“What he said often had double and even triple meanings so that, while the rest of us speak and think in single notes, he thought in chords.” — Robert Trivers on W.D. Hamilton, Vignettes of Famous Evolutionary Biologists, Large and Small, Unz Review, 27/iv/2015.
Tag Archives: biology
He Say, He Sigh, He Sow #25
When the biologist E.O. Wilson was asked by a friend what to do about the ants that had invaded his kitchen, Wilson said: “Watch where you step.” — Christopher Potter, How to Make a Human Being: A Body of Evidence (2014), pg. 214
Thalassobiblion
 Ocean: The Definitive Visual Guide, introduction by Fabien Cousteau (Dorling Kindersley 2014)
Ocean: The Definitive Visual Guide, introduction by Fabien Cousteau (Dorling Kindersley 2014)
A big book for a big subject: the sea. But “guide” isn’t the mot juste. “Encyclopaedia” is better, because the book covers all aspects of oceanography and marine life, drawing on physics, chemistry and biology to describe everything inorganic from waves and icebergs to whirlpools and underwater volcanoes, everything organic from a beautiful flower like beach morning-glory, Ipomoea imperati, to a grotesque fish like the Pacific blackdragon, Idiacanthus antrostomus. The flower is on the shore, the fish is in the abyss, but both of them descend from a single ancestor.
And that ancestor may have evolved in the sea. It certainly moved there before it gave rise to flowers and fish. This big subject is also a very important one: the sea is central to the evolution and continued existence of life on earth. Only the sun matters as much, but some marine life could potentially survive the disappearance of the sun:
Hydrothermal vents are similar to hot springs on land. Located near ocean ridges and rifts, at an average depth of 2,100m (7,000ft), they spew out mineral-rich, superheated seawater. Some have tall chimneys, formed from dissolved minerals that precipitate when the hot vent water meets cold, deep-ocean water. The mix of heat and chemicals supports animal communities around the vents – the first life known to exist entirely without the energy of sunlight. (pg. 188, “The Open Ocean and Ocean Floor”)
The deep ocean is a fascinating and little-known place: much nearer than the other side of the earth, but much harder to get to. Like climbing mountains, plumbing the abyss is difficult and dangerous. It’s interesting that both endeavours have been dominated by a particular group of human being: both the highest and lowest points on the planet were first reached by white males. Fabien Cousteau, who introduces this book, continues the tradition. He’s the grandson of Jacques Cousteau (1910-97), who popularized diving and marine biology for millions of people. Jacques saw huge advances in marine technology and science and his son and grandson have seen more. But the discoveries are still coming: as Fabien points out, it’s estimated that “over 90 per cent of the world’s biodiversity resides in its oceans”.

Discomedusae by Ernst Haeckel
Some of that biodiversity left the water for the land and evolved new forms. Some of those new forms went back to the water, like the ceteceans and sea-snakes. Like human beings, they’re descended from fish, the most varied of all vertebrate groups. But some marine life never left its cradle. Where else can you find the beauty and strangeness of groups like the jellyfish? Radial symmetry is a marine speciality and when H.P. Lovecraft was inventing his aliens, he looked to under-space as much as outer:
But to give it a name at this stage was mere folly. It looked like a radiate, but was clearly something more. It was partly vegetable, but had three-fourths of the essentials of animal structure. That it was marine in origin, its symmetrical contour and certain other attributes clearly indicated; yet one could not be exact as to the limit of its later adaptations. The wings, after all, held a persistent suggestion of the aerial. How it could have undergone its tremendously complex evolution on a new-born earth in time to leave prints in Archaean rocks was so far beyond conception as to make Lake whimsically recall the primal myths about Great Old Ones who filtered down from the stars and concocted earth life as a joke or mistake; and the wild tales of cosmic hill things from outside told by a folklorist colleague in Miskatonic’s English department. (At the Mountains of Madness, 1931)
Lovecraft would have enjoyed Ocean as much as Jacques Cousteau. It closes with a detailed “Atlas of the Oceans”, with maps of the ocean floor all around the world. Before that, you can learn how the Corryvreckan whirlpool nearly killed George Orwell in 1947, where to find manganese nodules, why so many deep-sea creatures are red and what the narwhale’s horn really is. You can also feast your eyes on photography that records everything from microscopic plankton to swirling hurricanes hundreds of kilometres across. Big subject, big book. Beautiful subject and beautiful book too.
