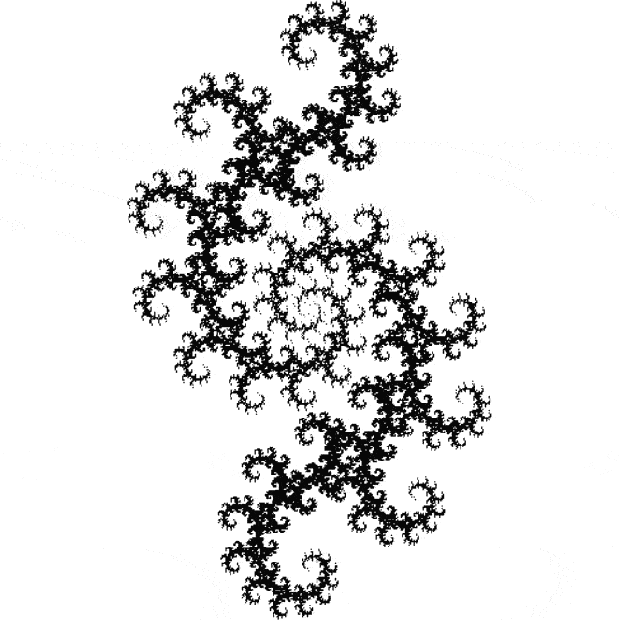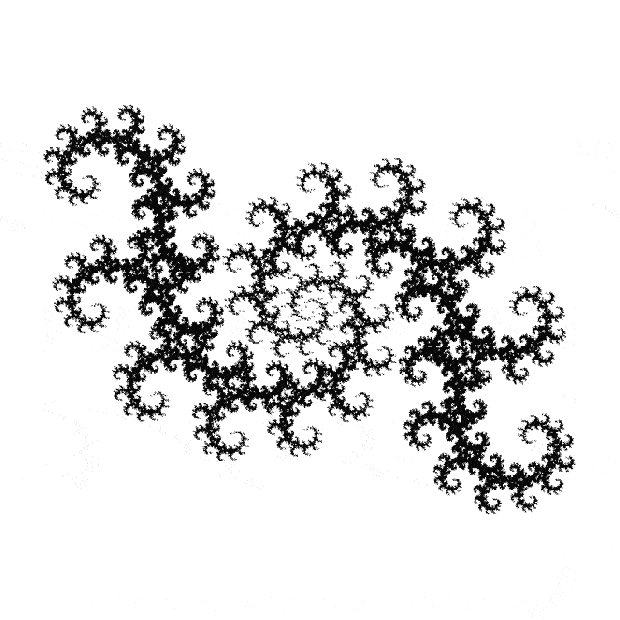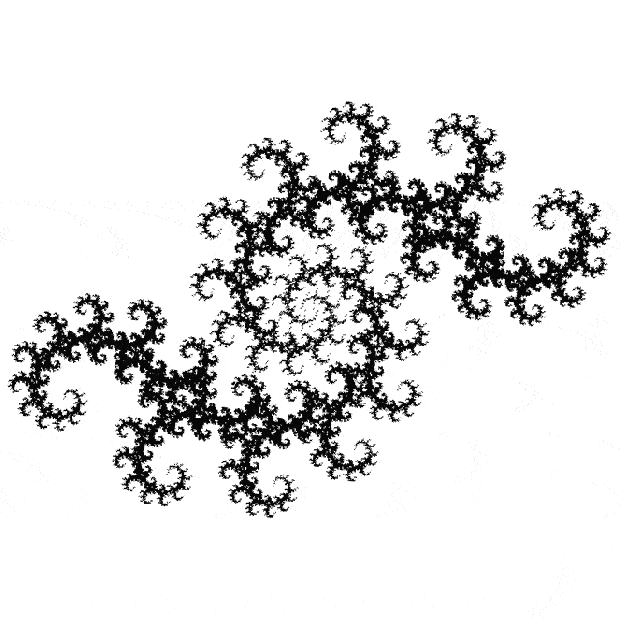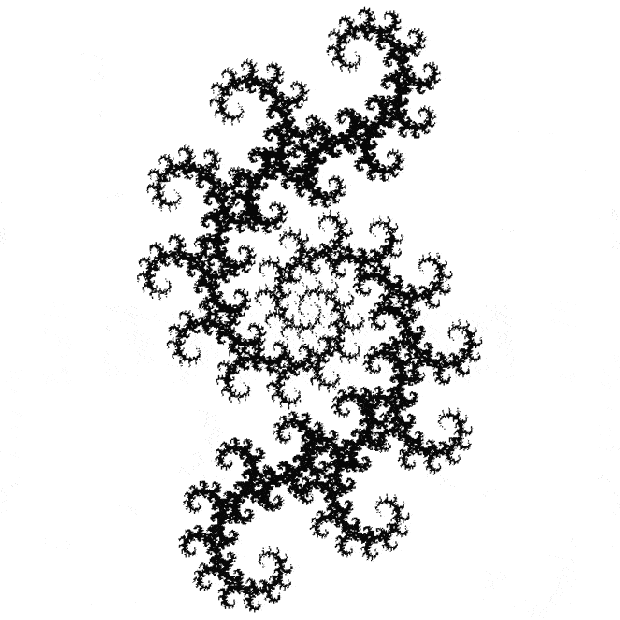
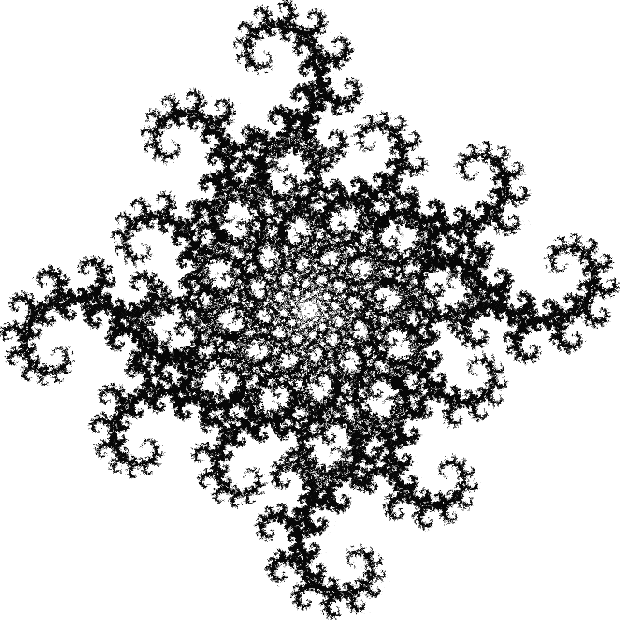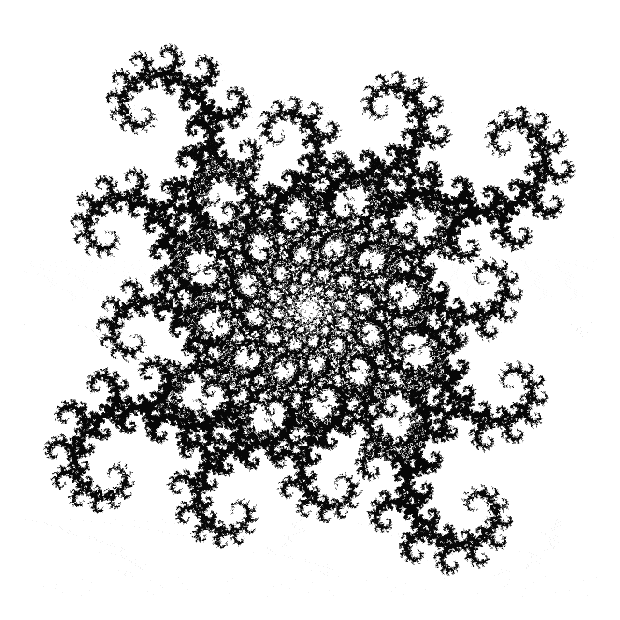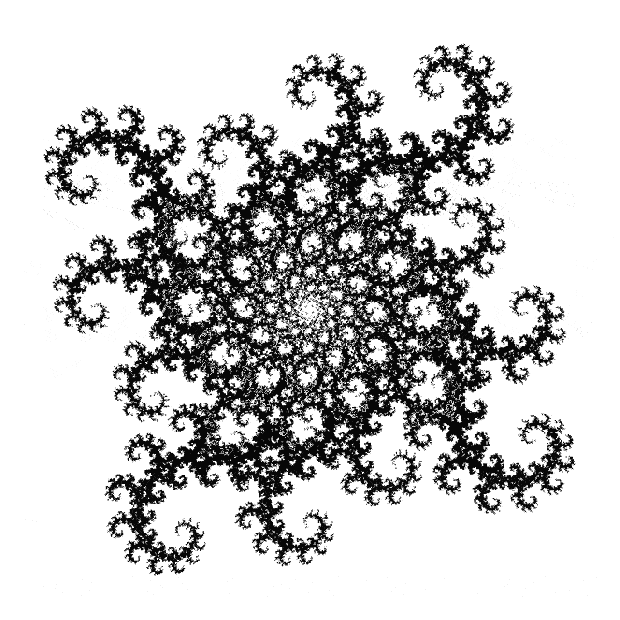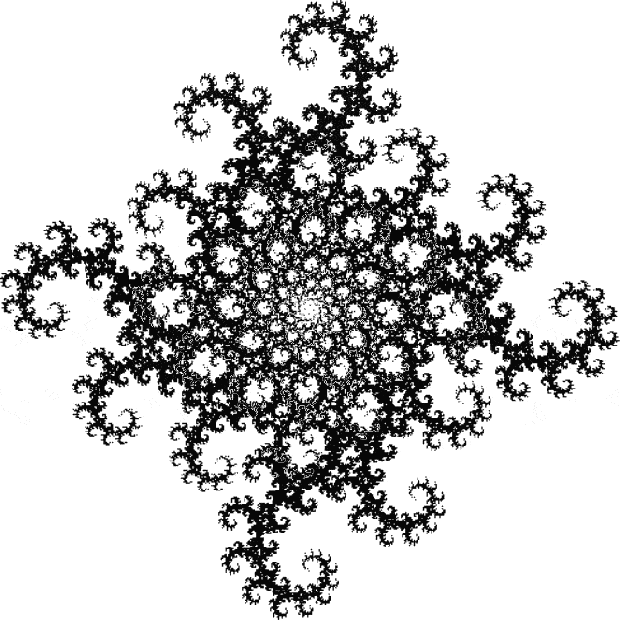
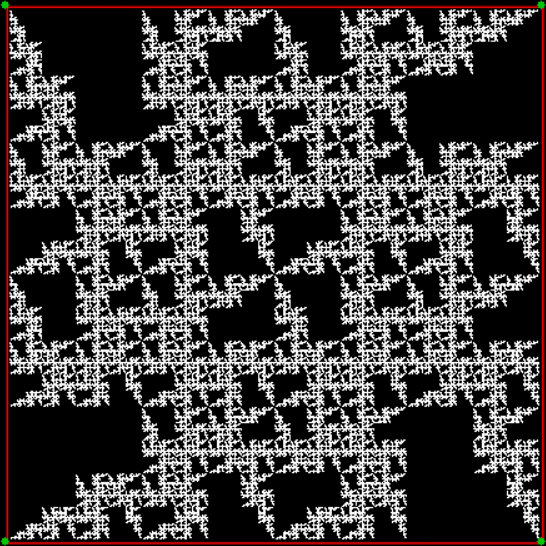
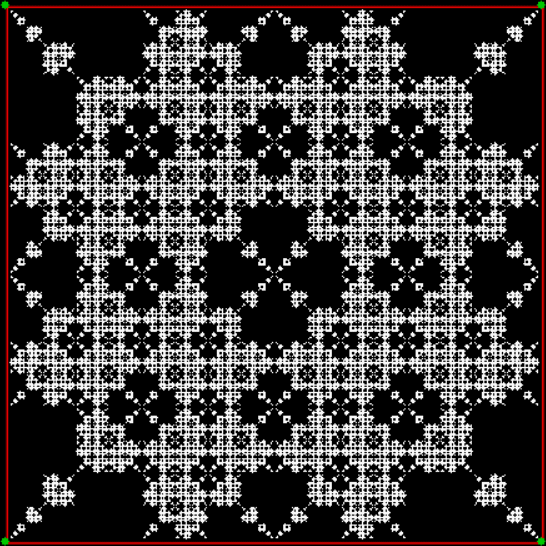
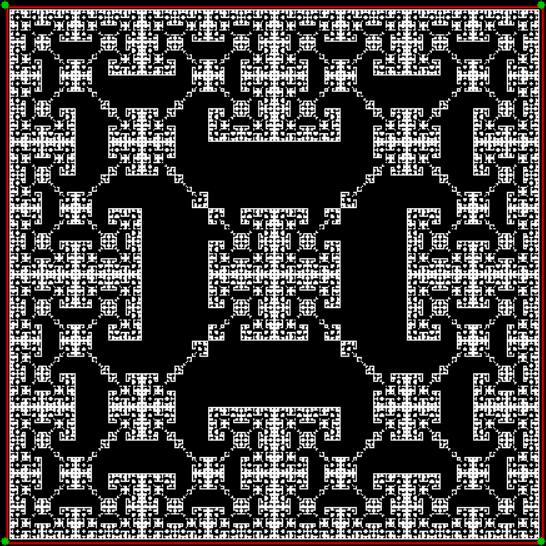
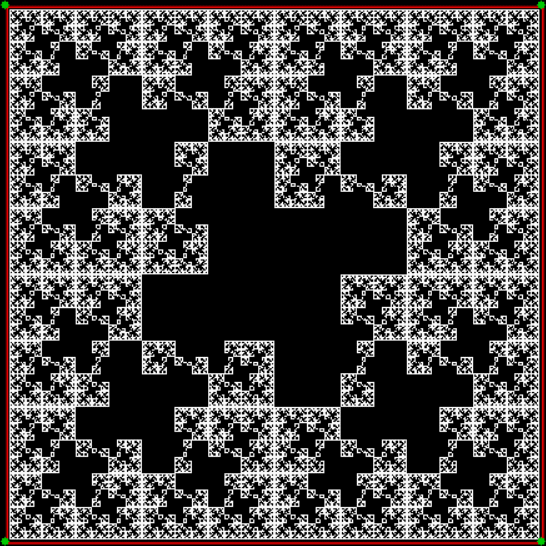
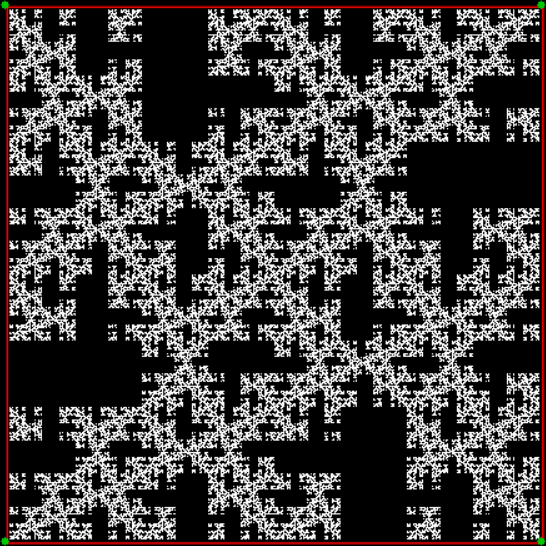
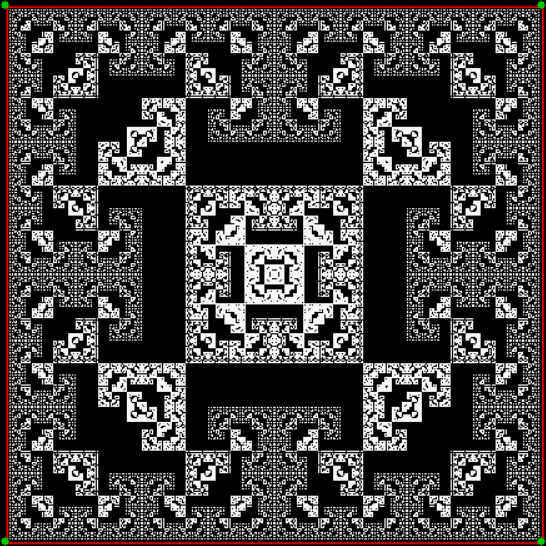
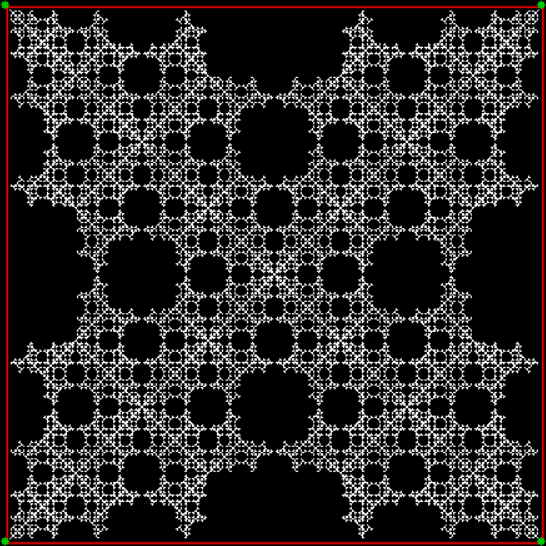
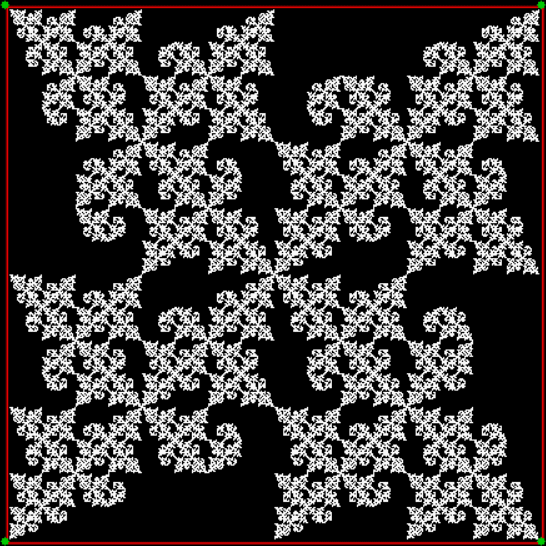
