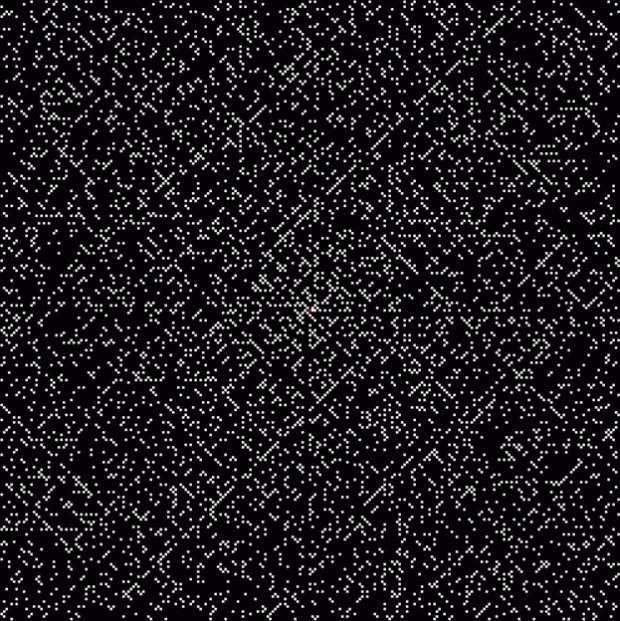
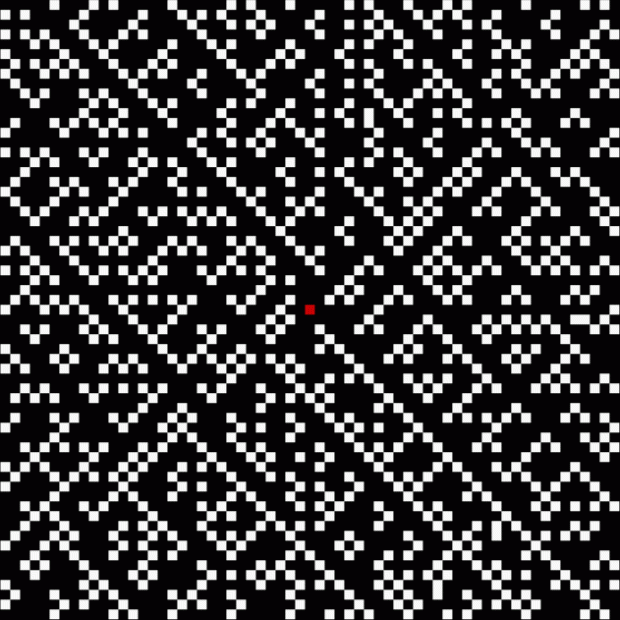
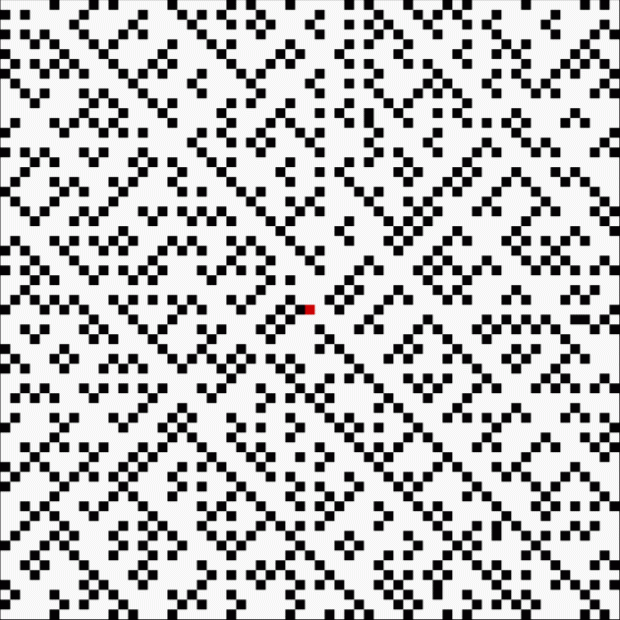
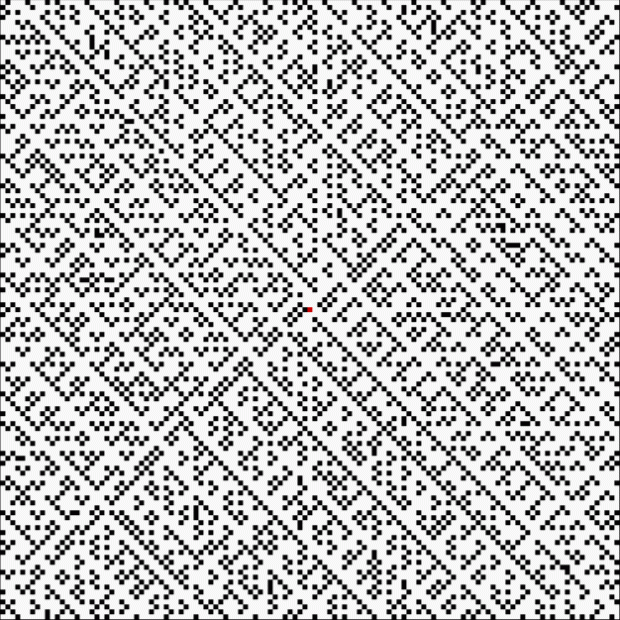
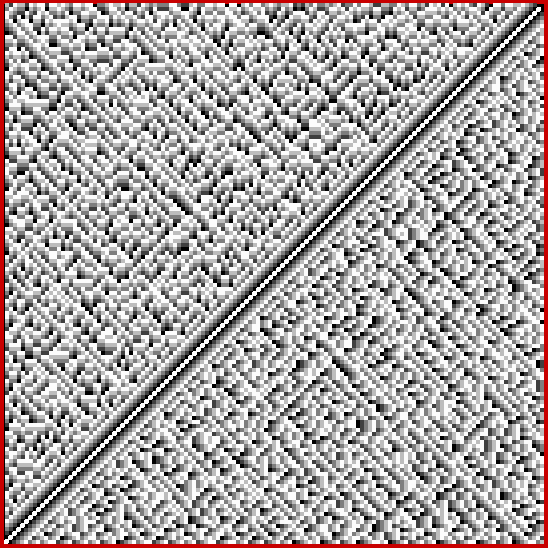
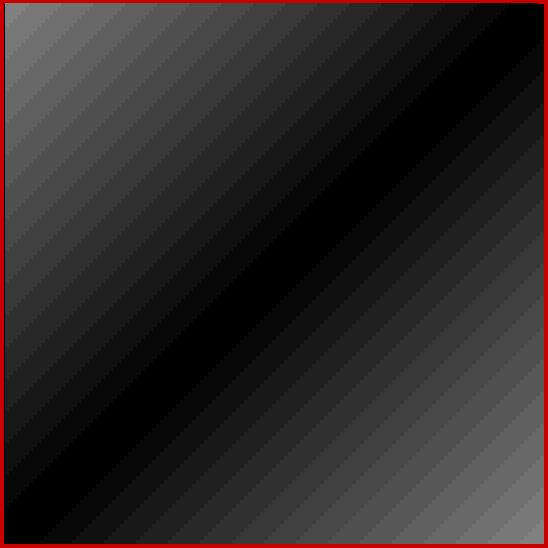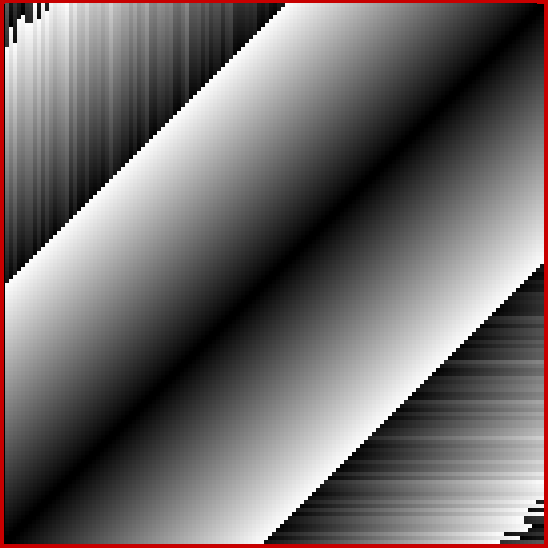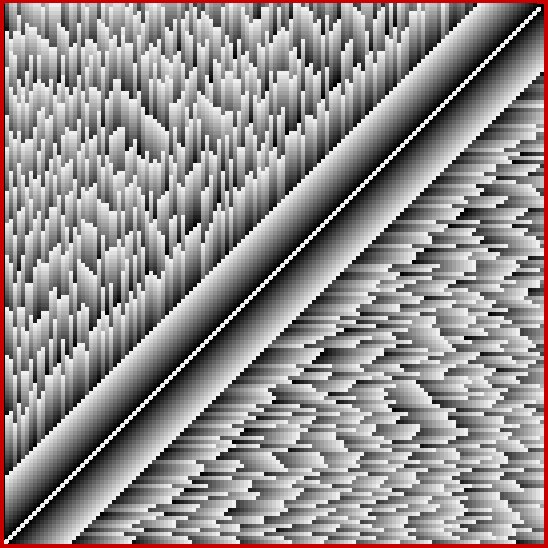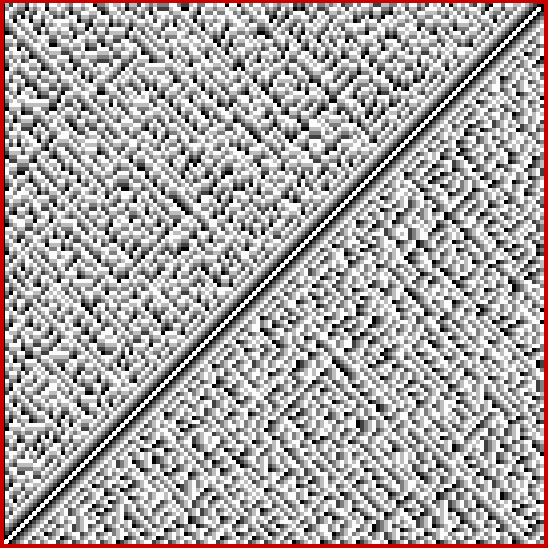
At least, I think it’s a fractal. I came across it when I was counting the ways in which the integers can be the sum of distinct Fibonacci numbers. Here for reference is the Fibonacci sequence, the beautiful and endlessly fertile sequence that’s seeded with “1, 1” and continued by summing the two previous numbers:
1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, 377, 610, 987, 1597, 2584, 4181, 6765, 10946, 17711, 28657, 46368, 75025, 121393, 196418, 317811, 514229, 832040…
I noticed some interesting patterns in the distinct-fib-num-sum count for the integers:
1 = 1 (count=1)
2 = 2 (count=1)
3 = 1+2 = 3 (count=2)
4 = 1+3 (c=1)
5 = 2+3 = 5 (c=2)
6 = 1+2+3 = 1+5 (c=2)
7 = 2+5 (c=1)