Honeycycle
Fins and Fangs
 The Fresh and Salt Water Fishes of the World, Edward C. Migdalski and George S. Fichter, illustrated by Norman Weaver (1977)
The Fresh and Salt Water Fishes of the World, Edward C. Migdalski and George S. Fichter, illustrated by Norman Weaver (1977)
A big book with a big subject: fish are the most numerous and varied of the vertebrates, from the bus-sized Rhincodon typus or whale shark, which feeds its vast bulk on plankton, to the little-finger-long Vandellia cirrhosa, the parasitic catfish that can give bathers a nasty surprise by swimming into their “uro-genitary openings” – “the pain is agonizing and the fish can be removed only by surgery”. The book is full of interesting asides like that, but I doubt that readers will read every page carefully. They’ll certainly look at every page carefully, to see Norman Weaver’s gorgeous drawings, which capture both the colour and the shine of fish’s bodies. Another aspect of the enormous variation of fish is not just their differences in size, shape and colouring, but their differences in aesthetic appeal. Some are among the most beautiful of living creatures, others among the most grotesque, like the Lovecraftian horrors that literally dwell in the abyss: inhabitants of the very deep ocean like Chauliodus macouni, the Pacific viperfish, whose teeth are too long and sharp for it to close its mouth.
The crushing pressure and freezing darkness in which these fish live are alien to human beings and so are the appearance and behaviour of the fish. But fish that live in shallow water, like the hammerhead shark and the electric eel, can seem alien too and some of the strangest fish of all, the horizontally flattened rays and mantas, can even fly briefly in the open air. Some of the piscine beauties, on the other hand, like Cheirodon axelrodi, the neon-bodied cardinal tetra, are routinely kept in aquariums, but then so is the very strange Anoptichthys jordani, the blind cavefish. There’s a blind torpedo ray too, Typhlonarke aysoni, “which has no functional eyes and ‘stumps’ along the bottom on its thick, leglike ventral fins”. But the appearance, behaviour and habitat of fish aren’t the only things man finds interesting about them. Some are good eating or offer good sport and the authors often discuss both cuisine and fishing in relation to a particular species or family. That raises the second of the two questions I keep asking myself when I look at this book. The first question is: “Why are some fish so beautiful and some so ugly?” The second is: “Are fish capable of suffering, and if they are, do they suffer much?”
I don’t know if the first question can be answered or is even sensible to ask; the second will, I hope, be answered by science in the negative. It’s not pleasant to think of what a positive answer would mean, because we’ve been hooking and hauling fish from fresh and salt water for countless generations. In the past, it was for food, but when we do it today it’s often for fun. I hope the fun isn’t at fish’s expense in more than the obvious sense: that it deprives them permanently of life or, for those returned to the water, temporarily of peaceful existence. I hope the deprivation is not painful in any strong sense. Either way, fish will continue to die at each other’s fangs and to serve as food for many species of mammal and bird. Nature is red in tooth and claw, after all, but it’s a lot more beside and this is one of the books that will show you how. From luminous sharks to uncannily accurate archerfish, from what men do to fish to what fish do to men: the 315 pages of the large and lavishly illustrated Fishes of the World can offer only a glimpse into a very rich and fascinating world, but a glimpse is dazzling.
Previously pre-posted (please peruse):
• Slug is a Drug — Collins Complete Guide to British Coastal Wildlife (2012)
They Saw, They Sigh, They Sow #4
“There is no theory yet that explains olfactory perception completely.” — Wikipedia entry for Olfaction, 6/vi/2014.
Blue is the Killer
 Eye Bogglers: A Mesmerizing Mass of Amazing Illusions, Gianni A. Sarcone and Marie-Jo Waeber (Carlton Books 2011; paperback 2013)
Eye Bogglers: A Mesmerizing Mass of Amazing Illusions, Gianni A. Sarcone and Marie-Jo Waeber (Carlton Books 2011; paperback 2013)
A simple book with some complex illusions. It’s aimed at children but scientists have spent decades understanding how certain arrangements of colour and line fool the eye so powerfully. I particularly like the black-and-white tiger set below a patch of blue on page 60. Stare at the blue “for 15 seconds”, then look quickly at a tiny cross set between the tiger’s eyes and the killer turns colour.