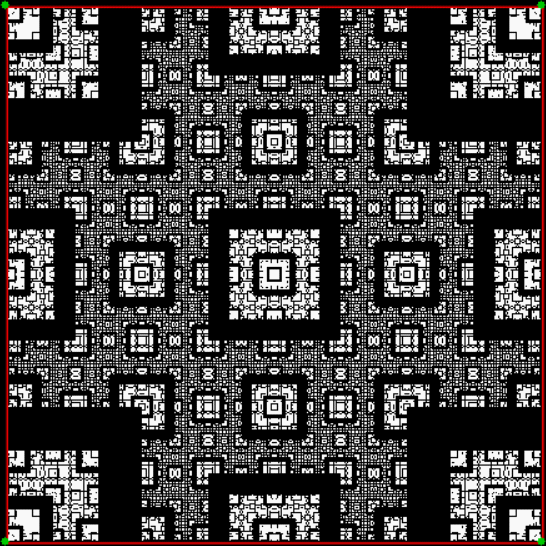
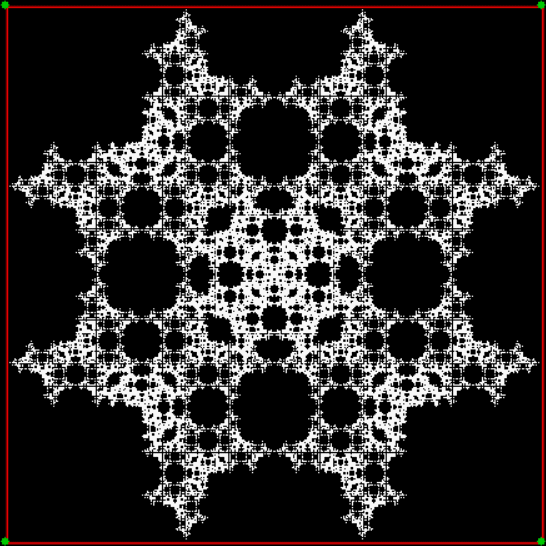
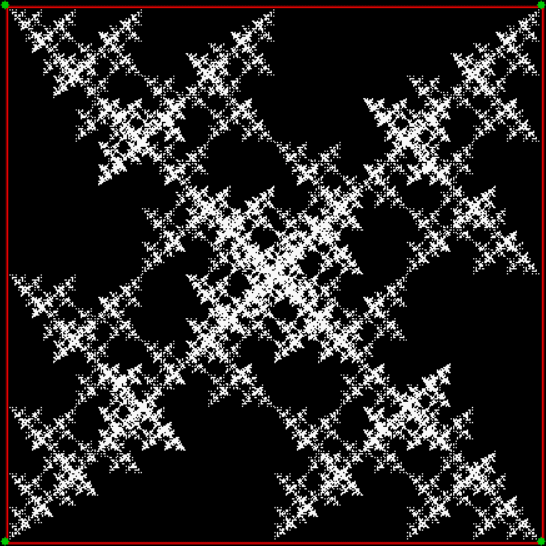
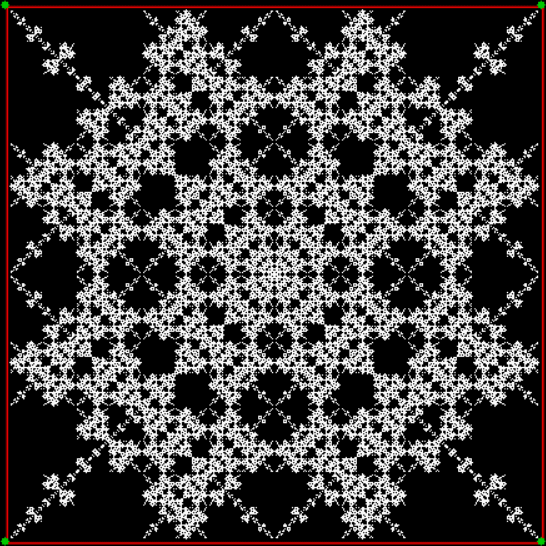
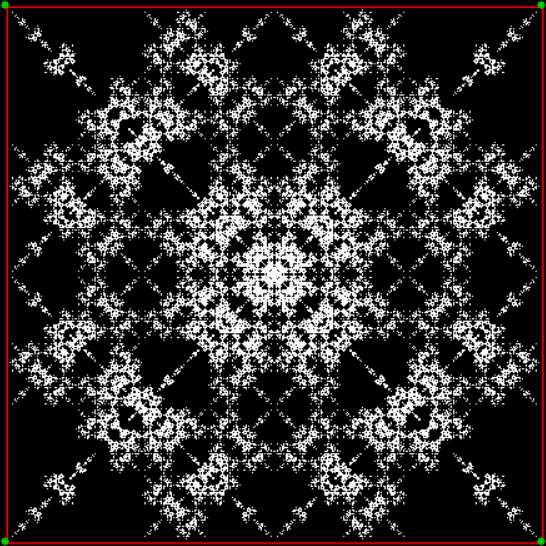
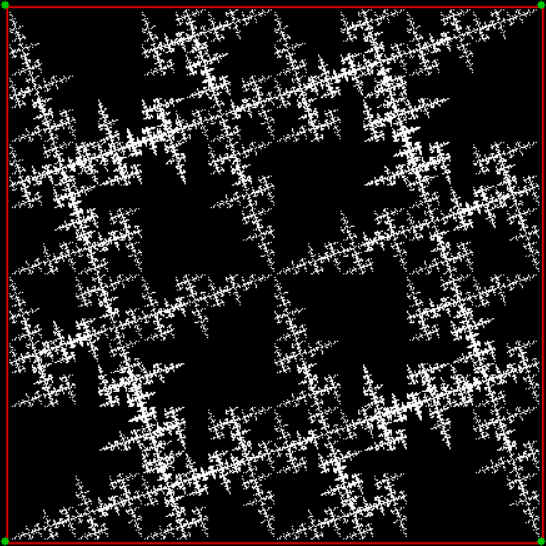
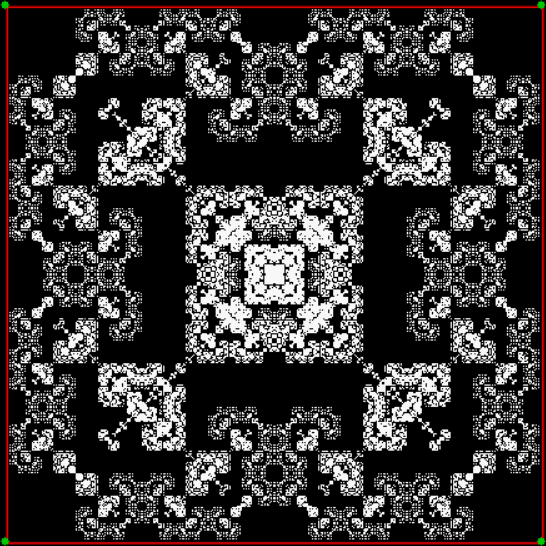
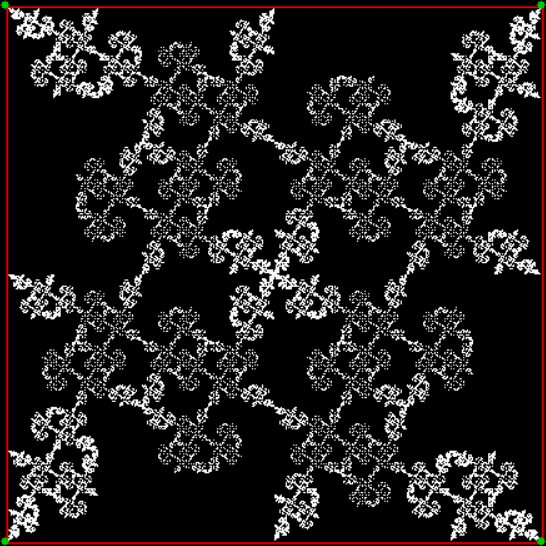
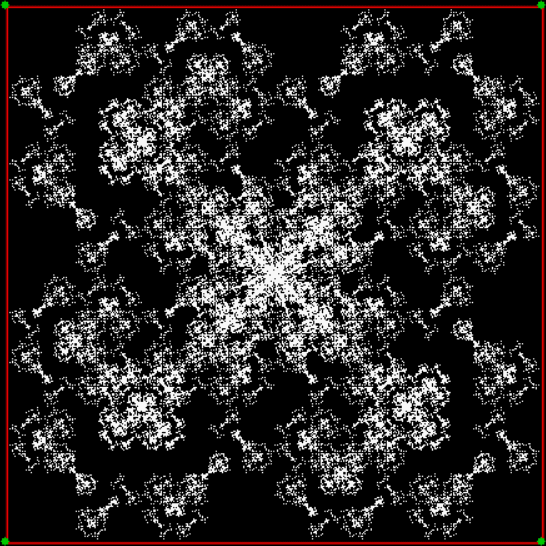
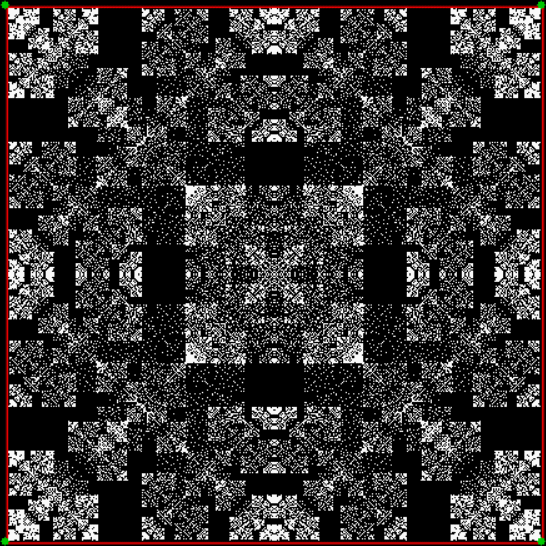
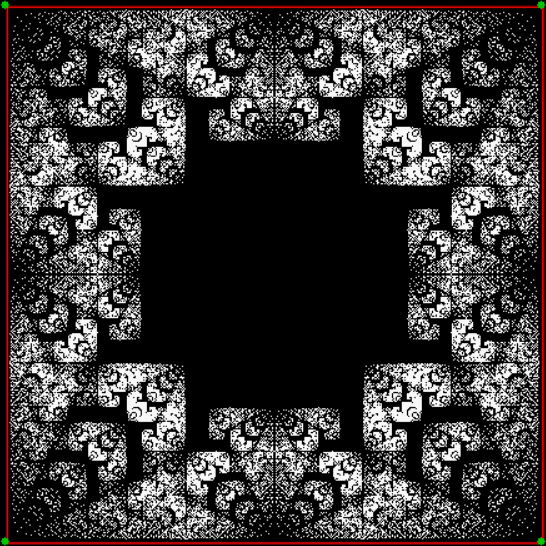
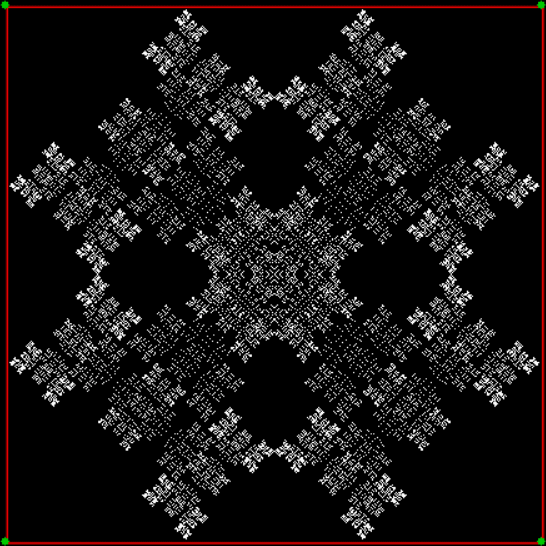
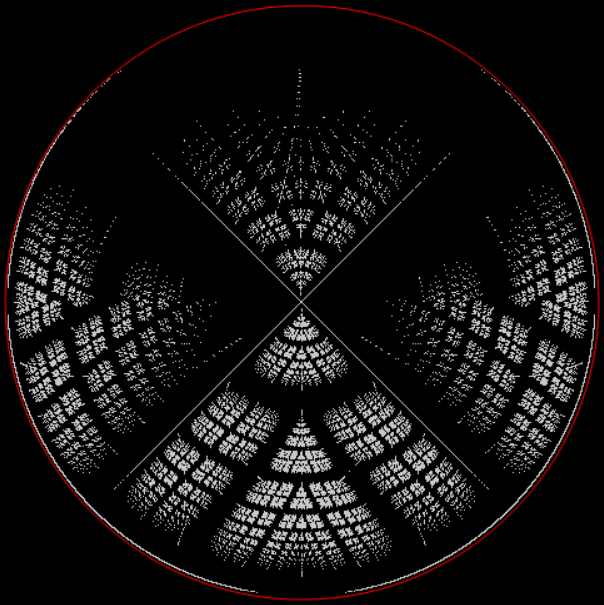
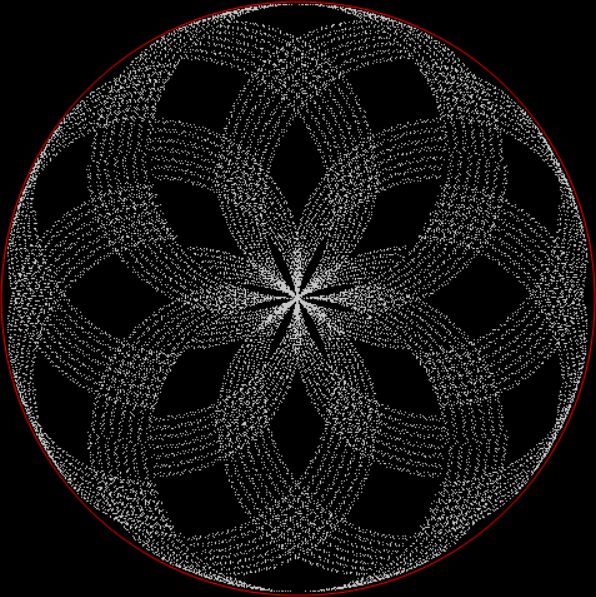
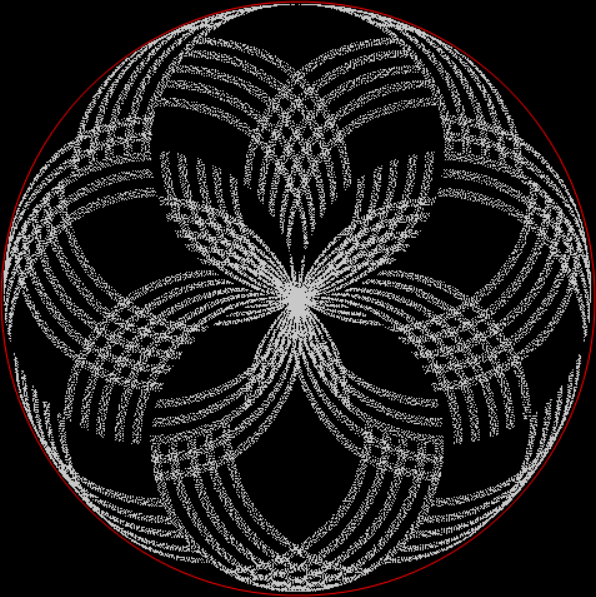
