As pre-previously described on OotÜ-F, the English mathematician John Conway invented the Game of Life. It’s played on a grid of squares with counters. First you put counters on the grid in any pattern you please, random or regular, then you add or remove counters according to three simple rules applied to each square of the grid:
1. If an empty square has exactly three counters as neighbors, put a new counter on the square.
2. If a counter has two or three neighbors, leave it where it is.
3. If a counter has less than two or more than three neighbors, remove it from the grid.
There are lots of variants on Life and I wondered what would happen if you turned the grid into a kind of two-dimensional Pascal’s triangle. You start with 1 in the central square, then apply this rule to each square, [x,y], of the grid:
1. Add all numbers in the eight squares surrounding [x,y], then put that value in [x,y] (as soon as you’ve summed all other squares).
When a square is on the edge of the grid, its [x] or [y] value wraps to the opposite edge. Here’s this Pascal’s Life in action:
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0Pascal's square #1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 1 0 1 0 0
0 0 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0Pascal's square #2
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 2 3 2 1 0
0 2 2 4 2 2 0
0 3 4 8 4 3 0
0 2 2 4 2 2 0
0 1 2 3 2 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0Pascal's square #3
01 03 06 07 06 03 01
03 06 12 12 12 06 03
06 12 27 27 27 12 06
07 12 27 24 27 12 07
06 12 27 27 27 12 06
03 06 12 12 12 06 03
01 03 06 07 06 03 01Pascal's square #4
021 038 056 067 056 038 021
038 070 100 124 100 070 038
056 100 132 168 132 100 056
067 124 168 216 168 124 067
056 100 132 168 132 100 056
038 070 100 124 100 070 038
021 038 056 067 056 038 021Pascal's square #5
0285 0400 0560 0615 0560 0400 0285
0400 0541 0755 0811 0755 0541 0400
0560 0755 1070 1140 1070 0755 0560
0615 0811 1140 1200 1140 0811 0615
0560 0755 1070 1140 1070 0755 0560
0400 0541 0755 0811 0755 0541 0400
0285 0400 0560 0615 0560 0400 0285Pascal's square #6
2996 3786 4697 5176 4697 3786 2996
3786 4785 5892 6525 5892 4785 3786
4697 5892 7153 7941 7153 5892 4697
5176 6525 7941 8840 7941 6525 5176
4697 5892 7153 7941 7153 5892 4697
3786 4785 5892 6525 5892 4785 3786
2996 3786 4697 5176 4697 3786 2996Pascal's square #7