8 = 1+2+5 = 3+5 = 8 (c=3)
9 = 1+3+5 = 1+8 (c=2)
10 = 2+3+5 = 2+8 (c=2)
11 = 1+2+3+5 = 1+2+8 = 3+8 (c=3)
12 = 1+3+8 (c=1)
13 = 2+3+8 = 5+8 = 13 (c=3)
14 = 1+2+3+8 = 1+5+8 = 1+13 (c=3)
15 = 2+5+8 = 2+13 (c=2)
16 = 1+2+5+8 = 3+5+8 = 1+2+13 = 3+13 (c=4)
17 = 1+3+5+8 = 1+3+13 (c=2)
18 = 2+3+5+8 = 2+3+13 = 5+13 (c=3)
19 = 1+2+3+5+8 = 1+2+3+13 = 1+5+13 (c=3)
20 = 2+5+13 (c=1)
21 = 1+2+5+13 = 3+5+13 = 8+13 = 21 (c=4)
22 = 1+3+5+13 = 1+8+13 = 1+21 (c=3)
23 = 2+3+5+13 = 2+8+13 = 2+21 (c=3)
24 = 1+2+3+5+13 = 1+2+8+13 = 3+8+13 = 1+2+21 = 3+21 (c=5)
25 = 1+3+8+13 = 1+3+21 (c=2)
26 = 2+3+8+13 = 5+8+13 = 2+3+21 = 5+21 (c=4)
27 = 1+2+3+8+13 = 1+5+8+13 = 1+2+3+21 = 1+5+21 (c=4)
28 = 2+5+8+13 = 2+5+21 (c=2)
29 = 1+2+5+8+13 = 3+5+8+13 = 1+2+5+21 = 3+5+21 = 8+21 (c=5)
30 = 1+3+5+8+13 = 1+3+5+21 = 1+8+21 (c=3)
31 = 2+3+5+8+13 = 2+3+5+21 = 2+8+21 (c=3)
32 = 1+2+3+5+8+13 = 1+2+3+5+21 = 1+2+8+21 = 3+8+21 (c=4)
33 = 1+3+8+21 (c=1)
34 = 2+3+8+21 = 5+8+21 = 13+21 = 34 (c=4)
35 = 1+2+3+8+21 = 1+5+8+21 = 1+13+21 = 1+34 (c=4)
36 = 2+5+8+21 = 2+13+21 = 2+34 (c=3)
37 = 1+2+5+8+21 = 3+5+8+21 = 1+2+13+21 = 3+13+21 = 1+2+34 = 3+34