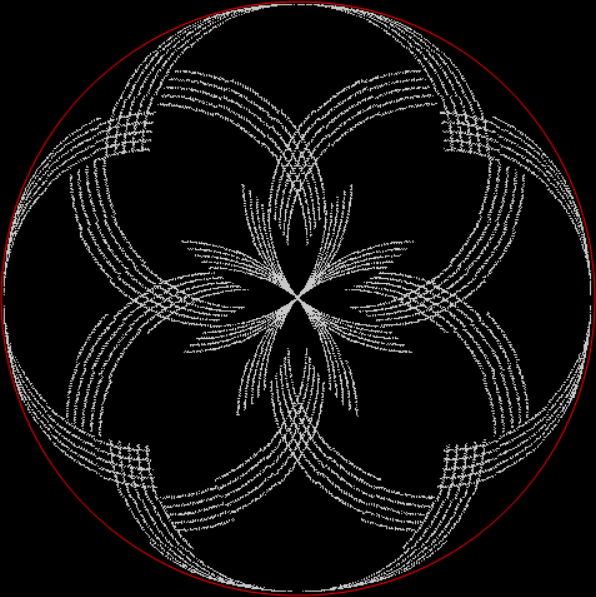
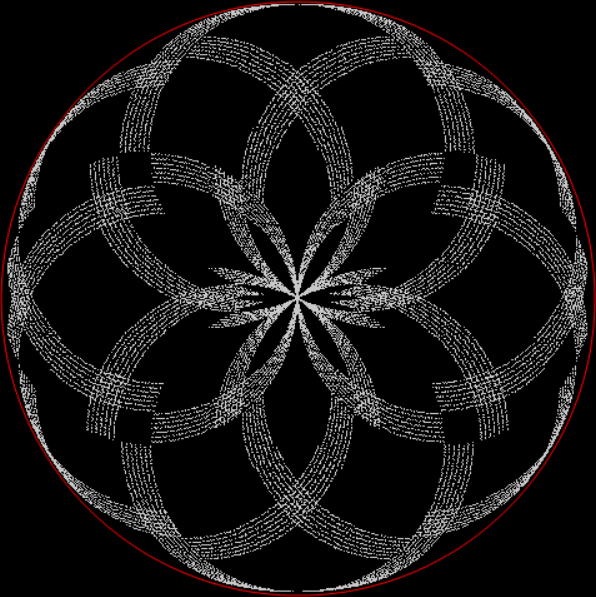
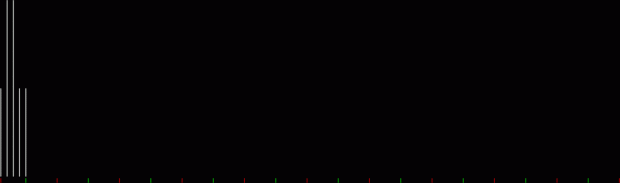
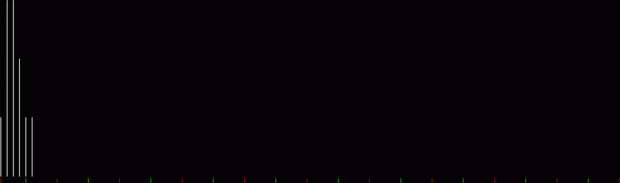
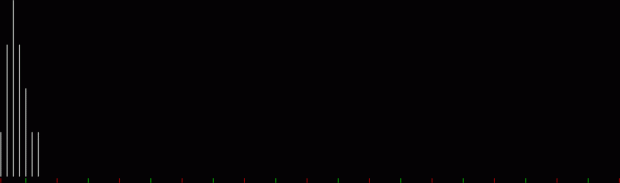
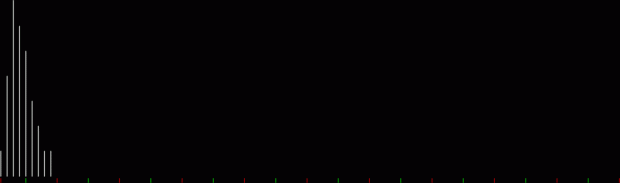
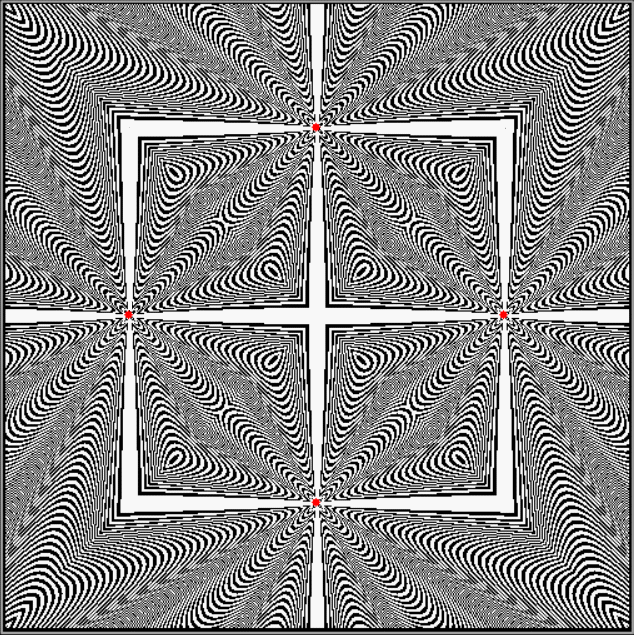
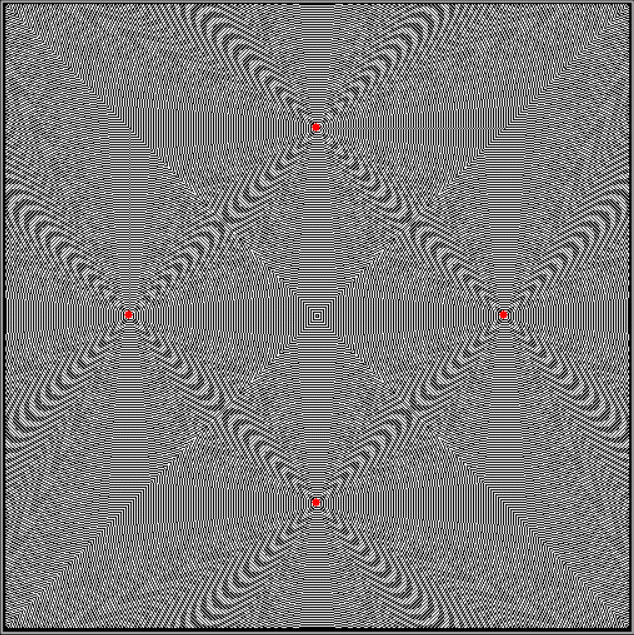
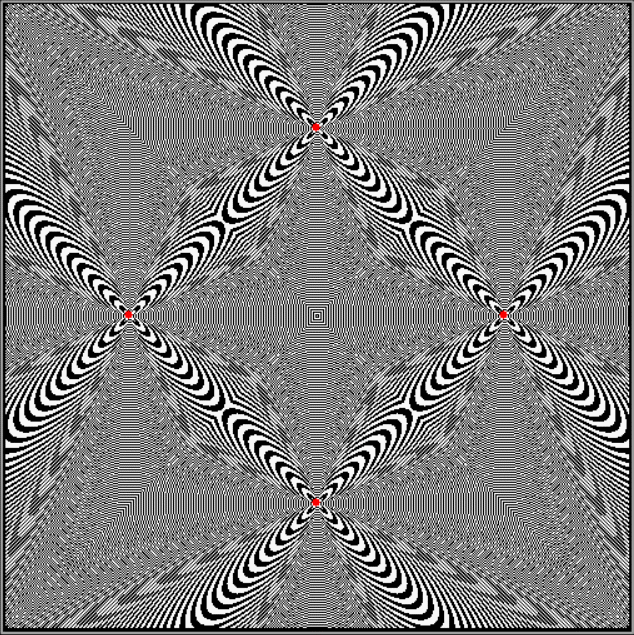
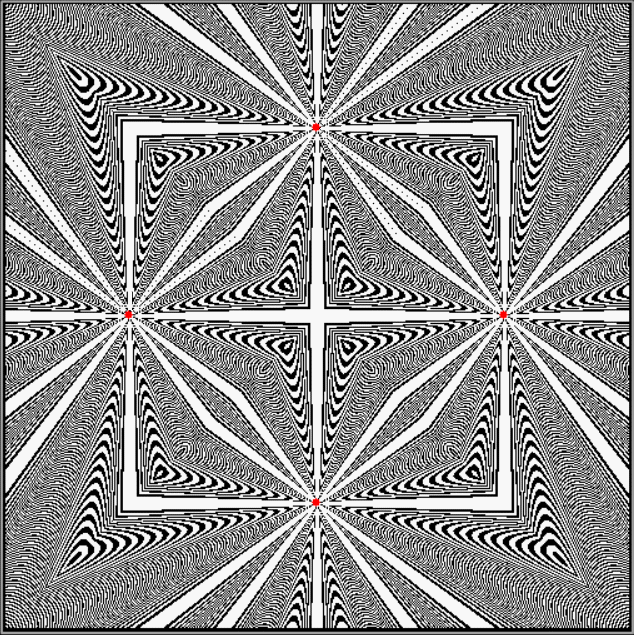
Flowers are modified leaves. That’s a scientific fact. And it must depend on the way the genetic program of a plant allows for change in variables of growth — in the relative dimensions, directions and forms of various collections of cells.