As you can see, the numbers quickly get big, so I adjusted the rule: sum the eight neighbors of [x,y], then put sum modulo 10 in [x,y]. The modulus of a number, n is its remainder when it’s divided by another number. For example, 3 modulo 10 = 3, 7 modulo 10 = 7, 10 modulo 10 = 0, 24 modulo 10 = 4, and so on. Pascal’s Life modulo 10 looks like this:
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0Pascal's square (n mod 10) #1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 1 0 1 0 0
0 0 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0Pascal's square (n mod 10) #2
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 2 3 2 1 0
0 2 2 4 2 2 0
0 3 4 8 4 3 0
0 2 2 4 2 2 0
0 1 2 3 2 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0Pascal's square (n mod 10) #3
1 3 6 7 6 3 1
3 6 2 2 2 6 3
6 2 7 7 7 2 6
7 2 7 4 7 2 7
6 2 7 7 7 2 6
3 6 2 2 2 6 3
1 3 6 7 6 3 1Pascal's square (n mod 10) #4
1 8 6 7 6 8 1
8 0 0 4 0 0 8
6 0 2 8 2 0 6
7 4 8 6 8 4 7
6 0 2 8 2 0 6
8 0 0 4 0 0 8
1 8 6 7 6 8 1Pascal's square (n mod 10) #5
5 0 0 5 0 0 5
0 1 5 1 5 1 0
0 5 0 0 0 5 0
5 1 0 0 0 1 5
0 5 0 0 0 5 0
0 1 5 1 5 1 0
5 0 0 5 0 0 5Pascal's square (n mod 10) #6
6 6 7 6 7 6 6
6 5 2 5 2 5 6
7 2 3 1 3 2 7
6 5 1 0 1 5 6
7 2 3 1 3 2 7
6 5 2 5 2 5 6
