 36 + 45 = 81
sq(10) = tri(9) + tri(10) = 45 + 55 = 100
But sometimes squares are the sum of two triangular numbers that aren’t consecutive:
sq(4) = tri(1) + tri(5) = 1+15 = 16
sq(9) = tri(2) + tri(12) = 3+78 = 81
sq(16) = tri(2) + tri(22) = 3+253 = 256
sq(52) = tri(2) + tri(73) = 3+2701 = 2704
sq(14) = tri(3) + tri(19) = 6+190 = 196
sq(21) = tri(3) + tri(29) = 6+435 = 441
sq(44) = tri(9) + tri(61) = 45+1891 = 1936
sq(51) = tri(9) + tri(71) = 45+2556 = 2601
sq(49) = tri(10) + tri(68) = 55+2346 = 2401
sq(56) = tri(10) + tri(78) = 55+3081 = 3136
sq(16) = tri(11) + tri(19) = 66+190 = 256
sq(38) = tri(11) + tri(52) = 66+1378 = 1444
sq(54) = tri(11) + tri(75) = 66+2850 = 2916
sq(87) = tri(47) + tri(113) = 1128+6441 = 7569
sq(77) = tri(48) + tri(97) = 1176+4753 = 5929
sq(121) = tri(64) + tri(158) = 2080+12561 = 14641
sq(141) = tri(96) + tri(174) = 4656+15225 = 19881
sq(121) = tri(100) + tri(138) = 5050+9591 = 14641
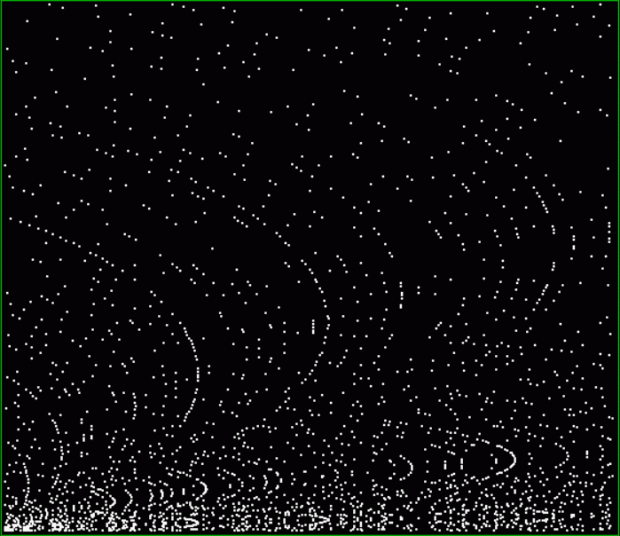