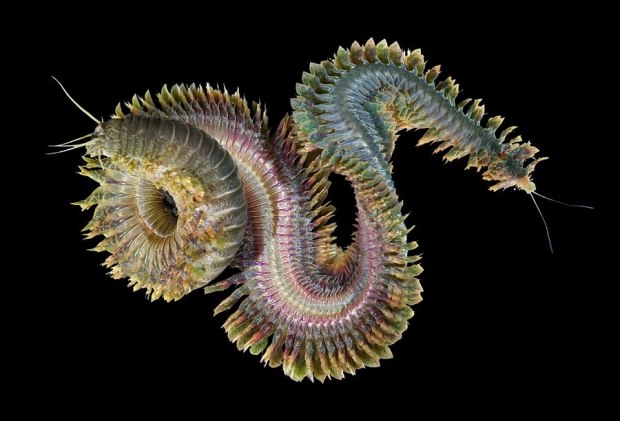
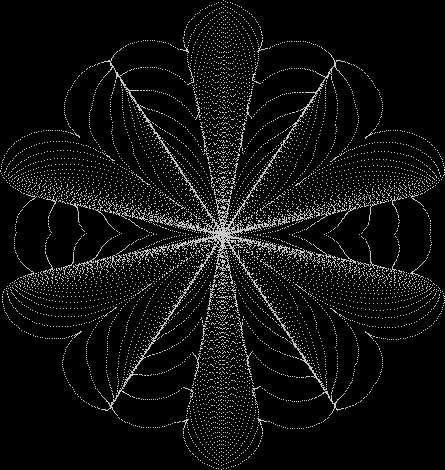
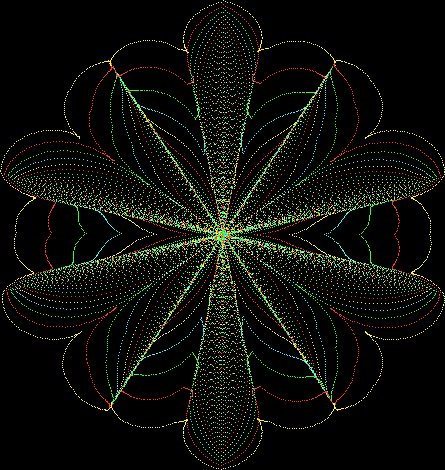
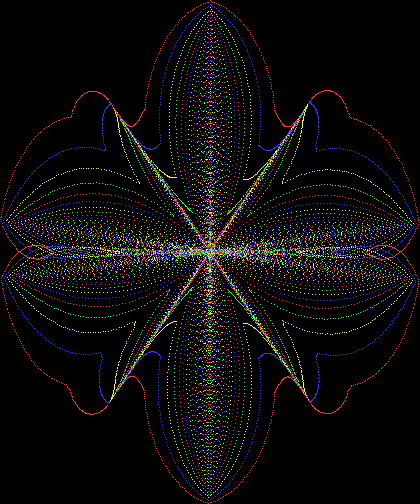
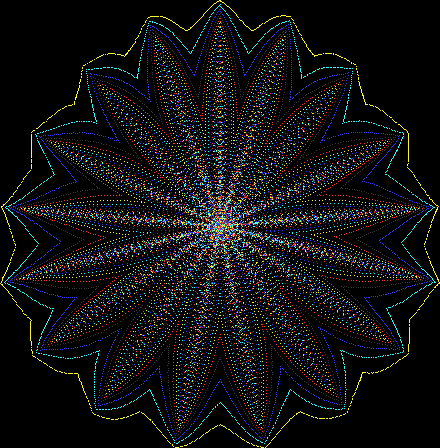
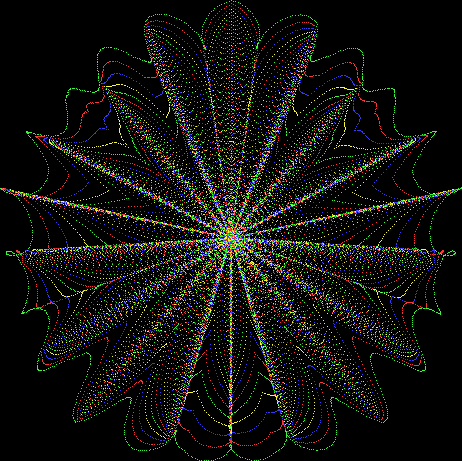
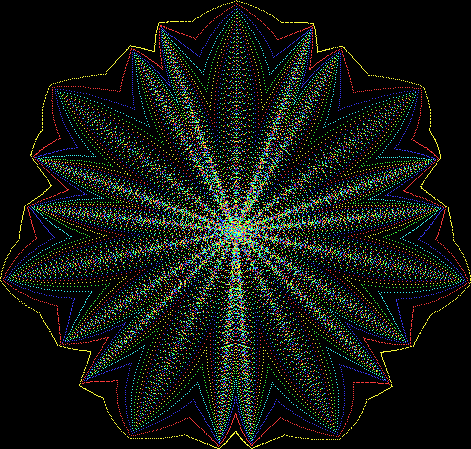
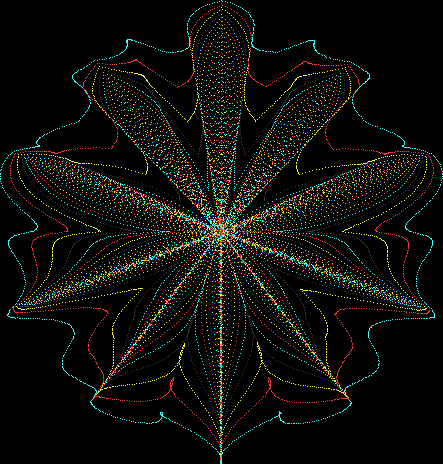
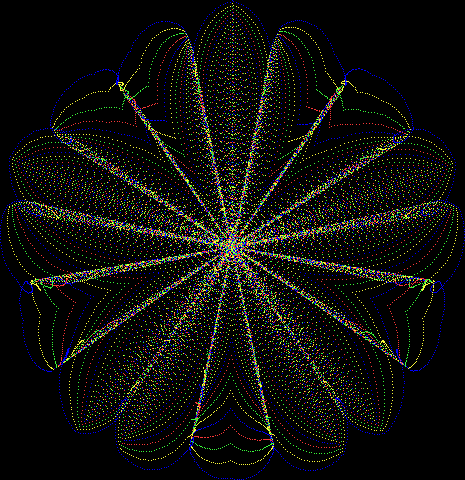
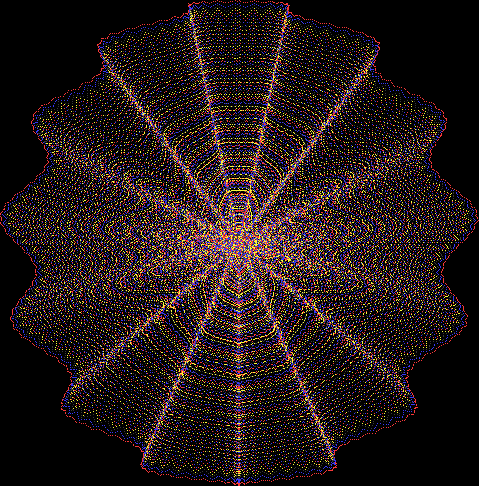
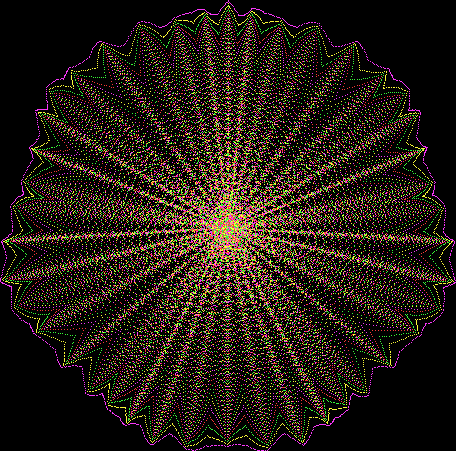
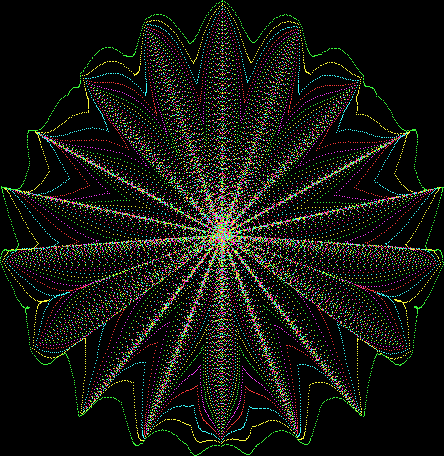
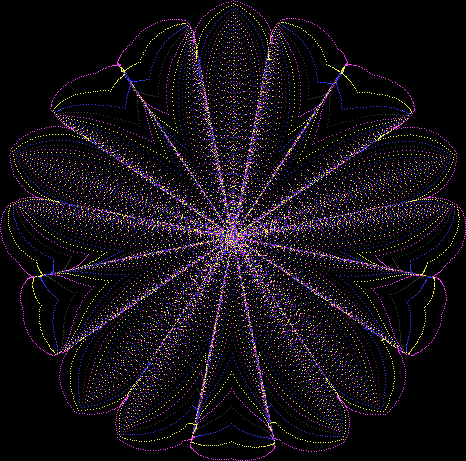
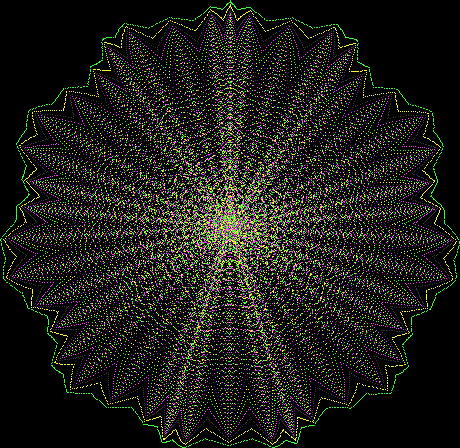
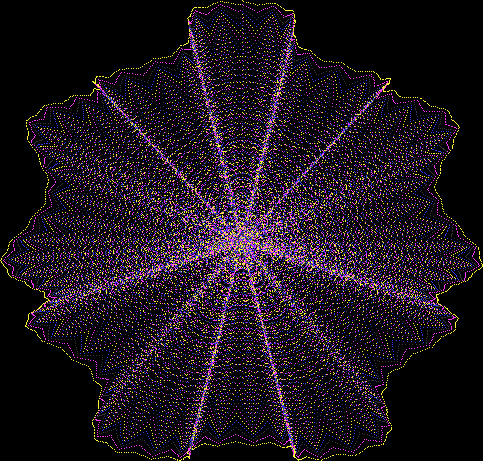
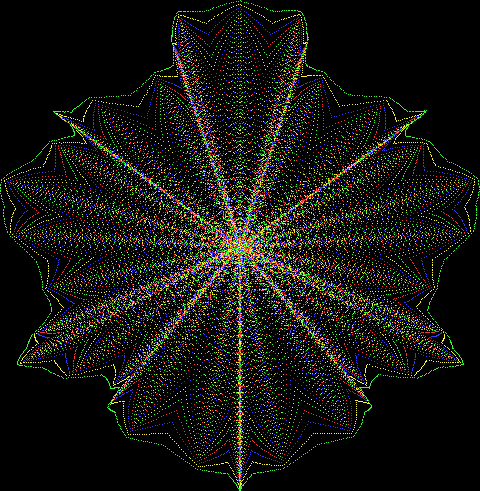
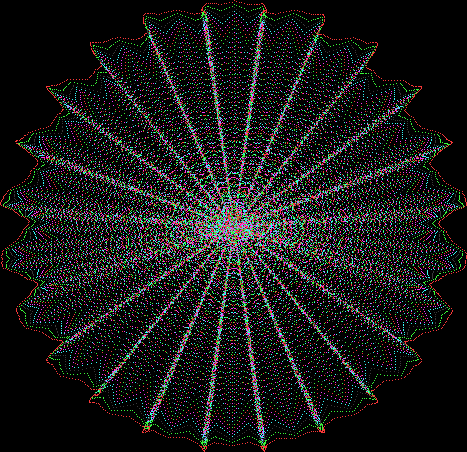
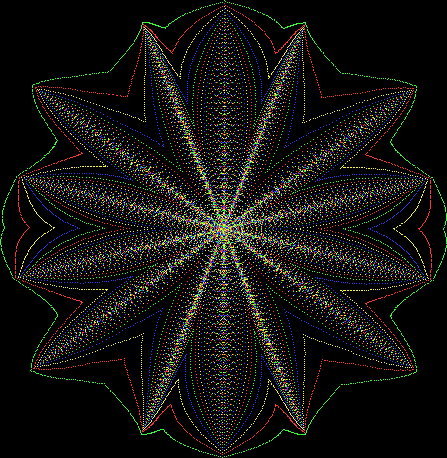
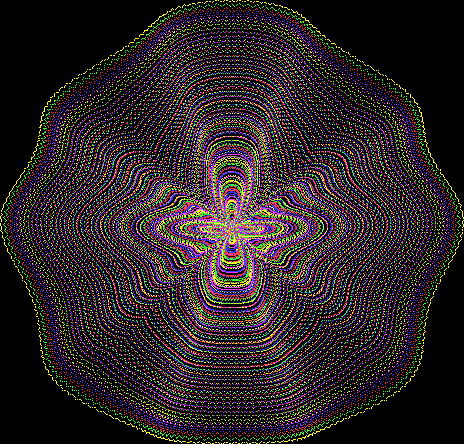
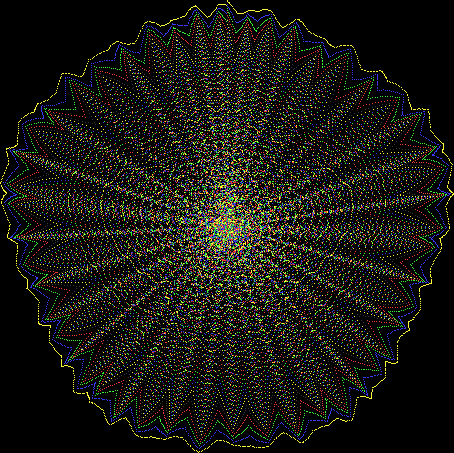
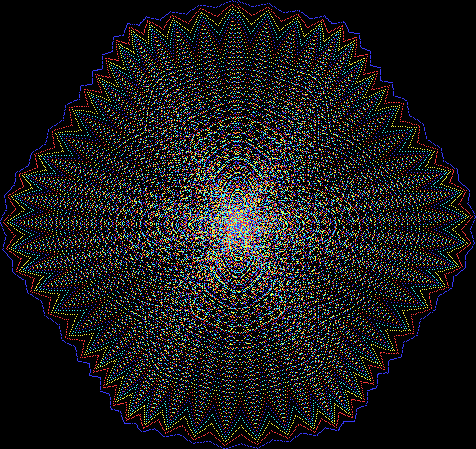
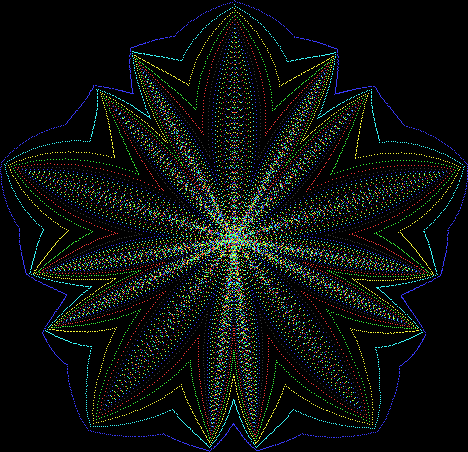
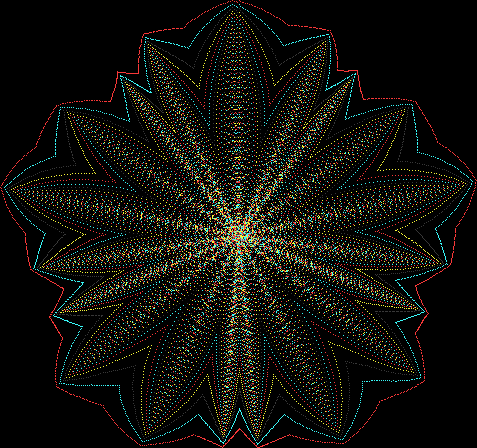
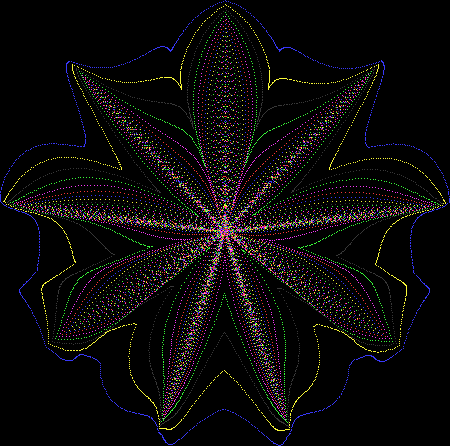
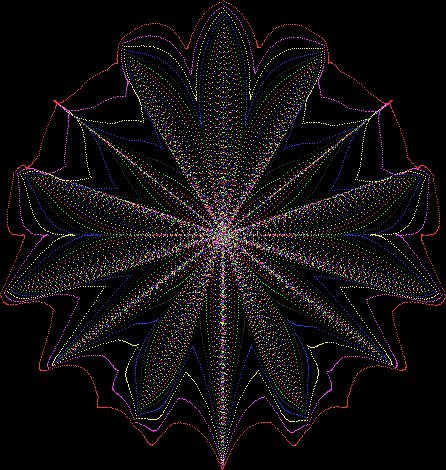
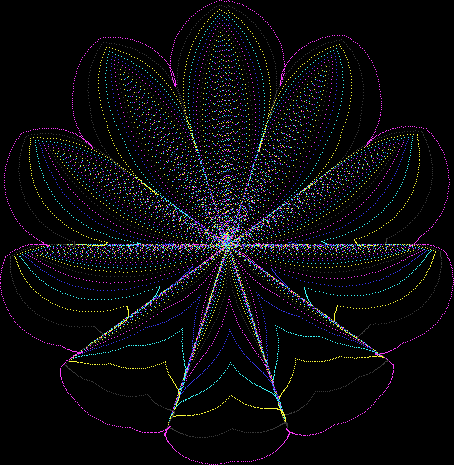
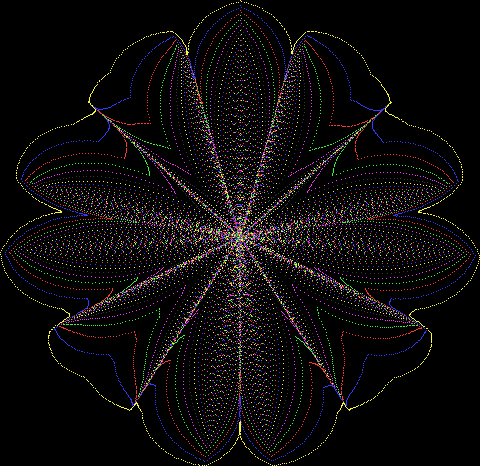
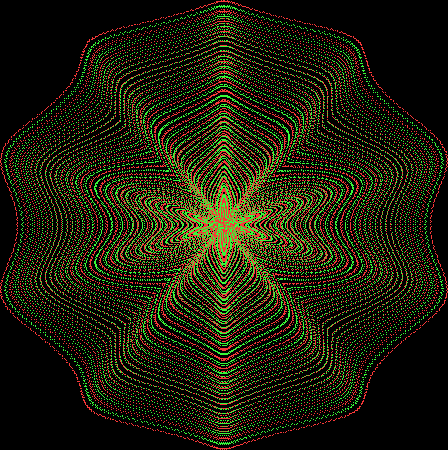
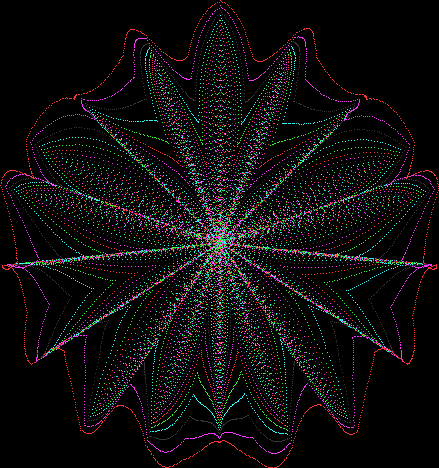
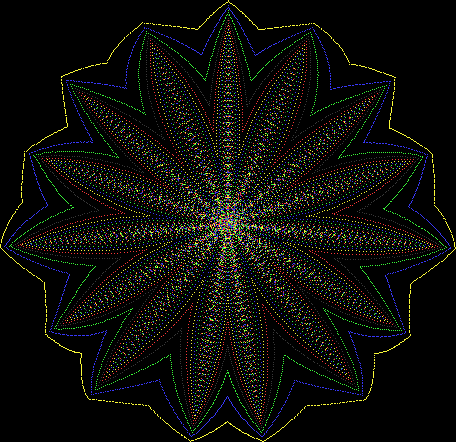
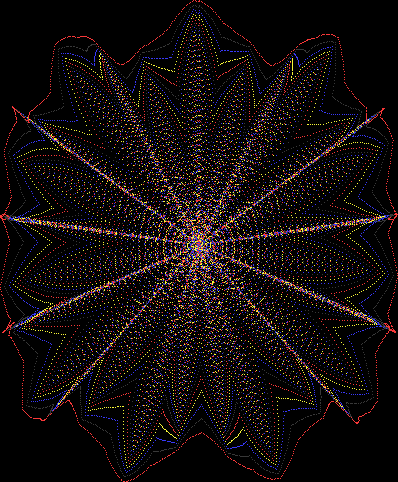
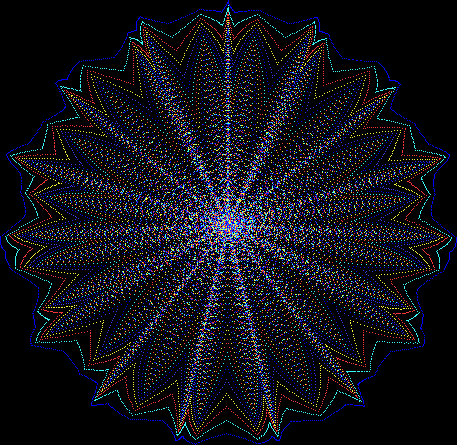
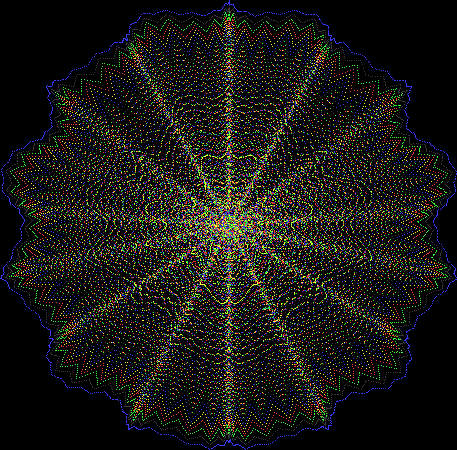