So what’s not there appears to be there, just as, elsewhere, what’s there appears not to be. Straight lines seem curved; large figures seem small; the same colour seems light on the right, dark on the left. There are also some impossible figures, as made famous by M.C. Escher and now studied seriously by geometricians, but the only true art here is a “Face of Fruits” by Arcimboldo. The rest is artful, not art, but it’s interesting to think what Escher might have made of some of the ideas here. Mind is mechanism; mechanism can be fooled. Optical illusions are the most compelling examples, because vision is the most powerful of our senses, but the lesson you learn here is applicable everywhere. This book fools you for fun; others try to fool you for profit. Caveat spectator.
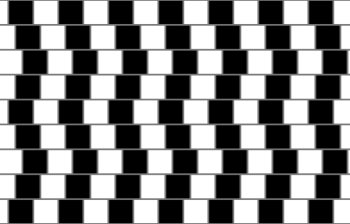
Simple but complex: The café wall illusion
Performativizing Papyrocentricity #23
Papyrocentric Performativity Presents:
• Face Paint – A Face to the World: On Self-Portraits, Laura Cumming (HarperPress 2009; paperback 2010)
• The Aesthetics of Animals – Life: Extraordinary Animals, Extreme Behaviour, Martha Holmes and Michael Gunton (BBC Books 2009)
• Less Light, More Night – The End of Night: Searching for Natural Darkness in an Age of Artifical Light, Paul Bogard (Fourth Estate 2013)
• The Power of Babel – Clark Ashton Smith, Huysmans, Maupassant
Or Read a Review at Random: RaRaR
Performativizing Papyrocentricity #22
Papyrocentric Performativity Presents:
• Plates from the Great – Shots from the Front: The British Soldier 1914-18, Richard Holmes (HarperPress 2008; paperback 2010)
• Math for the Mistress – A Mathematician’s Apology, G.H. Hardy (1940)
• Sinister Sinema – Scalarama: A Celebration of Subterranean Cinema at Its Sleazy, Slimy and Sinister Best, ed. Norman Foreman, B.A. (TransVisceral Books 2015)
• Rick Pickings – Lost, Stolen or Shredded: Stories of Missing Works of Art and Literature, Rick Gekoski (Profile Books 2013/2014)
• Slug is a Drug – Collins Complete Guide to British Coastal Wildlife, Paul Sterry and Andrew Cleave (HarperCollins 2012) (posted @ Overlord of the Über-Feral)
Or Read a Review at Random: RaRaR
This Mortal Doyle
Challenger chopped and changed. That is to say, in one important respect, Arthur Conan Doyle’s character Professor Challenger lacked continuity. His philosophical views weren’t consistent. At one time he espoused materialism, at another he opposed it. He espoused it in “The Land of Mist” (1927):
“Don’t tell me, Daddy, that you with all your complex brain and wonderful self are a thing with no more life hereafter than a broken clock!”
“Four buckets of water and a bagful of salts,” said Challenger as he smilingly detached his daughter’s grip. “That’s your daddy, my lass, and you may as well reconcile your mind to it.”
But earlier, in “The Poison Belt” (1913), he had opposed it:
“No, Summerlee, I will have none of your materialism, for I, at least, am too great a thing to end in mere physical constituents, a packet of salts and three bucketfuls of water. Here ― here” ― and he beat his great head with his huge, hairy fist ― “there is something which uses matter, but is not of it ― something which might destroy death, but which death can never destroy.”
That story was published just over a century ago, but Challenger’s boast has not been vindicated in the meantime. So far as science can see, matter rules mind, not vice versa. Conan Doyle thought the same as the earlier Challenger, but Conan Doyle’s rich and teeming brain seems to have ended in “mere physical constituents”. To all appearances, when the organization of his brain broke down, so did his consciousness. And that concluded the cycle described by A.E. Housman in “Poem XXXII” of A Shropshire Lad (1896):
From far, from eve and morning
And yon twelve-winded sky,
The stuff of life to knit me
Blew hither: here am I.Now – for a breath I tarry
Nor yet disperse apart –
Take my hand quick and tell me,
What have you in your heart.Speak now, and I will answer;
How shall I help you, say;
Ere to the wind’s twelve quarters
I take my endless way. (ASL, XXXII)
Continue reading This Mortal Doyle…