Here’s a graph of squares that are the sum of any two triangular numbers, that is, is_square(tri(k1)+tri(k2)). The x axis is 1..k1 and the y axis is 1..k2, so the graph is symmetrical:

tri(k1) + tri(k2) = square(k3)
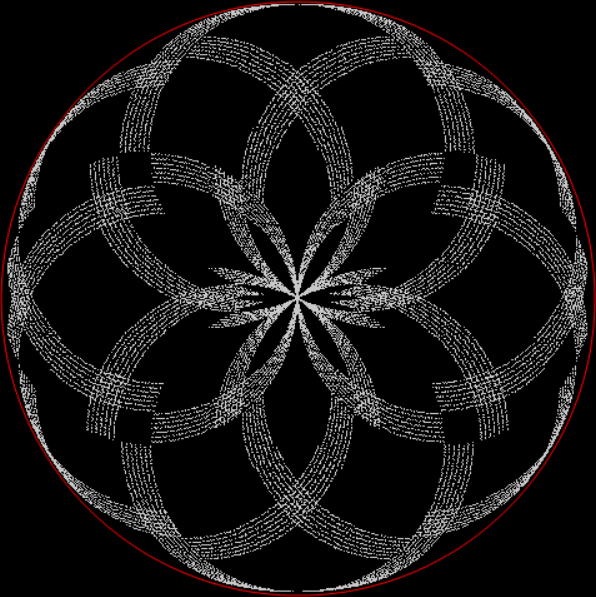
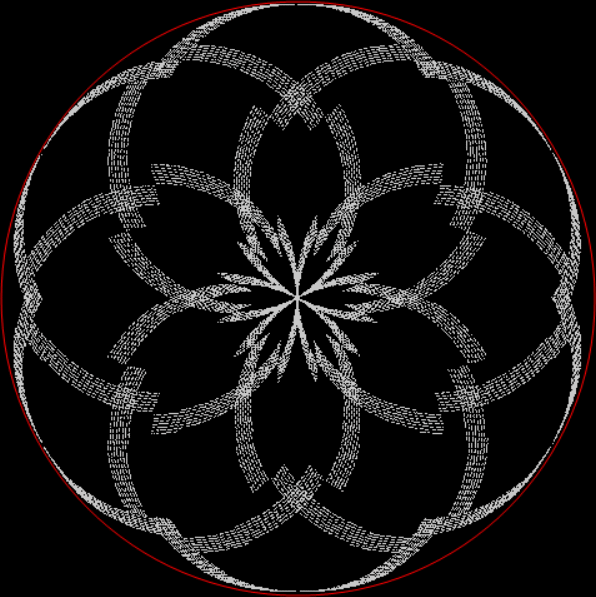
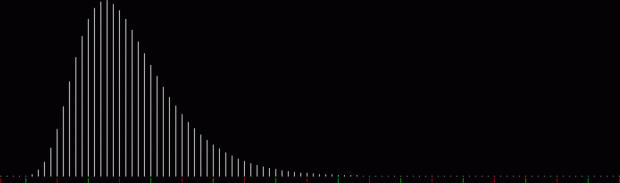
The (double) line at 45° represents squares that are the sum of consecutive triangulars. Other lines represent similarly regular patterns. Now for a bit of beauty. Things get more visually interesting when you test for squares that are the sums of any integer and a triangular number:
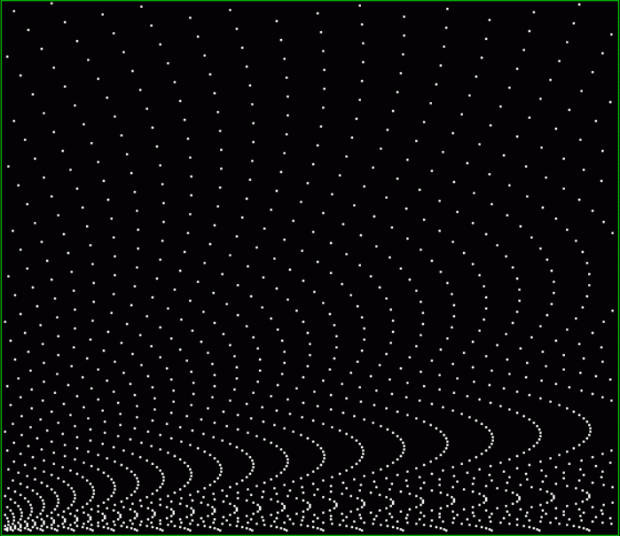
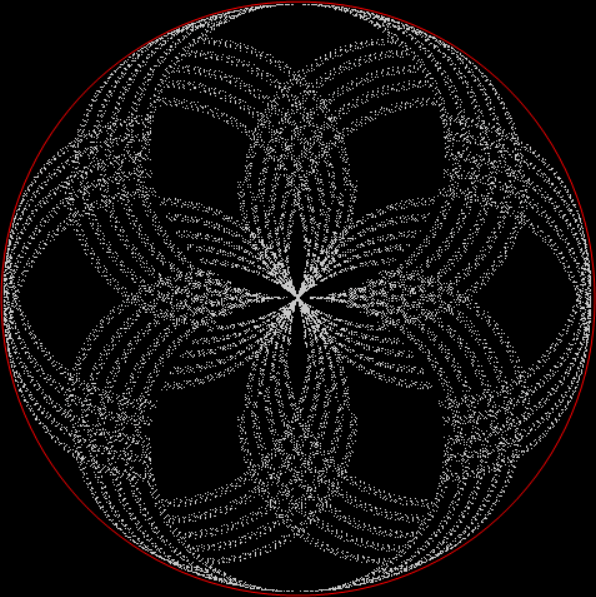
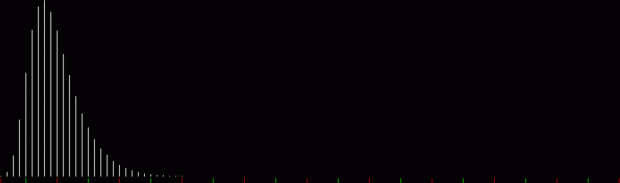
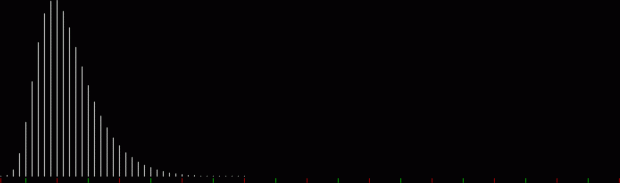
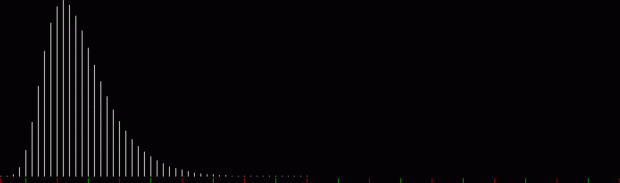
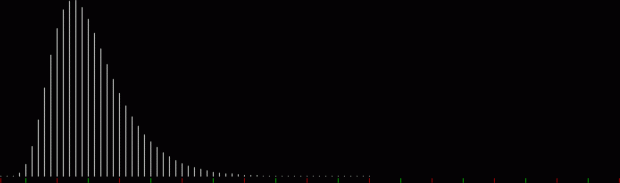
k1 + tri(k2) = square(k3)
The curves are optical oddities: where do they begin and end? The upper ones become lost to the eye in the lower ones. And vice versa. But you can force your eye to trace them further that it wants to.