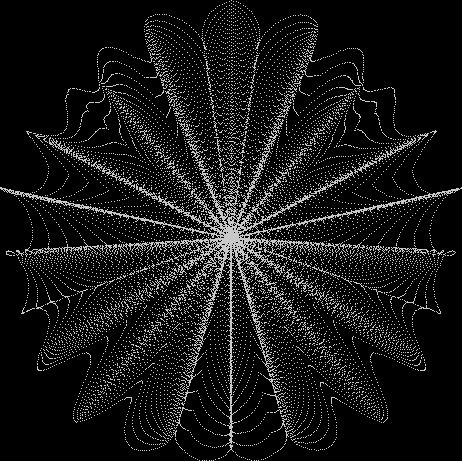
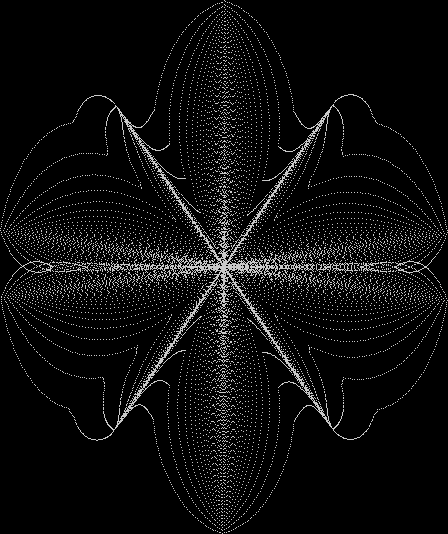
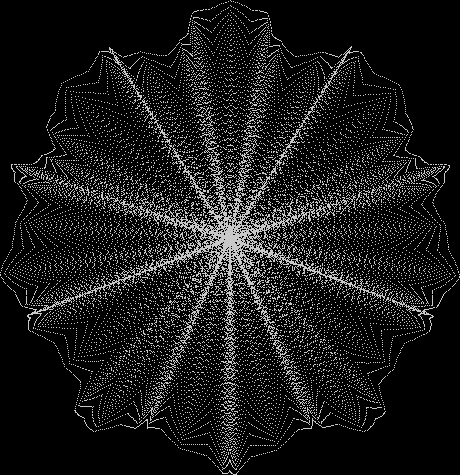
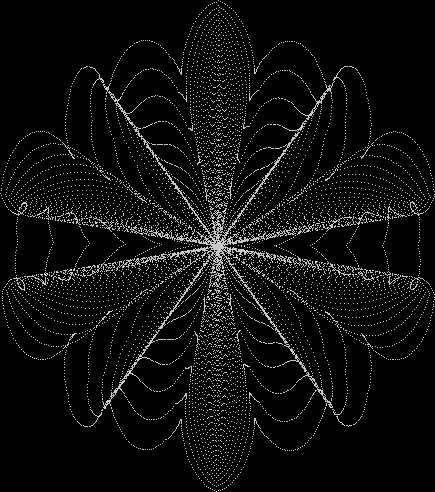
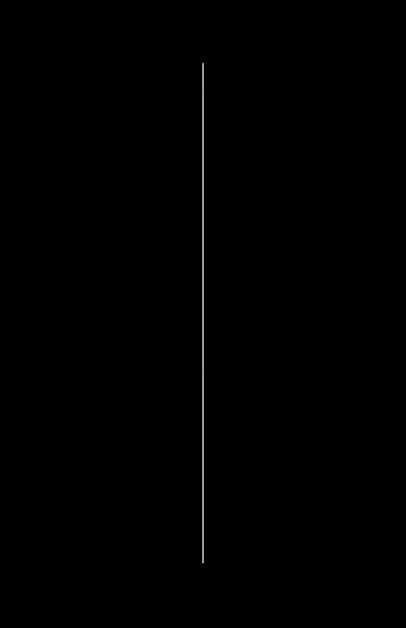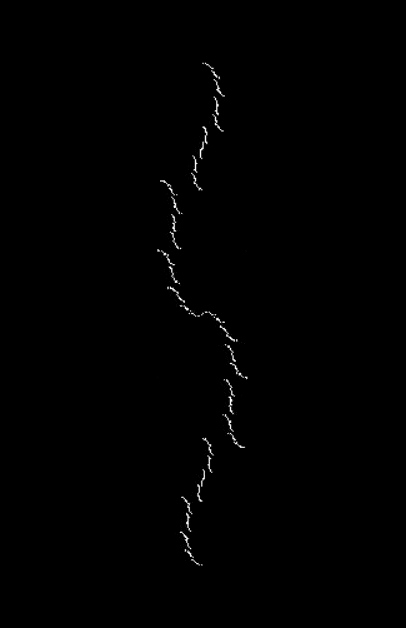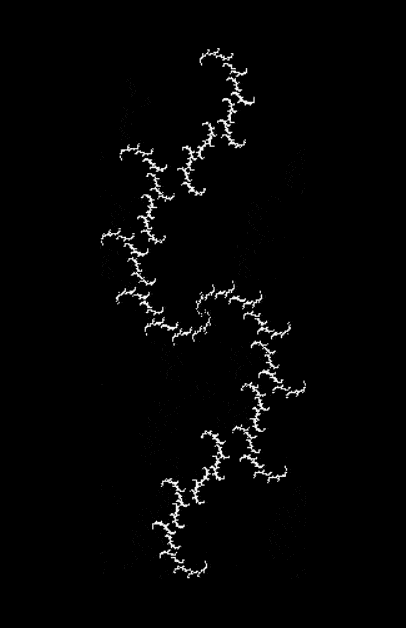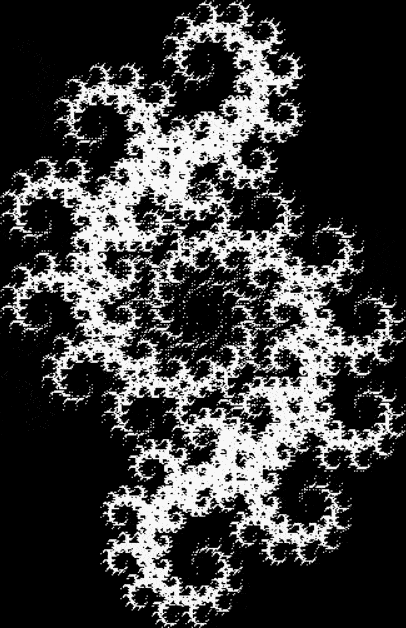
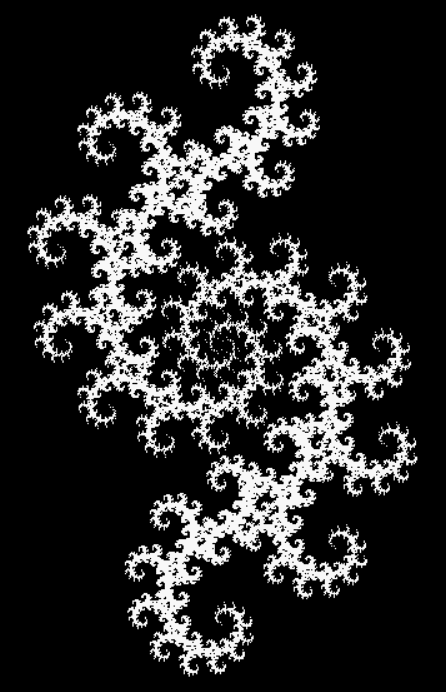
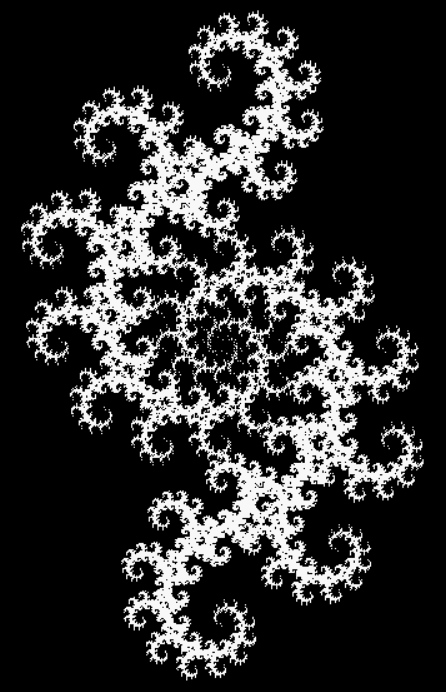
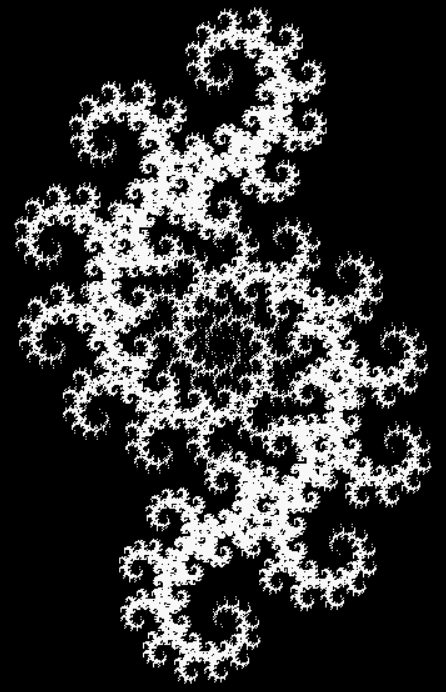
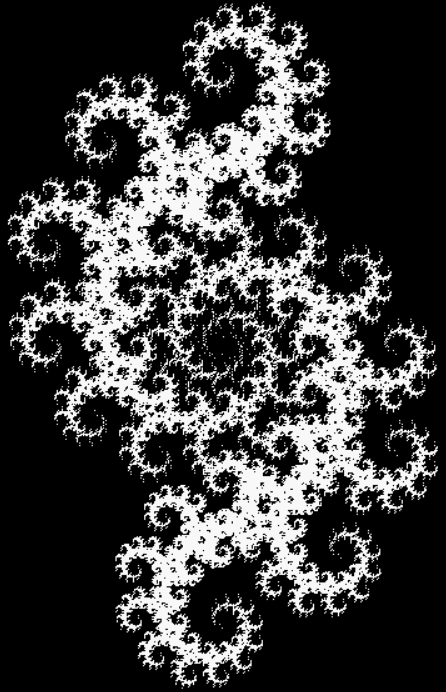
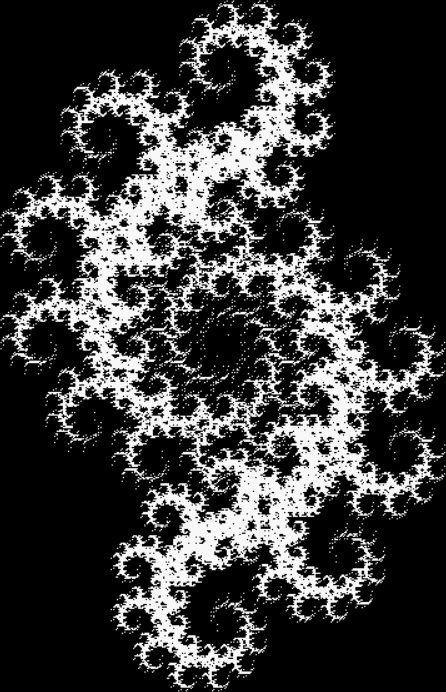
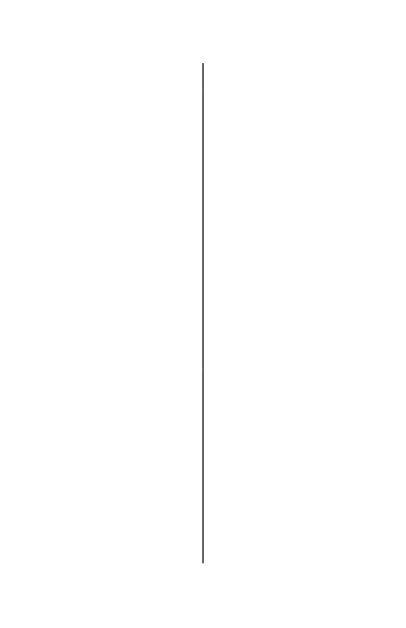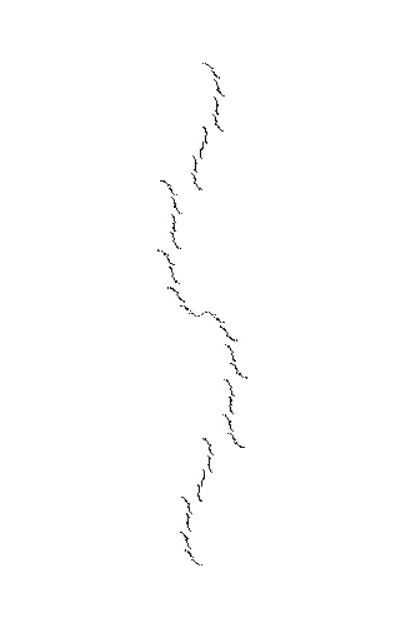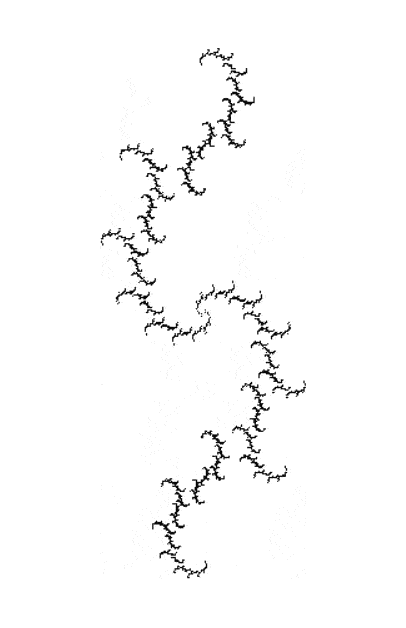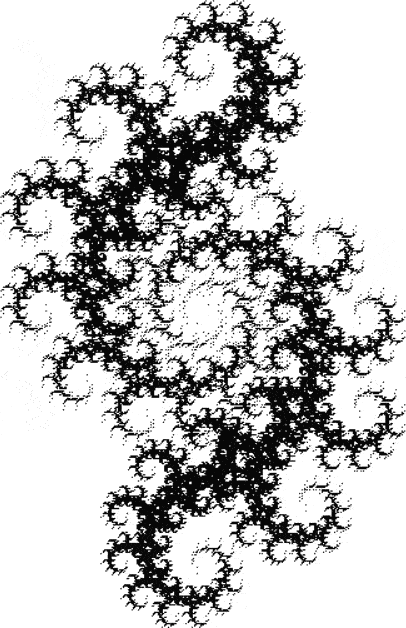
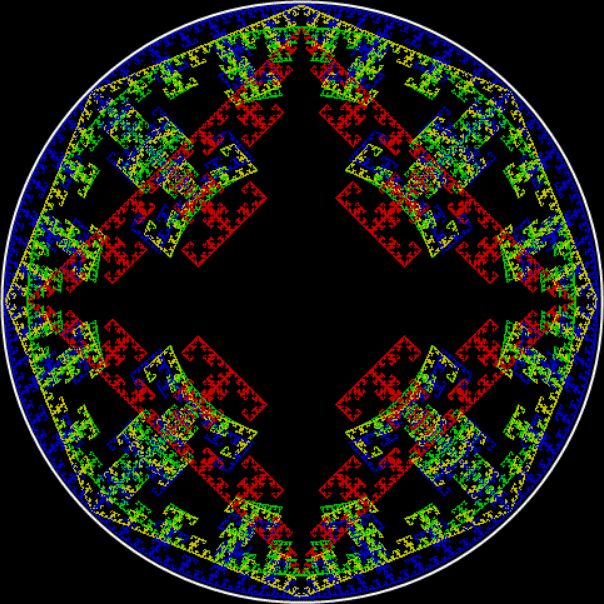
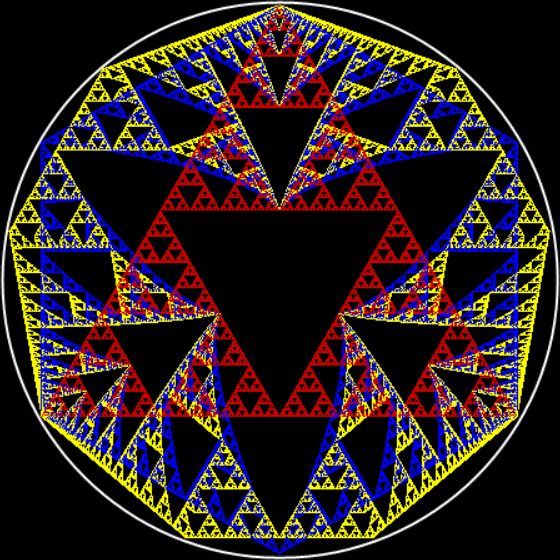
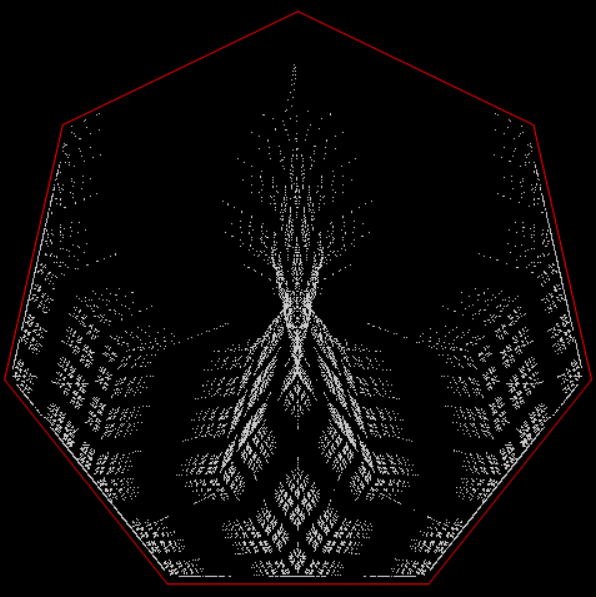
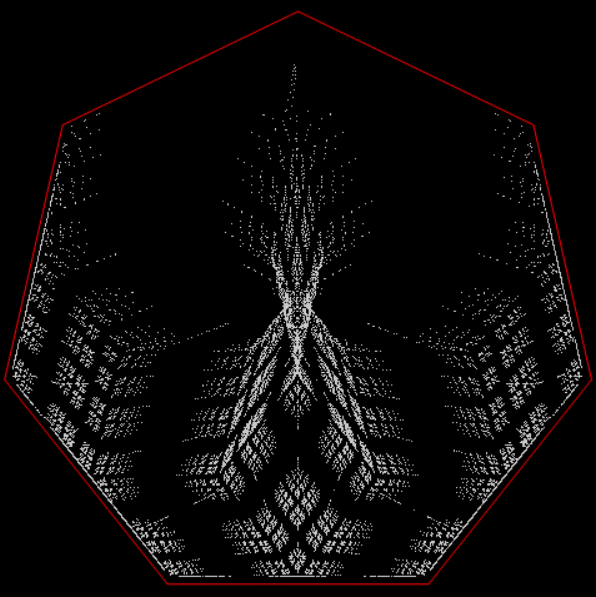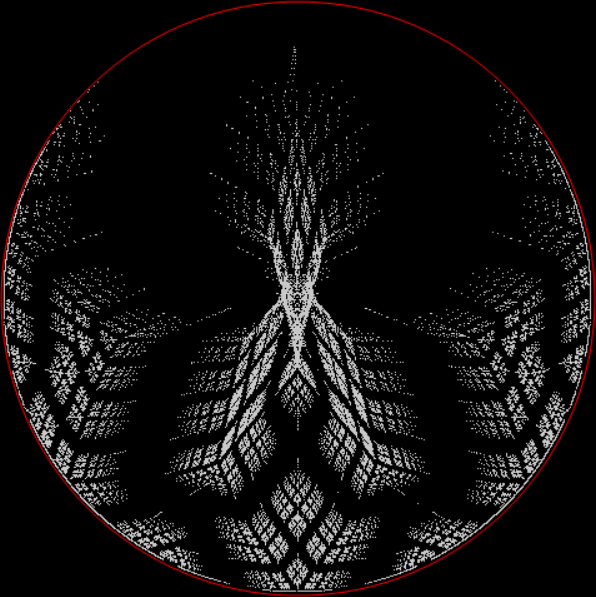
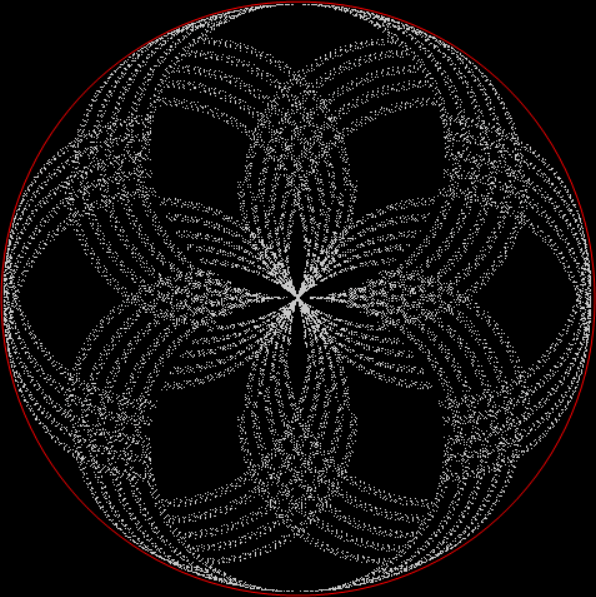
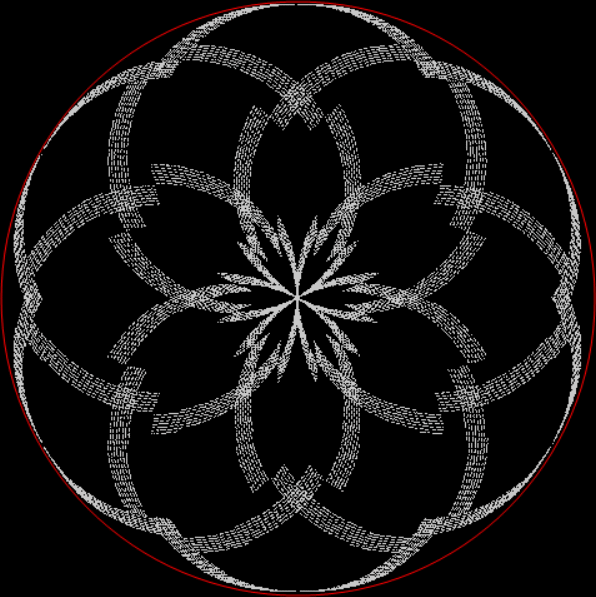
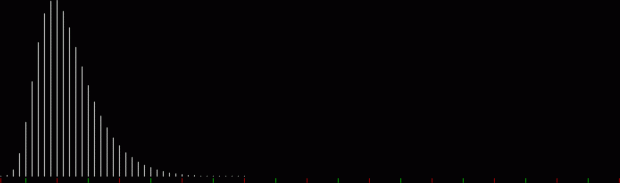
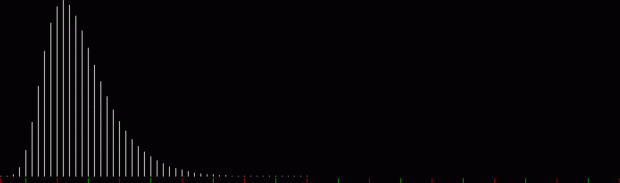
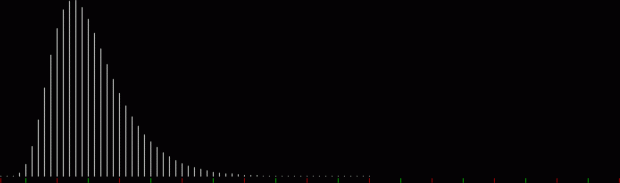
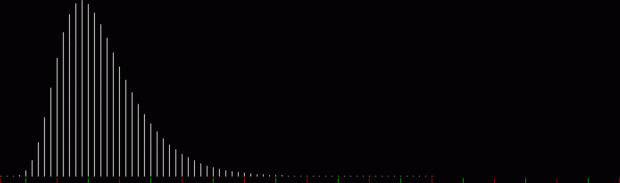
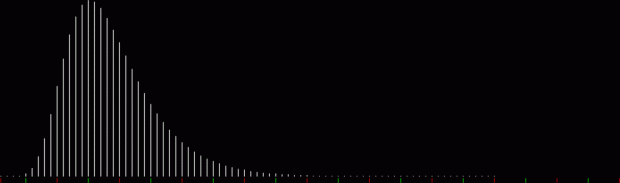
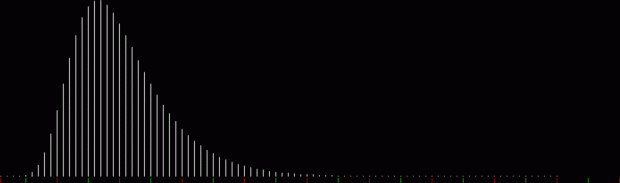
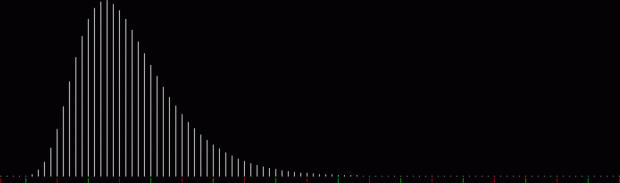
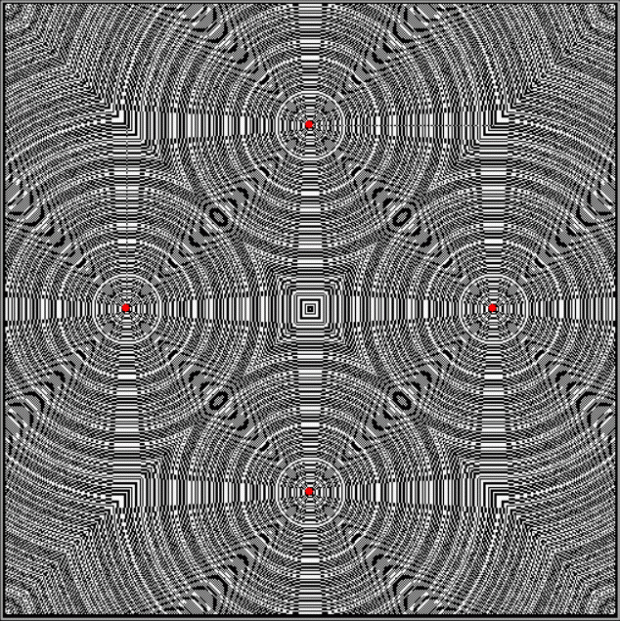
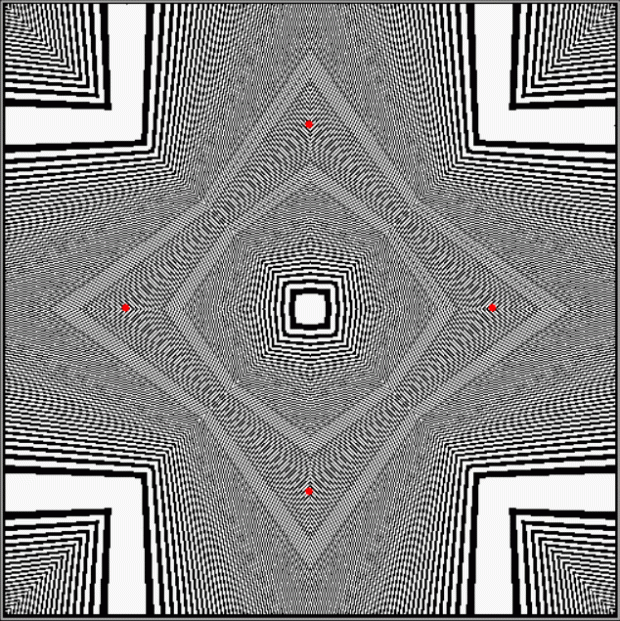
