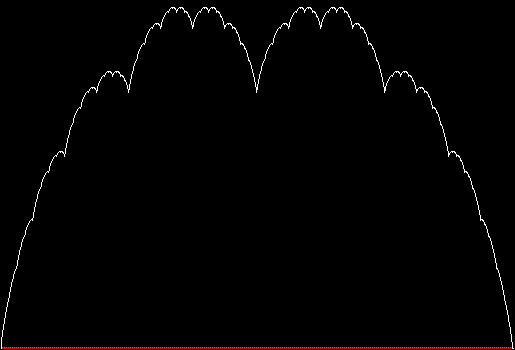
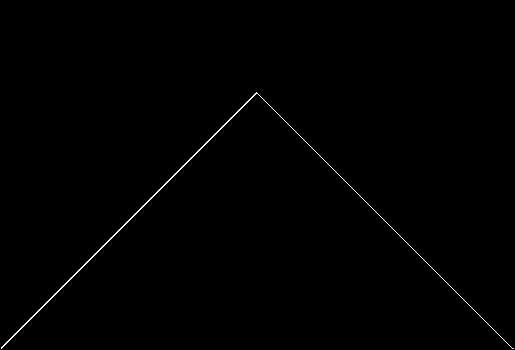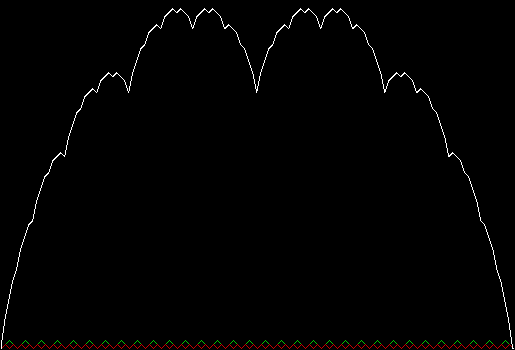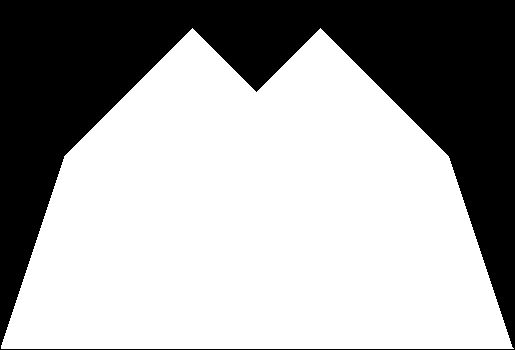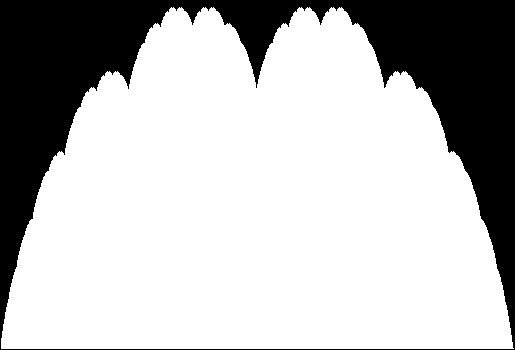
Here’s what you might call a Sisyphean sequence. It struggles upward, then slips back, over and over again:
1, 1, 2, 1, 2, 2, 3, 1, 2, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 4, 1, 2, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 4, 2, 3, 3, 4, 3, 4, 4, 5, 1, 2, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 4, 2, 3, 3, 4, 3, 4, 4, 5, 2, 3, 3, 4, 3, 4, 4, 5, 3, 4, 4, 5, 4, 5, 5, 6, 1, 2, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 4, 2, 3, 3, 4, 3, 4, 4, 5, 2, 3, 3, 4, 3, 4, 4, 5, 3, 4, 4, 5, 4, 5, 5, 6, 2, 3, 3, 4, 3, 4, 4, 5, 3, 4, 4, 5, 4, 5, 5, 6, 3, 4, 4, 5, 4, 5, 5, 6, 4, 5, 5, 6, 5, 6, 6, 7, 1, 2, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 4, 2...
The struggle goes on for ever. Every time it reaches a new maximum, it will fall back to 1 at the next step. And in fact 1, 2, 3 and all other integers occur infinitely often in the sequence, because it represents the digit-sums of binary numbers:
1 ← 1
1 = 1+0 ← 10 in binary = 2 in base ten
2 = 1+1 ← 11 = 3
1 = 1+0+0 ← 100 = 4
2 = 1+0+1 ← 101 = 5
2 = 1+1+0 ← 110 = 6
3 = 1+1+1 ← 111 = 7
1 = 1+0+0+0 ← 1000 = 8
2 = 1+0+0+1 ← 1001 = 9
2 = 1+0+1+0 ← 1010 = 10
3 = 1+0+1+1 ← 1011 = 11
2 = 1+1+0+0 ← 1100 = 12
3 = 1+1+0+1 ← 1101 = 13
3 = 1+1+1+0 ← 1110 = 14
4 = 1+1+1+1 ← 1111 = 15
1 = 1+0+0+0+0 ← 10000 = 16
2 = 1+0+0+0+1 ← 10001 = 17
2 = 1+0+0+1+0 ← 10010 = 18
3 = 1+0+0+1+1 ← 10011 = 19
2 = 1+0+1+0+0 ← 10100 = 20
Now here’s a related sequence in which all integers do not occur infinitely often:
1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 6, 4, 5, 6, 7, 7, 8, 9, 10, 5, 6, 7, 8, 8, 9, 10, 11, 9, 10, 11, 12, 12, 13, 14, 15, 6, 7, 8, 9, 9, 10, 11, 12, 10, 11, 12, 13, 13, 14, 15, 16, 11, 12, 13, 14, 14, 15, 16, 17, 15, 16, 17, 18, 18, 19, 20, 21, 7, 8, 9, 10, 10, 11, 12, 13, 11, 12, 13, 14, 14, 15, 16, 17, 12, 13, 14, 15, 15, 16, 17, 18, 16, 17, 18, 19, 19, 20, 21, 22, 13, 14, 15, 16, 16, 17, 18, 19, 17, 18, 19, 20, 20, 21, 22, 23, 18, 19, 20, 21, 21, 22, 23, 24, 22, 23, 24, 25, 25, 26, 27, 28, 8, 9, 10, 11, 11, 12, 13, 14, 12, 13, 14, 15, 15...
The sequence represents the sum of the values of occupied columns in the binary numbers, reading from right to left:
10 in binary = 2 in base ten
21 (column values from right to left)
2*1 + 1*0 = 2
11 = 3
21
2*1 + 1*1 = 3
100 = 4
321 (column values from right to left)
3*1 + 2*0 + 1*0 = 3
101 = 5
321
3*1 + 2*0 + 1*1 = 4
110 = 6
321
3*1 + 2*1 + 1*0 = 5
111 = 7
321
3*1 + 2*1 + 1*1 = 6
1000 = 8
4321
4*1 + 3*0 + 2*0 + 1*0 = 4
1001 = 9
4321
4*1 + 3*0 + 2*0 + 1*1 = 5
1010 = 10
4321
4*1 + 3*0 + 2*1 + 1*0 = 6
1011 = 11
4321
4*1 + 3*0 + 2*1 + 1*1 = 7
1100 = 12
4321
4*1 + 3*1 + 2*0 + 1*0 = 7
1101 = 13
4321
4*1 + 3*1 + 2*0 + 1*1 = 8
1110 = 14
4321
4*1 + 3*1 + 2*1 + 1*0 = 9
1111 = 15
4321
4*1 + 3*1 + 2*1 + 1*1 = 10
10000 = 16
54321
5*1 + 4*0 + 3*0 + 2*0 + 1*0 = 5
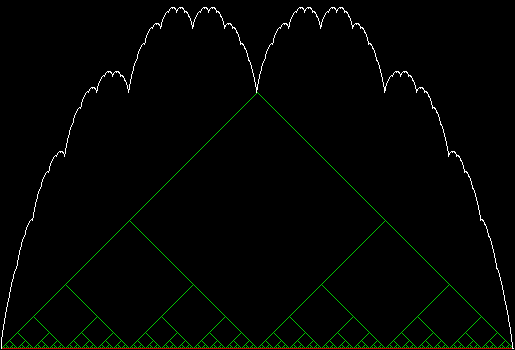
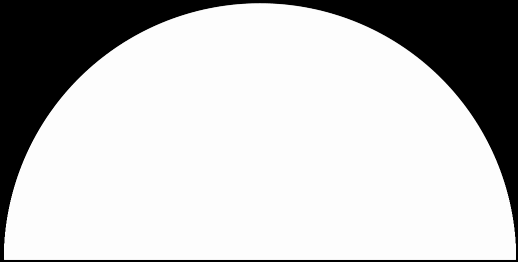
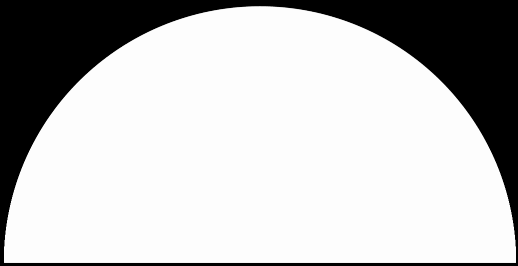
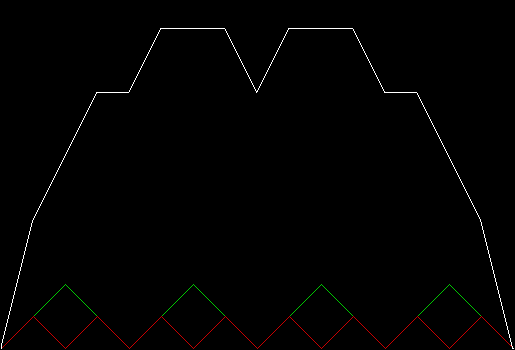
In that sequence, although no number occurs infinitely often, some numbers occur more often than others. If you represent the count of sums up to a certain digit-length as a graph, you get a famous shape:

Bell curve formed by the count of column-sums in base 2
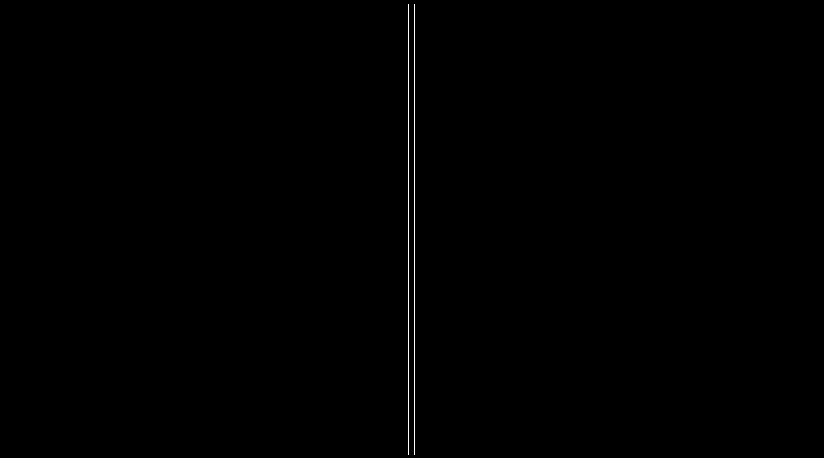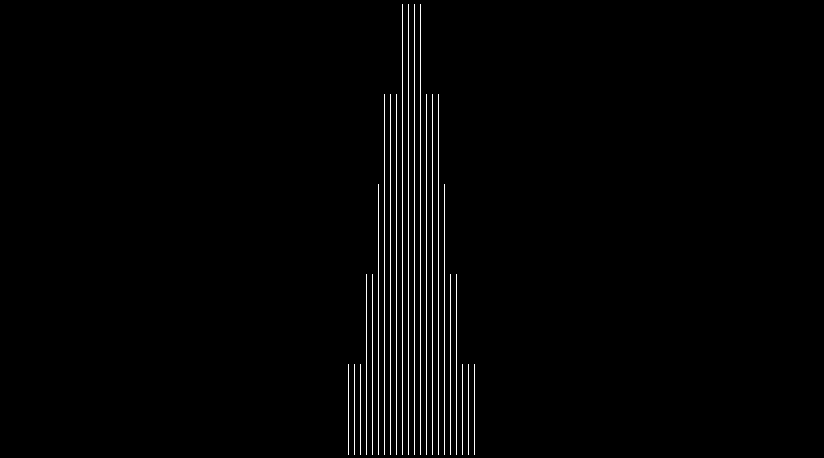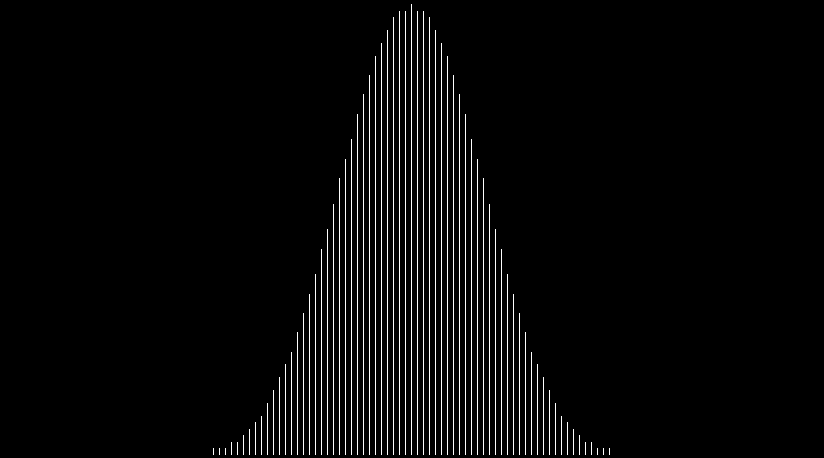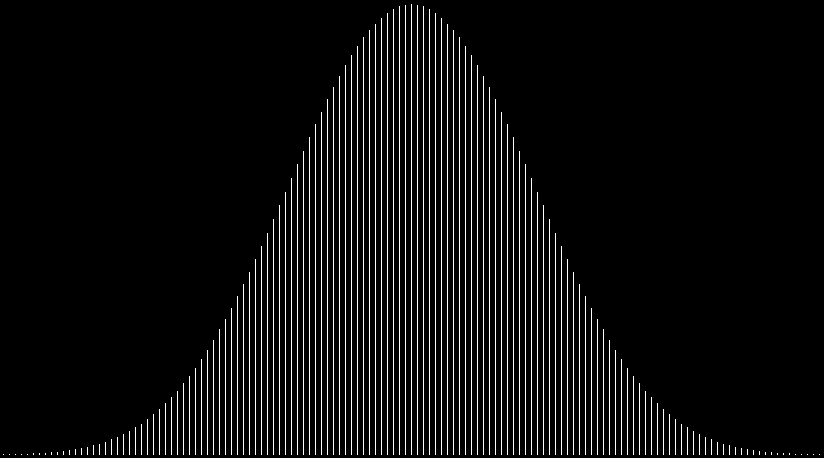
Bi-bell curves for 1 to 16 binary digits (animated)
In “Pi in the Bi”, I looked at that way of forming the bell curve and called it the bi-bell curve. Now I want to go further. Suppose that you assign varying values to the columns and try other bases. For example, what happens if you assign the values 2^p + 1 to the columns, reading from right to left, then use base 3 to generate the sums? These are the values of 2^p + 1:
2, 3, 5, 9, 17, 33, 65, 129, 257, 513, 1025...
And here’s an example of how you generate a column-sum in base 3:
2102 in base 3 = 65 in base ten
9532 (column values from right to left)
2*9 + 1*5 + 0*3 + 2*2 = 27
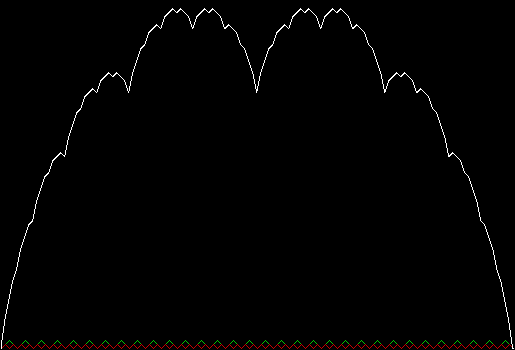
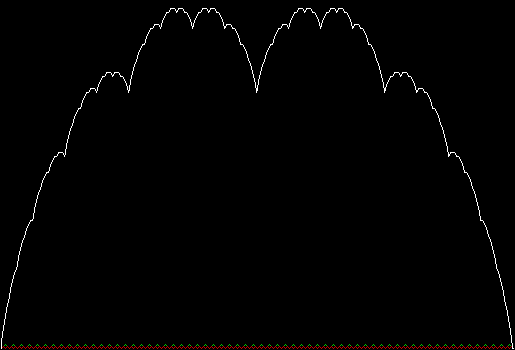
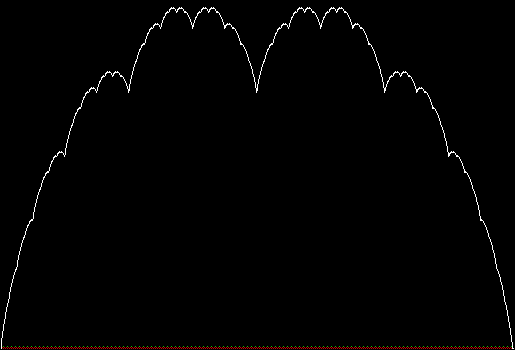
The graphs for these column-sums using base 3 look like this as the digit-length rises. They’re no longer bell-curves (and please note that widths and heights have been normalized so that all graphs fit the same space):