Now try sums of integers and other polygonal numbers:
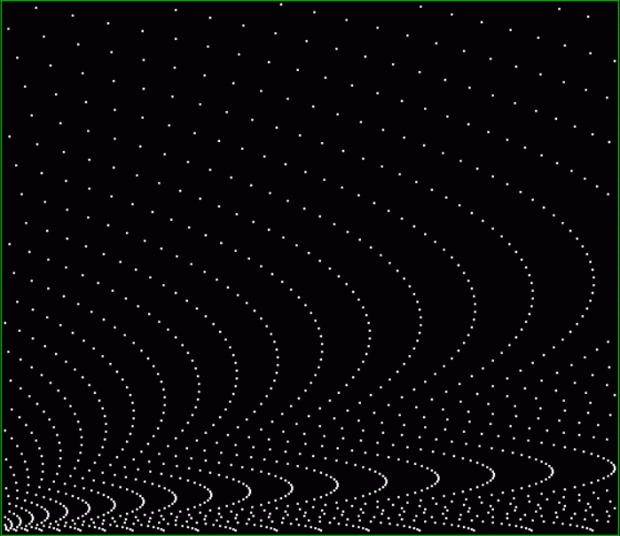
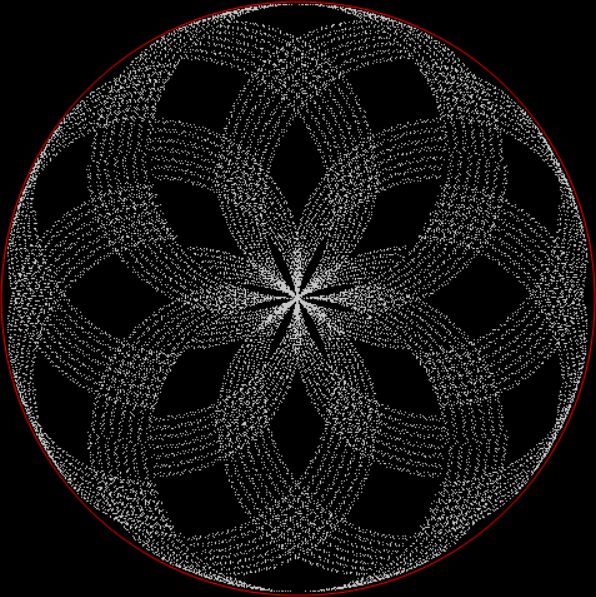
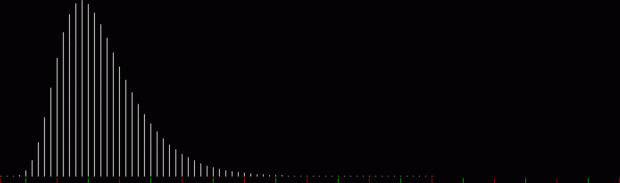
k1 + tri(k2) = pentagonal(k3)

k1 + square(k2) = pentagonal(k3)
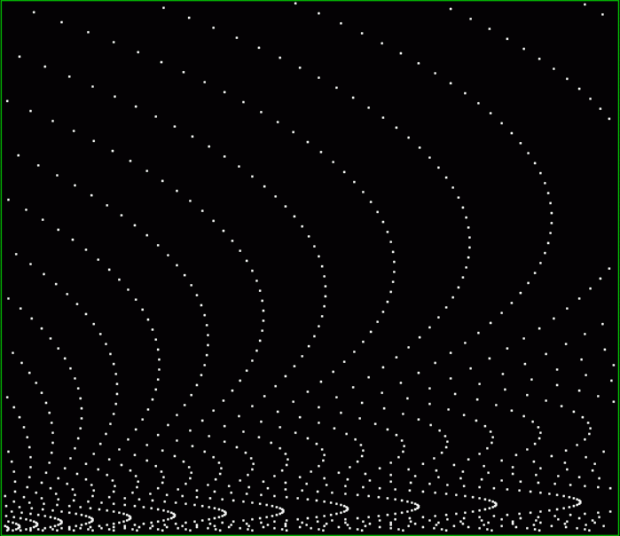
k1 + pentagonal(k2) = square(k3)