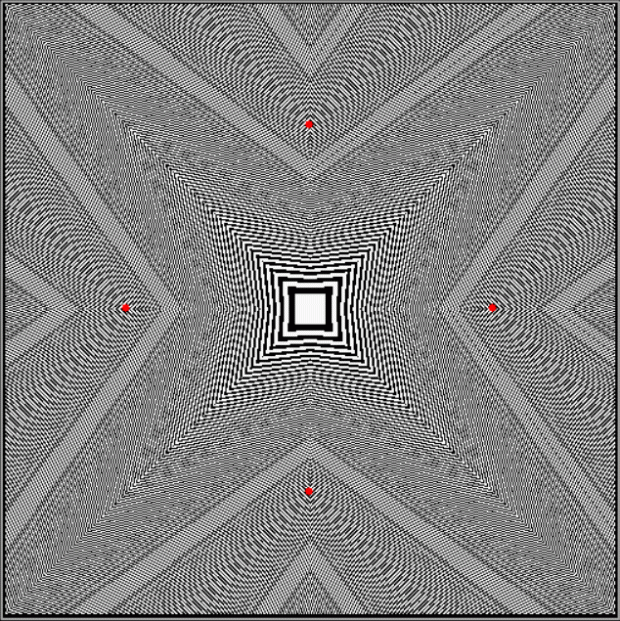
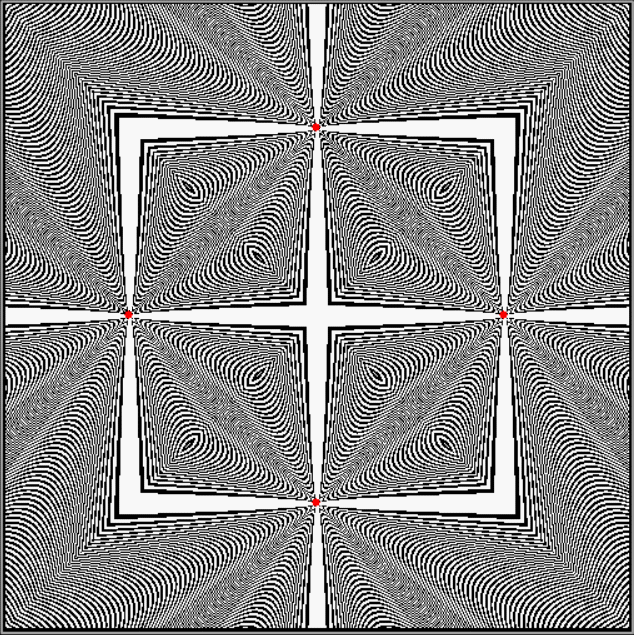
But I wasn’t thinking of flowers or leaves or botany when I wrote a program to trace the path taken by a point moving in various ways between the center and perimeter of a circle. After I’d run the program, I was definitely thinking of flowers and leaves. How could I not be, when they appeared on the screen in front of my eyes? By adjusting variables in the program, I could produce either flowers or leaves or something between the two:
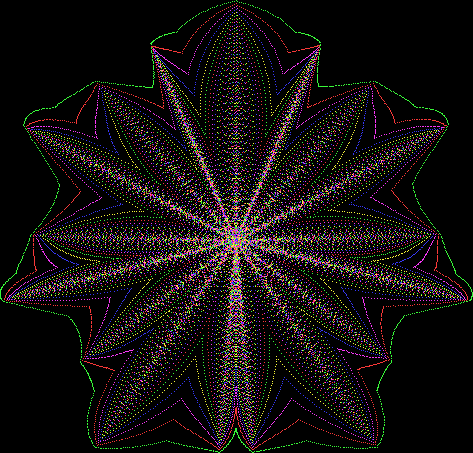
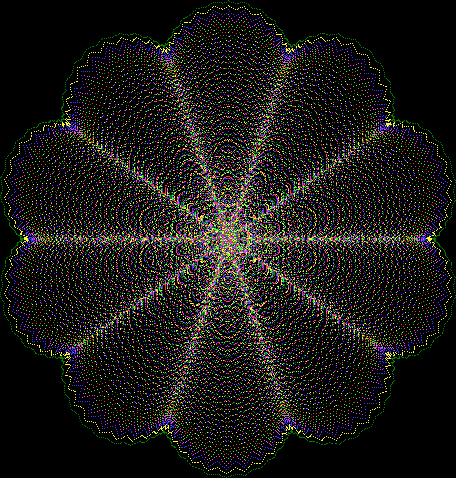
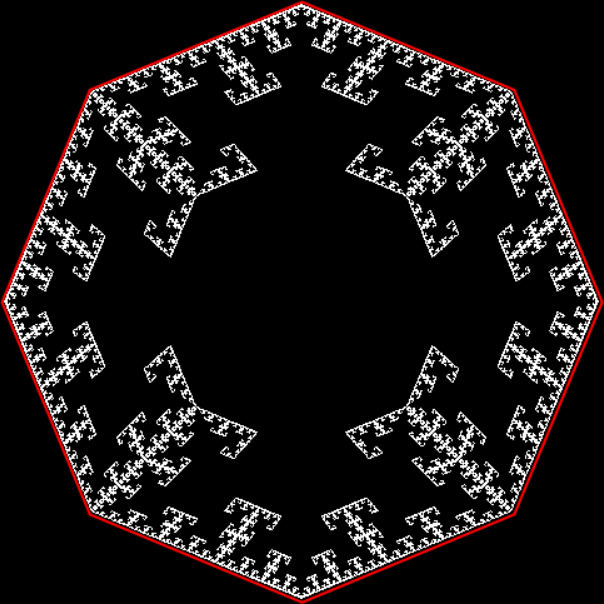
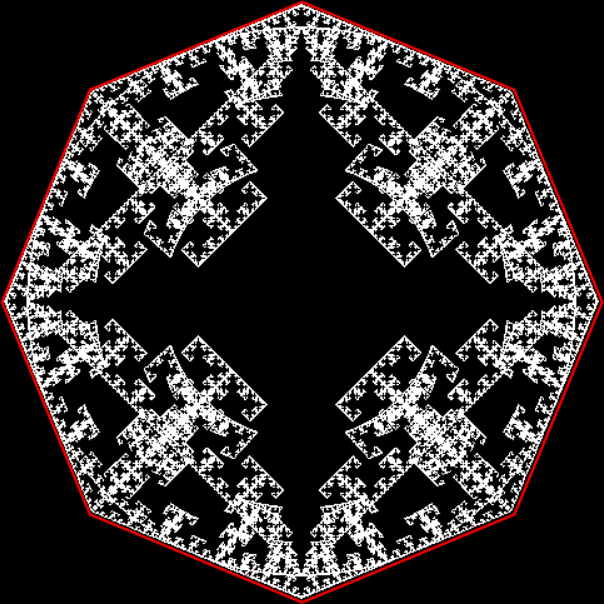
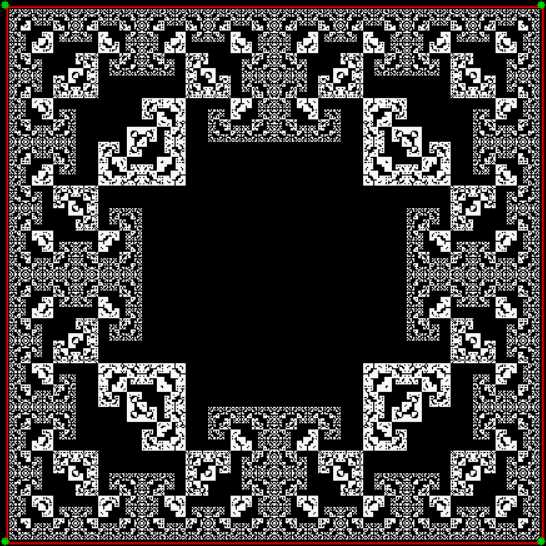
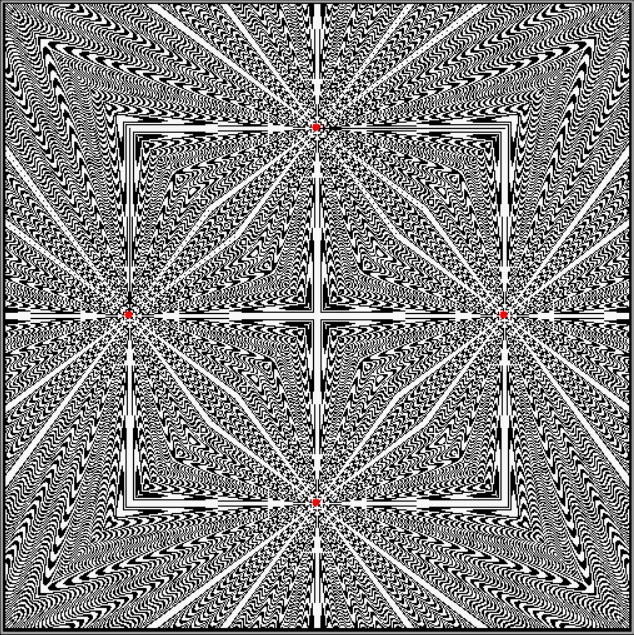
Flower without color
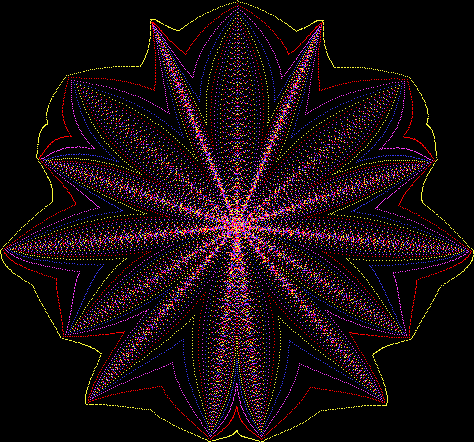
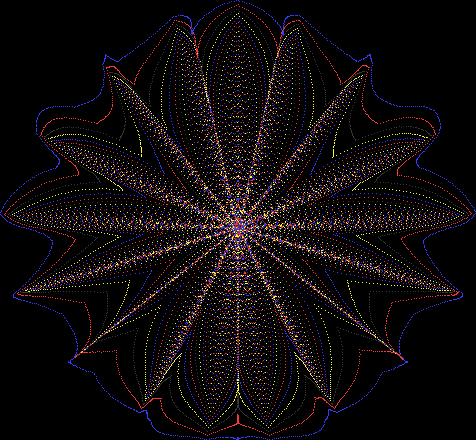
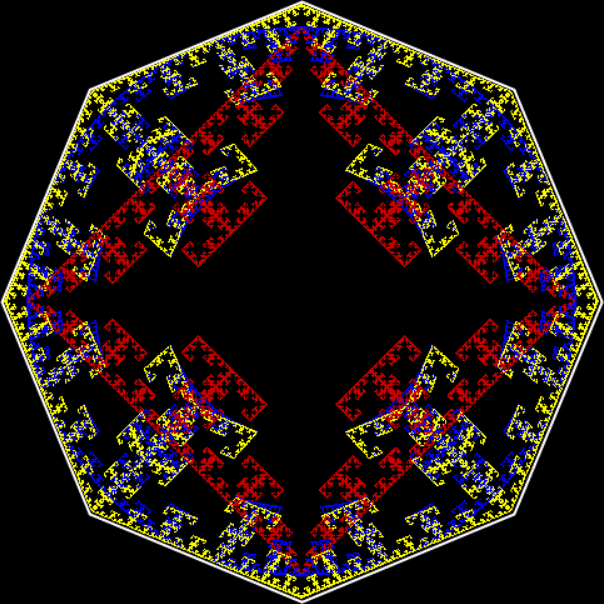
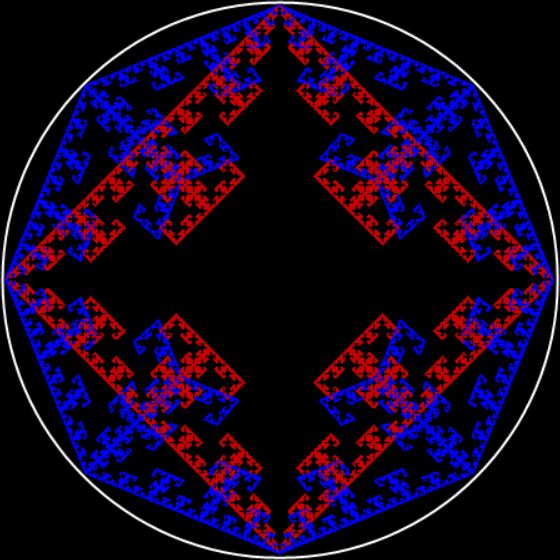
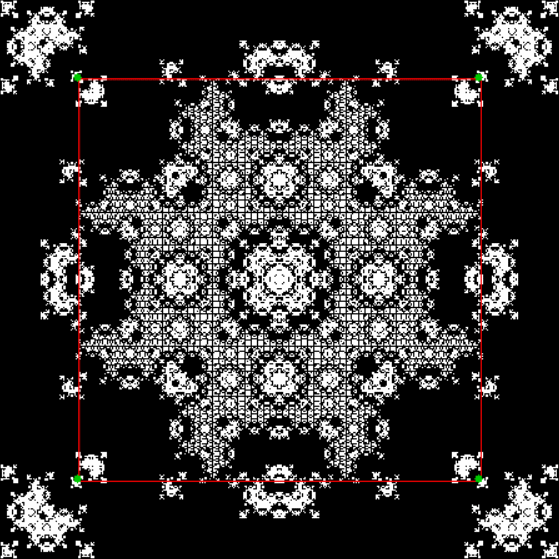
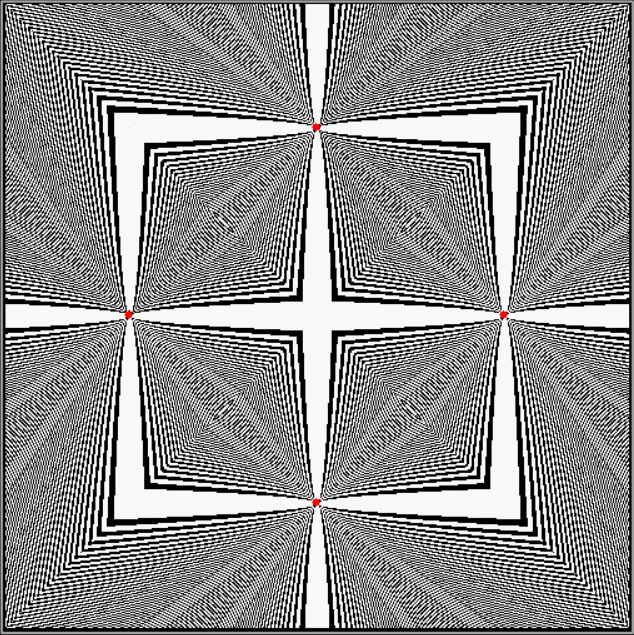
Flower with color
Some of the flower-shapes reminded me of orchids, so I called them mathemorchids. The variables I used governed this procedure:
defprocmathemorchid
rd = 0
jump = jmin
jinc = +1
repeat
xr = xc + int(sin(rd) * rdius + sin(rd * xmult) * xminl)
yr = yc + int(cos(rd) * rdius + cos(rd * ymult) * yminl)