Graph for the count of column-sums in base 3 using 2^p + 1 (digit-length <= 7)
(width and height are normalized)

Graph for base 3 and 2^p + 1 (dl<=8)

Graph for base 3 and 2^p + 1 (dl<=9)

Graph for base 3 and 2^p + 1 (dl<=10)

Graph for base 3 and 2^p + 1 (dl<=11)

Graph for base 3 and 2^p + 1 (dl<=12)

Graph for base 3 and 2^p + 1 (animated)
Now try base 3 and column-values of 2^p + 2 = 3, 4, 6, 10, 18, 34, 66, 130, 258, 514, 1026…

Graph for base 3 and 2^p + 2 (dl<=7)

Graph for base 3 and 2^p + 2 (dl<=8)

Graph for base 3 and 2^p + 2 (dl<=9)

Graph for base 3 and 2^p + 2 (dl<=10)

Graph for base 3 and 2^p + 2 (animated)
Now try base 5 and 2^p + 1 for the columns. The original bell curve has become like a fractal called the blancmange curve:

Graph for base 5 and 2^p + 1 (dl<=7)

Graph for base 5 and 2^p + 1 (dl<=8)

Graph for base 5 and 2^p + 1 (dl<=9)

Graph for base 5 and 2^p + 1 (dl<=10)

Graph for base 5 and 2^p + 1 (animated)
And finally, return to base 2 and try the Fibonacci numbers for the columns:

Graph for base 2 and Fibonacci numbers = 1,1,2,3,5… (dl<=7)

Graph for base 2 and Fibonacci numbers (dl<=9)

Graph for base 2 and Fibonacci numbers (dl<=11)

Graph for base 2 and Fibonacci numbers (dl<=13)

Graph for base 2 and Fibonacci numbers (dl<=15)

Graph for base 2 and Fibonacci numbers (animated)
Previously Pre-Posted…
• Pi in the Bi — bell curves generated by binary digits