6 6 7 6 7 6 6Pascal's square (n mod 10) #7
7 5 3 3 3 5 7
5 9 5 1 5 9 5
3 5 1 7 1 5 3
3 1 7 6 7 1 3
3 5 1 7 1 5 3
5 9 5 1 5 9 5
7 5 3 3 3 5 7Pascal's square (n mod 10) #8
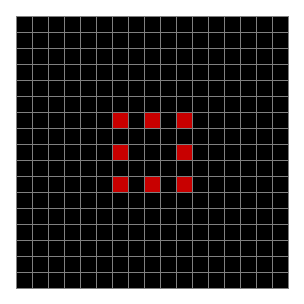
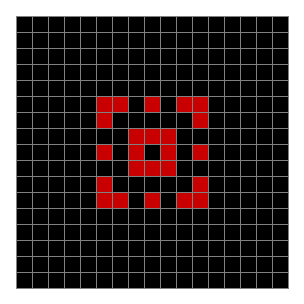
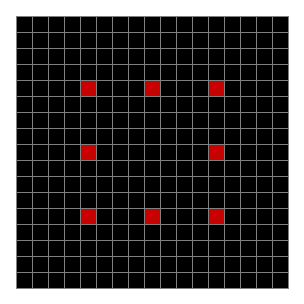
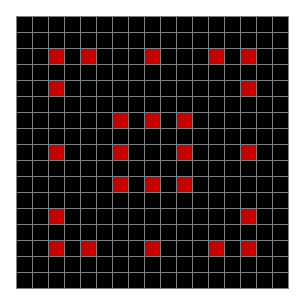
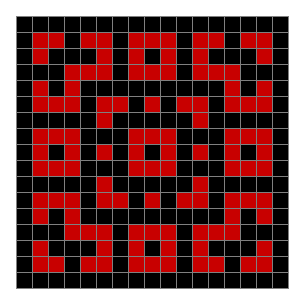
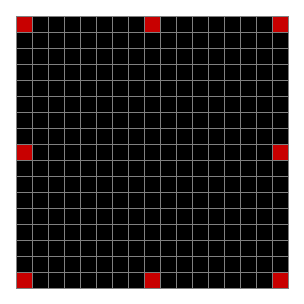
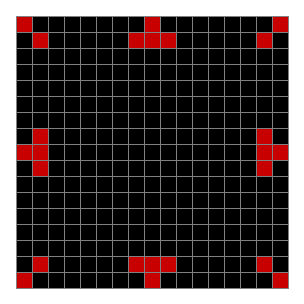
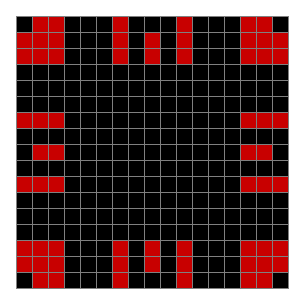
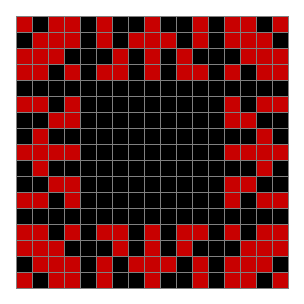
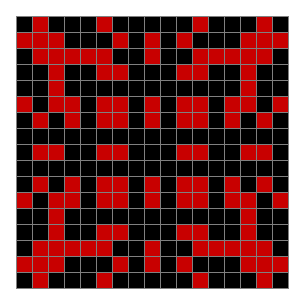
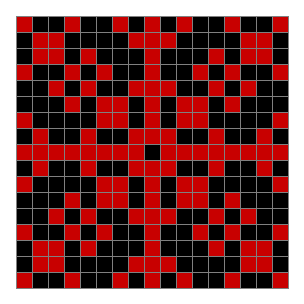
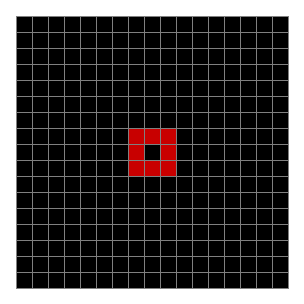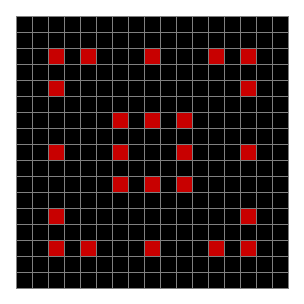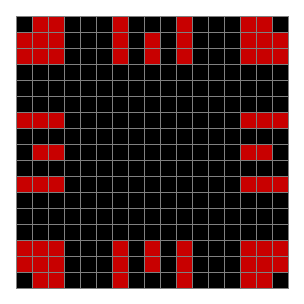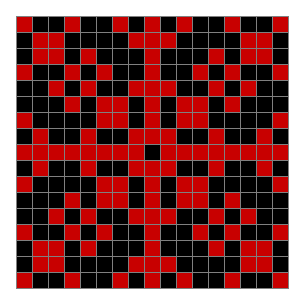
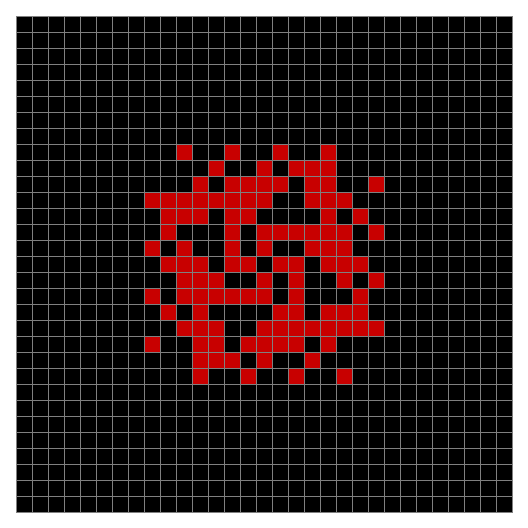
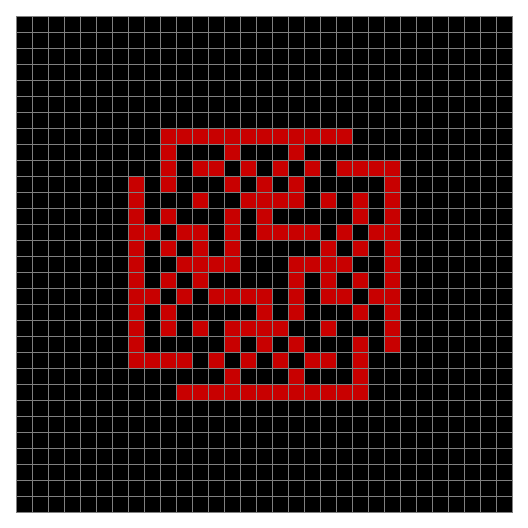
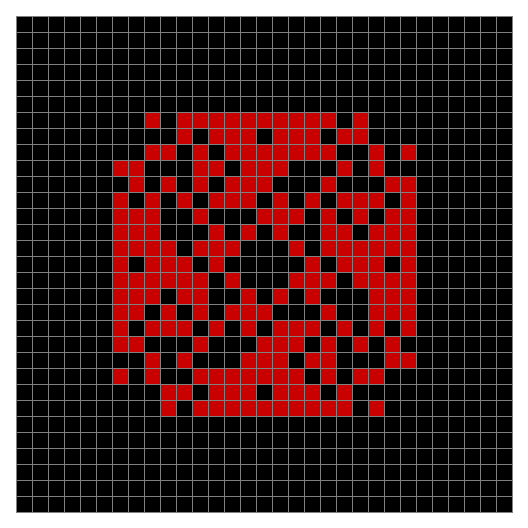
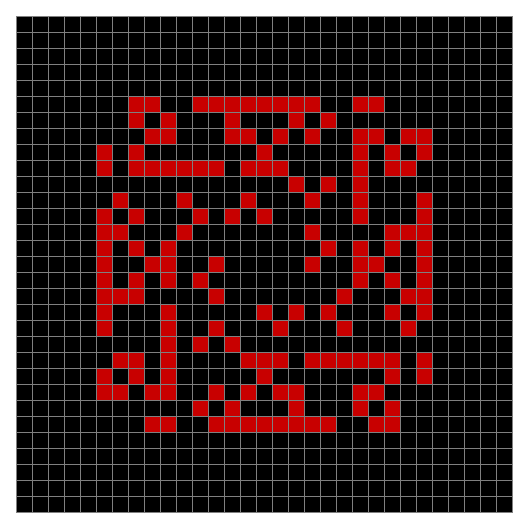
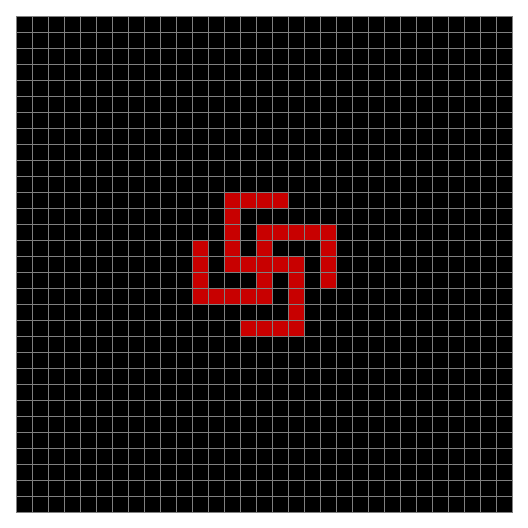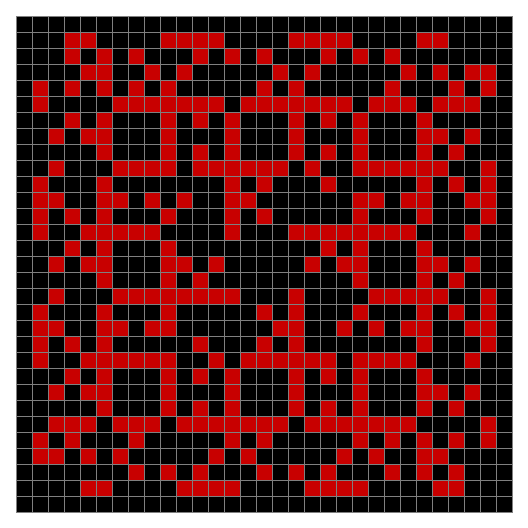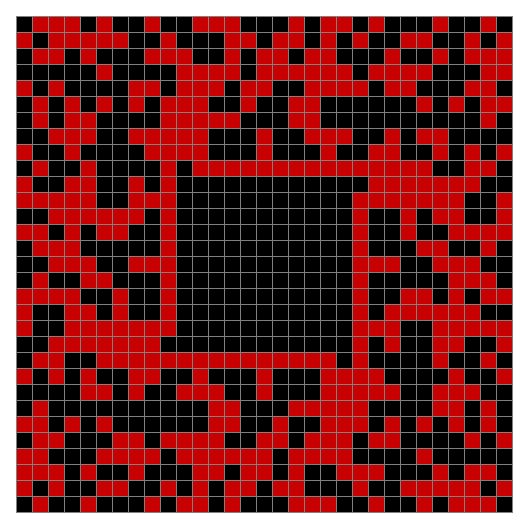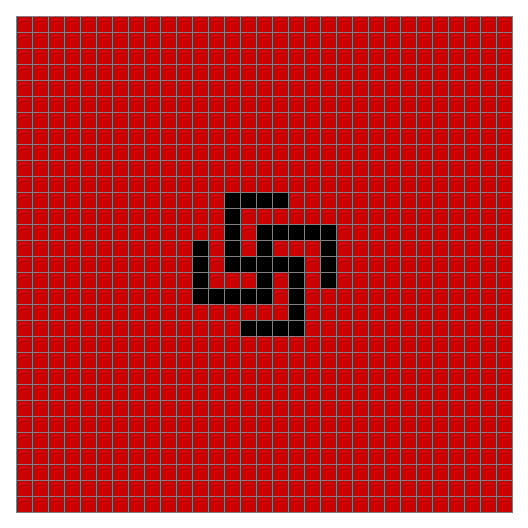
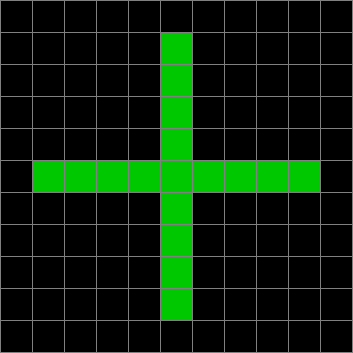
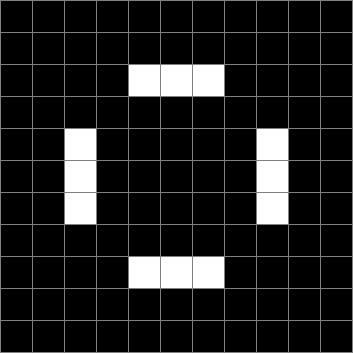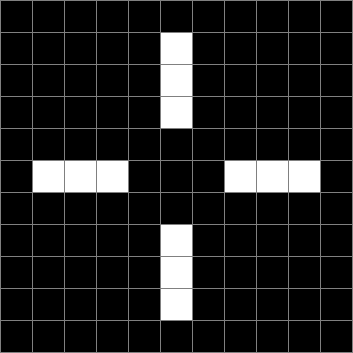