(c=6)
38 = 1+3+5+8+21 = 1+3+13+21 = 1+3+34 (c=3)
39 = 2+3+5+8+21 = 2+3+13+21 = 5+13+21 = 2+3+34 = 5+34 (c=5)
40 = 1+2+3+5+8+21 = 1+2+3+13+21 = 1+5+13+21 = 1+2+3+34 = 1+5+34
(c=5)
41 = 2+5+13+21 = 2+5+34 (c=2)
42 = 1+2+5+13+21 = 3+5+13+21 = 8+13+21 = 1+2+5+34 = 3+5+34 = 8+3
4 (c=6)
43 = 1+3+5+13+21 = 1+8+13+21 = 1+3+5+34 = 1+8+34 (c=4)
44 = 2+3+5+13+21 = 2+8+13+21 = 2+3+5+34 = 2+8+34 (c=4)
45 = 1+2+3+5+13+21 = 1+2+8+13+21 = 3+8+13+21 = 1+2+3+5+34 = 1+2+
8+34 = 3+8+34 (c=6)
46 = 1+3+8+13+21 = 1+3+8+34 (c=2)
47 = 2+3+8+13+21 = 5+8+13+21 = 2+3+8+34 = 5+8+34 = 13+34 (c=5)
48 = 1+2+3+8+13+21 = 1+5+8+13+21 = 1+2+3+8+34 = 1+5+8+34 = 1+13+
34 (c=5)
49 = 2+5+8+13+21 = 2+5+8+34 = 2+13+34 (c=3)
50 = 1+2+5+8+13+21 = 3+5+8+13+21 = 1+2+5+8+34 = 3+5+8+34 = 1+2+1
3+34 = 3+13+34 (c=6)
51 = 1+3+5+8+13+21 = 1+3+5+8+34 = 1+3+13+34 (c=3)
52 = 2+3+5+8+13+21 = 2+3+5+8+34 = 2+3+13+34 = 5+13+34 (c=4)
53 = 1+2+3+5+8+13+21 = 1+2+3+5+8+34 = 1+2+3+13+34 = 1+5+13+34 (c=4)
54 = 2+5+13+34 (c=1)
55 = 1+2+5+13+34 = 3+5+13+34 = 8+13+34 = 21+34 = 55 (c=5)