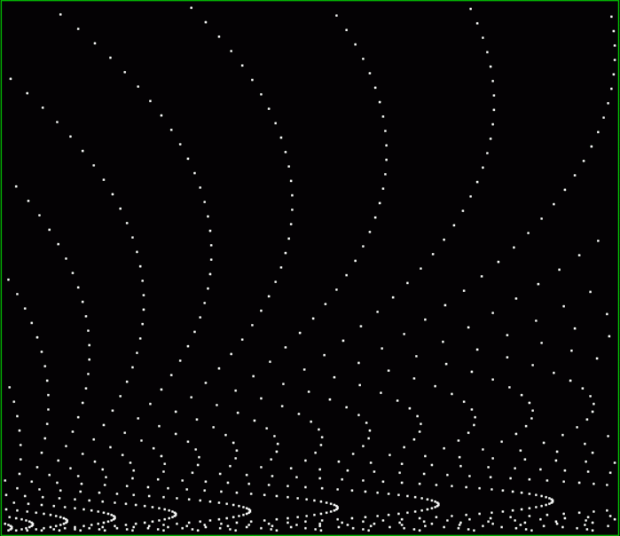
k1 + hexagonal(k2) = pentagonal(k3)
And try other number sequences, like multiples of 4 with polygonals:
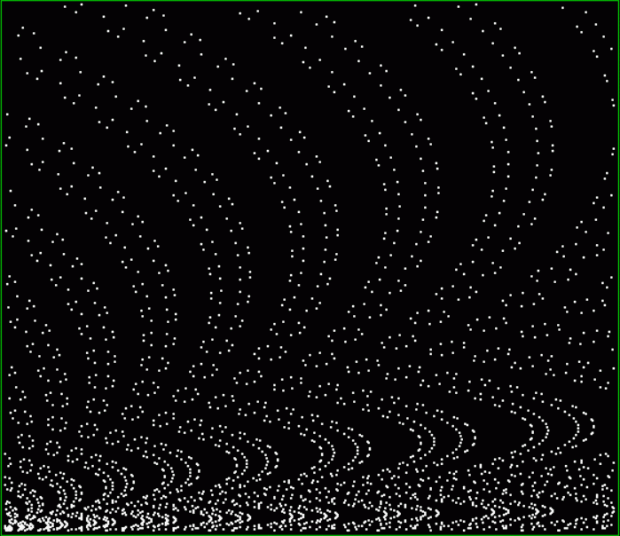
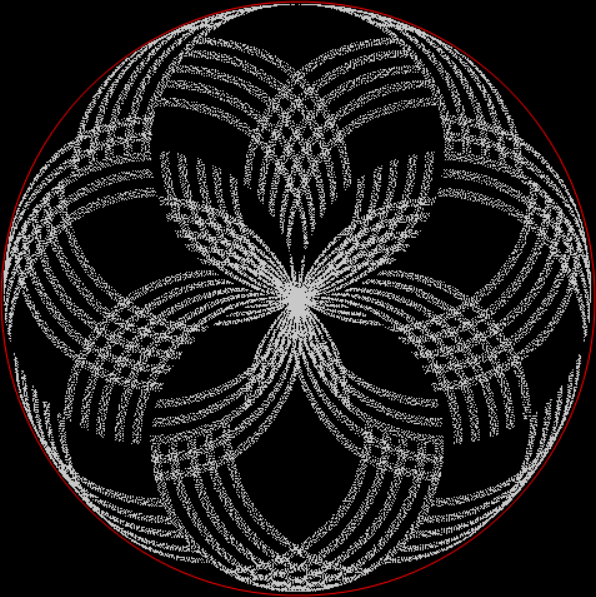
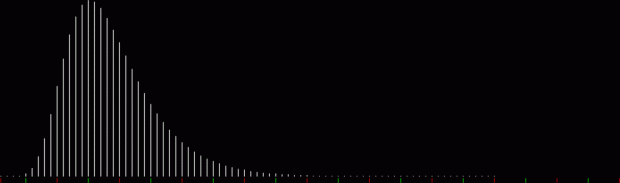
k1*4 + pentagonal(k2) = tri(k3)