jump = jump + jinc
if(jump = jmin) or (jump >= jmax) then jinc = -jinc
procDrawLine(xr,yr,xc,yc,jump)
rd = rd + rdinc
until rd > maxrd
endproc
Here are explanations of the variables:
rd — short for radian and setting the angle of the point, 0 to maxrd = pi * 2, as it moves between the center and perimeter of the circle
rdinc — the amount by which rd is incremented
xc, yc — the center of the circle
rdius — the radius of the circle
xr, yr — the adjustable radiuses used in trigonometric calculations for the x and y dimensions
xmult, ymult — used to multiply rd for further trig-calcs using…
xminl, yminl — the lengths by which xr and yr are adjusted
jmin, jmax — these are the lower and upper bounds for a rising and falling variable called jump, which determines how far the point moves before it’s marked on the screen
If you look at the use of the sine and cosine functions, you’ll see that the point can swing back on its path or swing ahead of itself, as it were. That’s how the path of the point can simulate three-dimensionality as it lays down thicker or thinner patches of pixels.
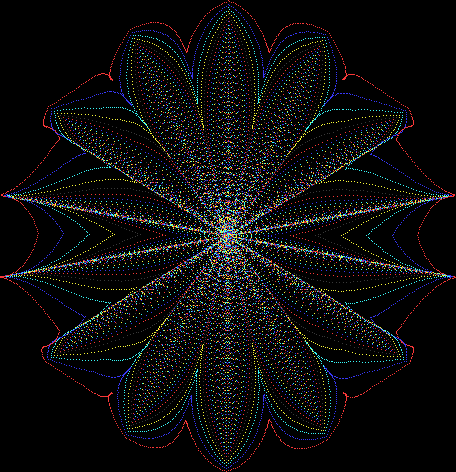
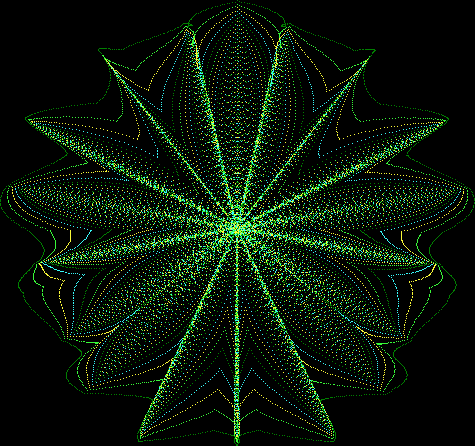
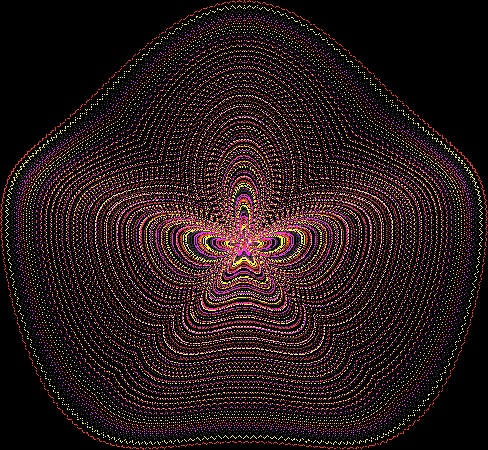
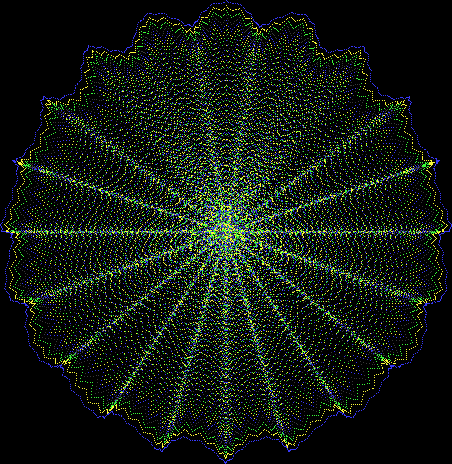