56 = 1+3+5+13+34 = 1+8+13+34 = 1+21+34 = 1+55 (c=4)
The patterns are easier to see when the counts are set out like this:
1, 1, 2, 1, 2, 2, 1, 3, 2, 2, 3, 1, 3, 3, 2, 4, 2, 3, 3, 1, 4, 3, 3, 5, 2, 4, 4, 2, 5, 3, 3, 4, 1, 4, 4, 3, 6, 3, 5, 5, 2, 6, 4, 4, 6, 2, 5, 5, 3, 6, 3, 4, 4, 1, 5, 4, 4, 7, 3, 6, 6, 3, 8, 5, 5, 7, 2, 6, 6, 4, 8, 4, 6, 6, 2, 7, 5, 5, 8, 3, 6, 6, 3, 7, 4, 4, 5, 1, 5, 5, 4, 8, 4, 7, 7, 3, 9, 6, 6, 9, 3, 8, 8, 5, 10, 5, 7, 7, 2, 8, 6, 6, 10, 4, 8, 8, 4, 10, 6, 6, 8, 2, 7, 7, 5, 10, 5, 8, 8, 3, 9, 6, 6, 9, 3, 7, 7, 4, 8, 4, 5, 5, 1, 6, 5, 5, 9, 4, 8, 8… 1… — See A000119, Number of representations of n as a sum of distinct Fibonacci numbers, at the Online Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences (OEIS)
The numbers between each pair of 1s are symmetrical:
1, 2, 1,
1, 2, 2, 1,
1, 3, 2, 2, 3, 1,
1, 3, 3, 2, 4, 2, 3, 3, 1
1, 4, 3, 3, 5, 2, 4, 4, 2, 5, 3, 3, 4, 1
And when fibsumcount(n) = 1, then n = fib(i)-1, i.e. n is one less than a Fibonacci number:
1 = 1 (c=1)
2 = 2 (c=1)
4 = 1+3 (c=1)
7 = 2+5 (c=1)
12 = 1+3+8 (c=1)
20 = 2+5+13 (c=1)