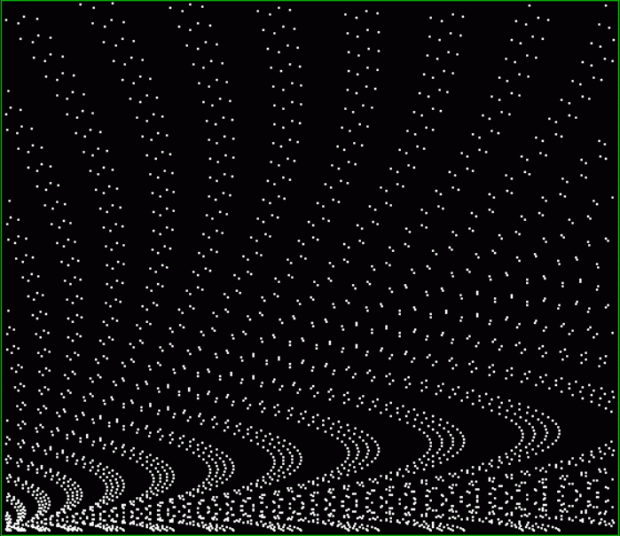
k1*4 + square(k2) = tri(k3)
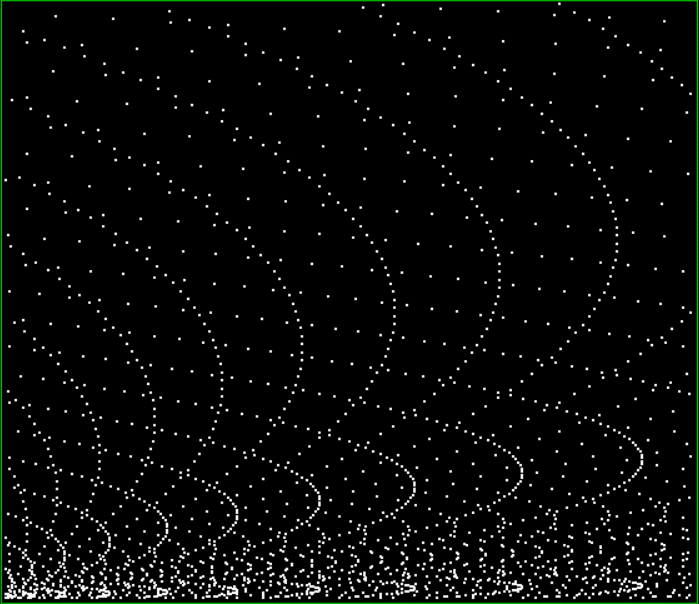
k1*4 + heptagonal(k2) = tri(k3)
And primes with polygonals:

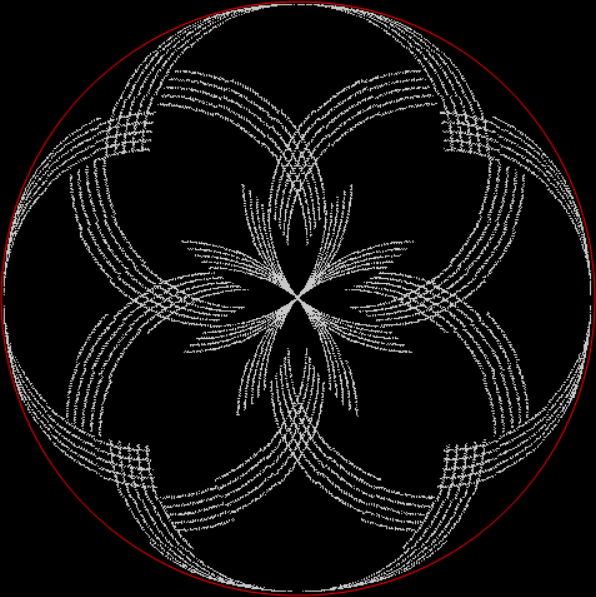
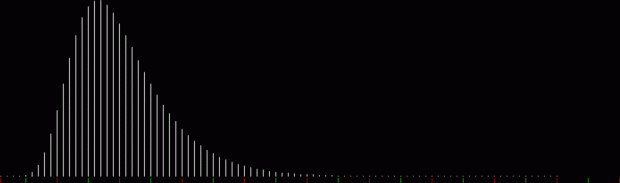
tri(k1) + prime(k2) = tri(k3)