Here are the mathemorchids, leaves, scallops and other shapes created by adjusting the variables described above (with more of the generating program as an appendix):
Mathemorchid for jmin = 6, jmax = 69, xmult = 7, ymult = 7, xminl = 40, yminl = 88 (see file-name)
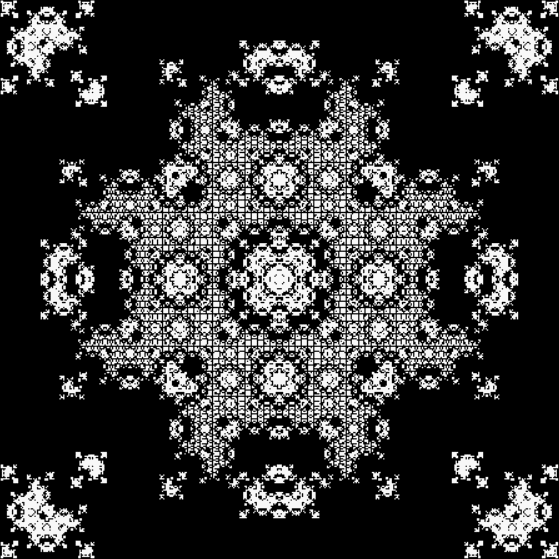
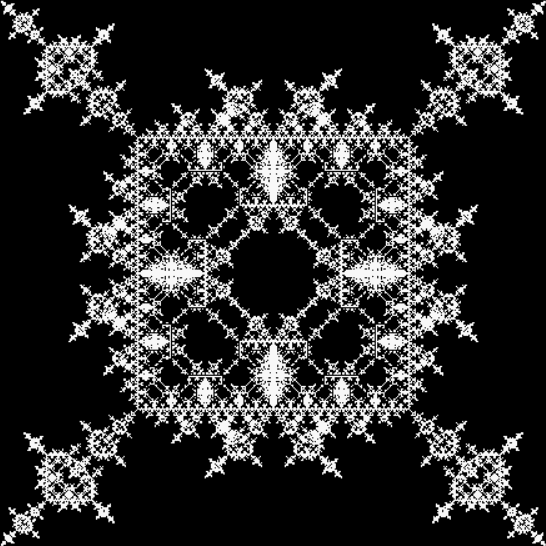
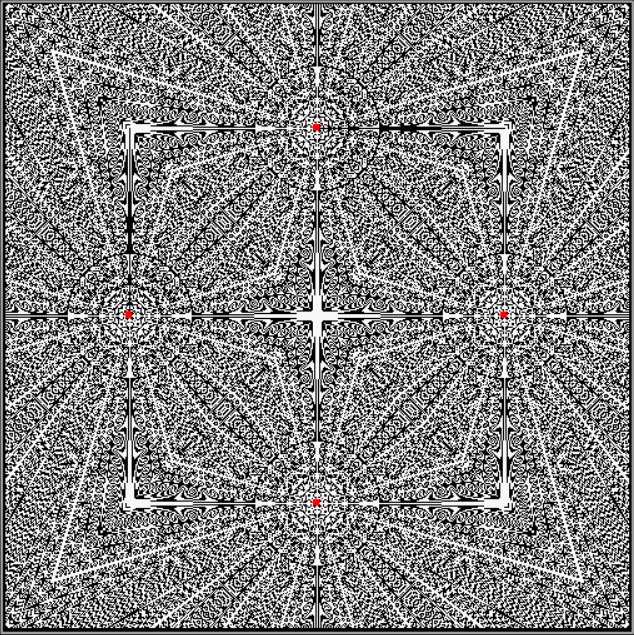
And here are a few more examples of the mathemorchids and other shapes look like without color:
Code for creating the Mathemorchids
defprocmathemorchid
rd = 0
rd = 0
jump = jmin
jinc = +1
repeat
xr = xc + int(sin(rd) * rdius + sin(rd * xmult) * xminl)
yr = yc + int(cos(rd) * rdius + cos(rd * ymult) * yminl)
jump = jump + jinc
if(jump = jmin) or (jump >= jmax) then jinc = -jinc
procDrawLine(xr,yr,xc,yc,jump)
rd = rd + rdinc
k=inkey(0)
until rd > maxrd or k > -1
endproc
defprocDrawLine(x1,y1,x2,y2,puttest)
xdiff = x1 – x2
ydiff = y1 – y2
if abs(xdiff) > abs(ydiff) then
yinc = -ydiff / abs(xdiff)
if xdiff < 0 then xinc = +1 else xinc = -1
else
xinc = -xdiff / abs(ydiff)
if ydiff colrmx then col = 1
put = 0
endif
if int(x) x2 then x = x + xinc
if int(y) y2 then y = y + yinc
iffunc=2then
ifx<x_lo x_lo=x
ifyx_hi x_hi=x
ify>y_hi y_hi=y
endif
until fnreached
endproc
deffnreached
if xinc > 0 then
xreached = int(x) >= x2
else
xreached = int(x) 0 then
yreached = int(y) >= y2
else
yreached = int(y) <= y2
endif
= xreached and yreached
end