33 = 1+3+8+21 (c=1)
54 = 2+5+13+34 (c=1)
88 = 1+3+8+21+55 (c=1)
143 = 2+5+13+34+89 (c=1)
232 = 1+3+8+21+55+144 (c=1)
376 = 2+5+13+34+89+233 (c=1)
609 = 1+3+8+21+55+144+377 (c=1)
986 = 2+5+13+34+89+233+610 (c=1)
1596 = 1+3+8+21+55+144+377+987 (c=1)
2583 = 2+5+13+34+89+233+610+1597 (c=1)
4180 = 1+3+8+21+55+144+377+987+2584 (c=1)
6764 = 2+5+13+34+89+233+610+1597+4181 (c=1)
10945 = 1+3+8+21+55+144+377+987+2584+6765 (c=1)
17710 = 2+5+13+34+89+233+610+1597+4181+10946 (c=1)
[…]
I also noticed a pattern relating to the maximum count reached in the numbers between the 1s. Suppose the function max(fib(i)-1..fib(i+1)-1) returns the highest count of ways to represent the numbers from fib(i)-1 to fib(i+1)-1. Notice how max() increases:
max(2..4) = 2
max(4..7) = 2
max(7..12) = 3
max(12..20) = 4
max(20..33) = 5
max(33..54) = 6
max(54..88) = 8
max(88..143) = 10
max(143..232) = 13
max(232..376) = 16
max(376..609) = 21
max(609..986) = 26
max(986..1596) = 34
max(1596..2583) = 42
max(2583..4180) = 55
max(4180..6764) = 68
[…]