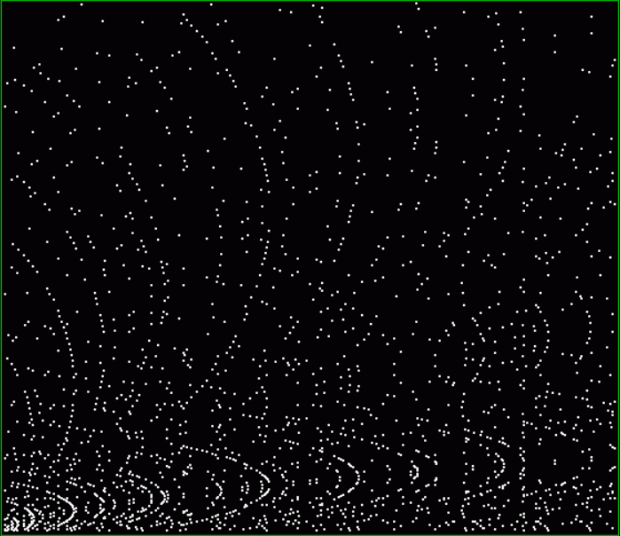
prime(k1) + tri(k2) = square(k3)
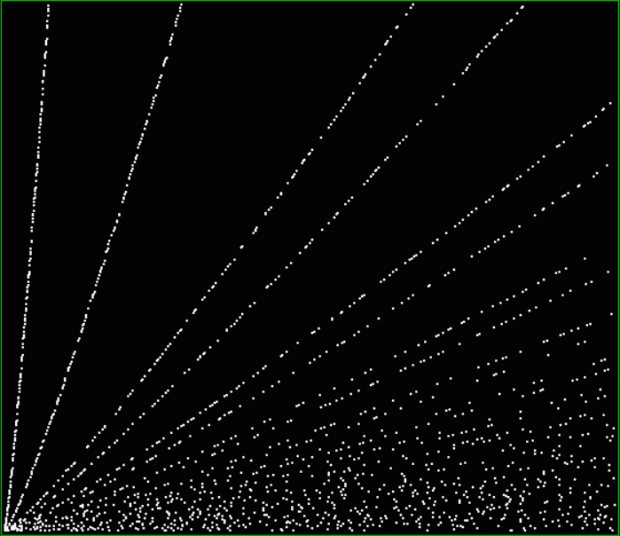
prime(k1) + octagonal(k2) = square(k3)

prime(k1) + pentagonal(k2) = square(k3)
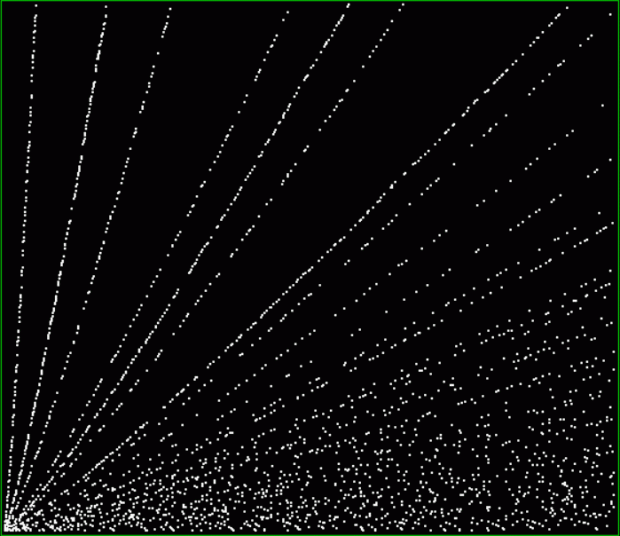
prime(k1) + square(k2) = decagonal(k3)
prime(k1) + tri(k2) = hendecagonal(k3)