The pattern is described like this at the Online Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences:
a(n) = 1 if and only if n+1 is a Fibonacci number. The length of such a quasi-period (from Fib(i)-1 to Fib(i+1)-1, inclusive) is a Fibonacci number + 1. The maximum value of a(n) within each subsequent quasi-period increases by a Fibonacci number. For example, from n = 143 to n = 232, the maximum is 13. From 232 to 376, the maximum is 16, an increase of 3. From 376 to 609, 21, an increase of 5. From 609 to 986, 26, increasing by 5 again. Each two subsequent maxima seem to increase by the same increment, the next Fibonacci number. – Kerry Mitchell, Nov 14 2009
The maxima of the quasi-periods are in A096748. – Max Barrentine, Sep 13 2015 — See commentary for A000119 at OEIS
Here is A096748:
1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 13, 16, 21, 26, 34, 42, 55, 68, 89, 110, 144, 178, 233, 288, 377, 466, 610, 754, 987, 1220, 1597, 1974, 2584, 3194, 4181, 5168, 6765, 8362, 10946, 13530, 17711, 21892, 28657, 35422, 46368, 57314, 75025, 92736, 121393, 150050 — A096748, Expansion of (1+x)^2/(1-x^2-x^4), at OEIS
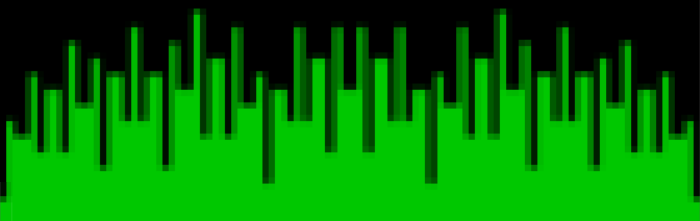
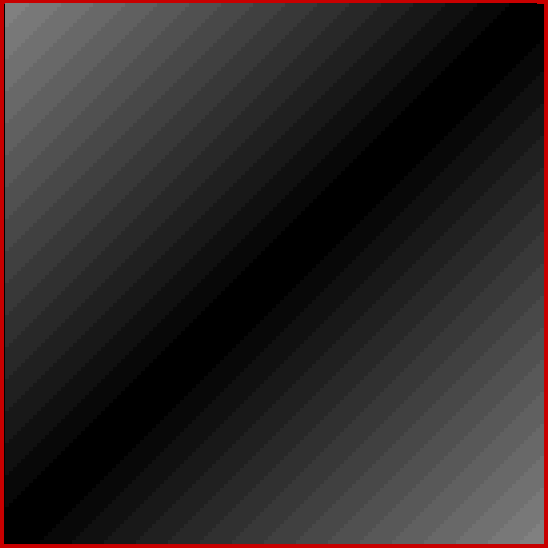
These maxima are the succesive highest points in a graph of A000119, Number of representations of n as a sum of distinct Fibonacci numbers:
Graph of count of ways in which 1,2,3… can be sum of distinct Fibonacci numbers
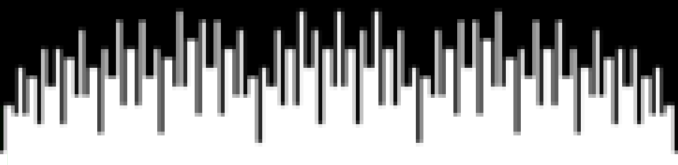
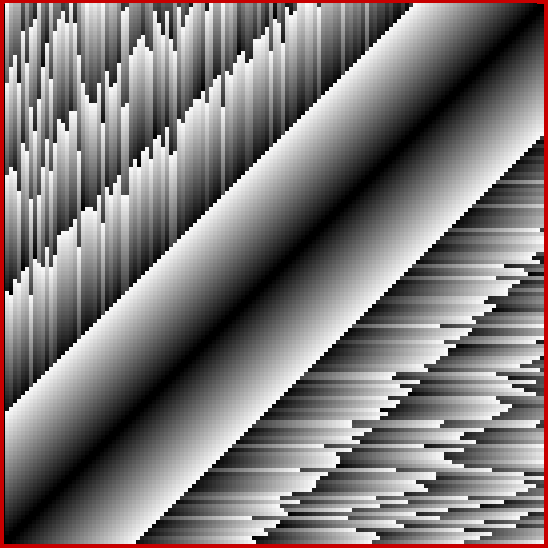
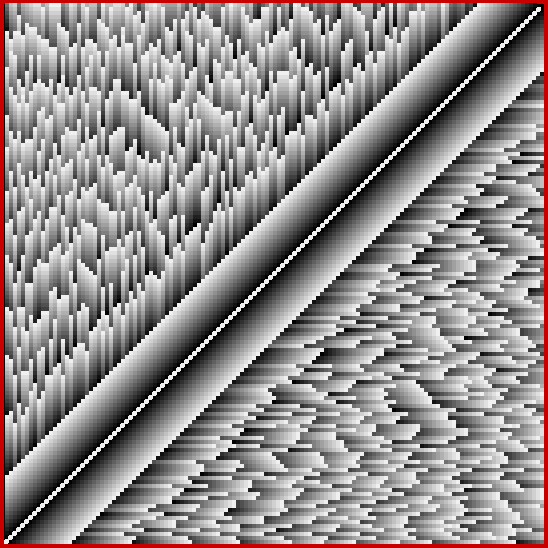
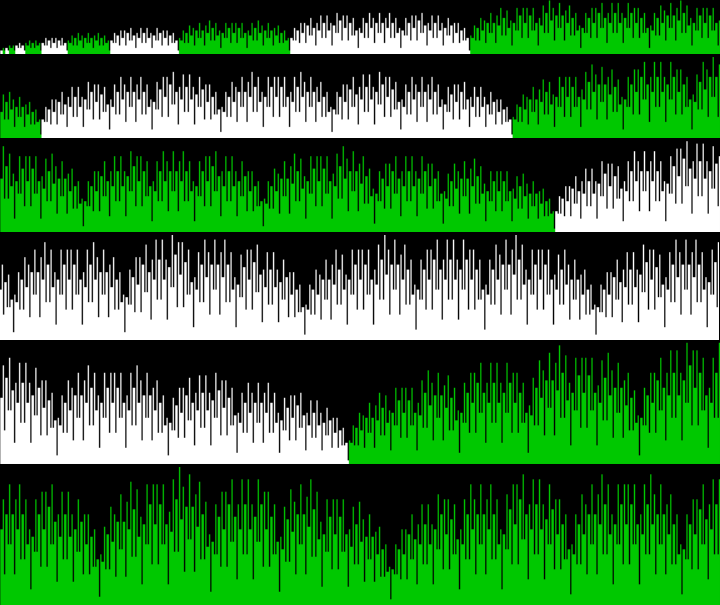
The graph looks like a furry caterpillar or similar and the symmetry of counts between the 1s is more obvious there:
fibsumcounts for 33..54
fibsumcounts for 54..88
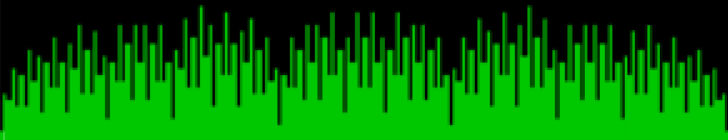
fibsumcounts for 88..143
fibsumcounts for 143..232
fibsumcounts for 232..376
fibsumcounts for 376..609
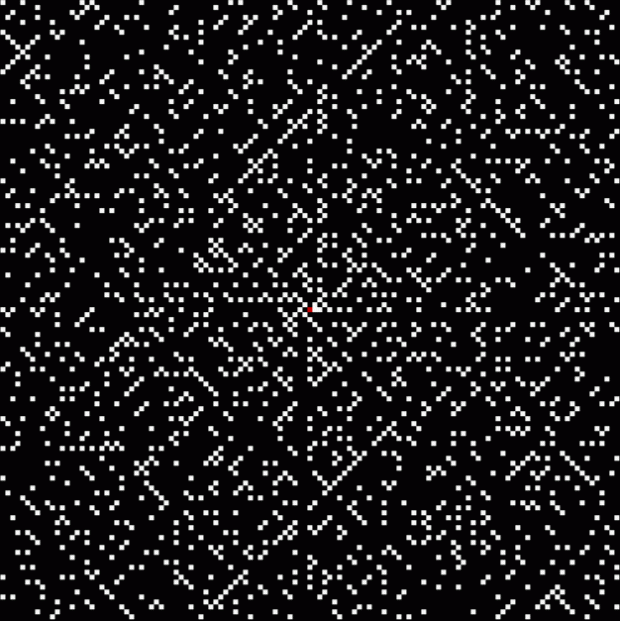
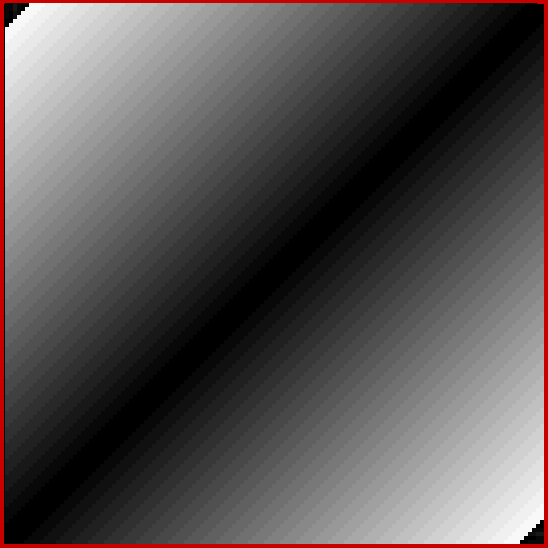
And the fractal nature of the counts is more obvious when the graph is rotated by 90° and then mirrored:
Rotated and mirrored graph of count of ways in which 1,2,3… can be sum of distinct Fibonacci numbers