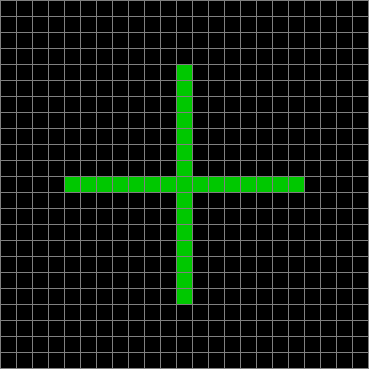
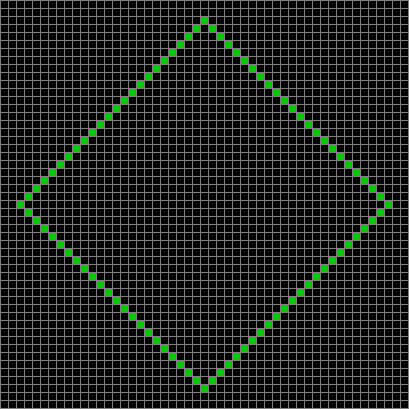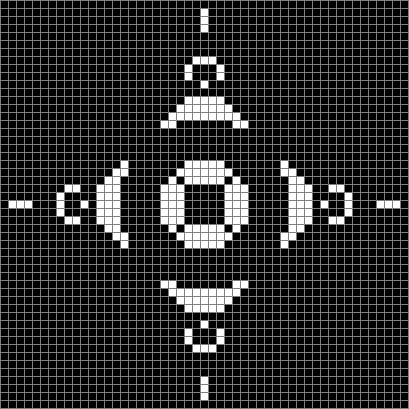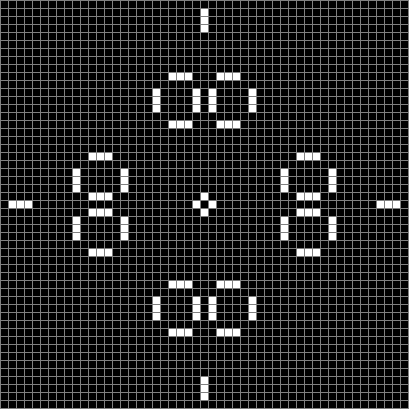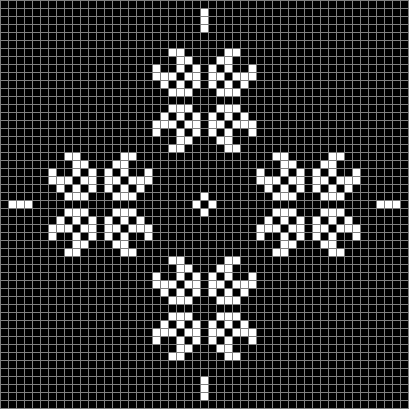
Now add graphics and use n modulo 2 (where all even numbers → 0 and all odd numbers → 1). If you start with a 17×17 square with a square pattern of 1s, you’ll see it evolve like this when 0s are represented in black and 1s are represented in red:
n mod 2 on 17×17 square #1
n mod 2 #2
n mod 2 #3
n mod 2 #4
n mod 2 #5
n mod 2 #6
n mod 2 #7
n mod 2 #8
n mod 2 #9
n mod 2 #10
n mod 2 #11
n mod 2 #12
n mod 2 #13
n mod 2 #14
n mod 2 #15
n mod 2 #16
n mod 2 (animated)
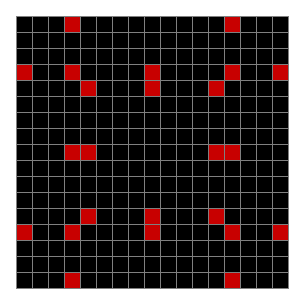
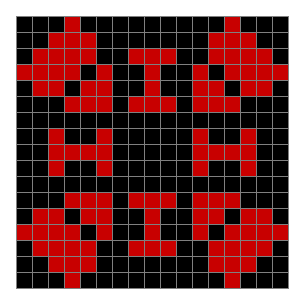
As you can see, the original square re-appears. So do other patterns. Here’s an animated gif for n modulo 2 seeded with a pattern of 1s spelling LIFE:
Now try a spiral as the seed:
Spiral with n mod 2 #1
Spiral with n mod 2 #2
Spiral with n mod 2 #3
Spiral with n mod 2 #4
Spiral with n mod 2 #5
Spiral with n mod 2 #6
Spiral with n mod 2 #7
Spiral with n mod 2 #8
Spiral with n mod 2 #9
Spiral with n mod 2 #10
Spiral with n mod 2 #11
Spiral mod 2 (animated)
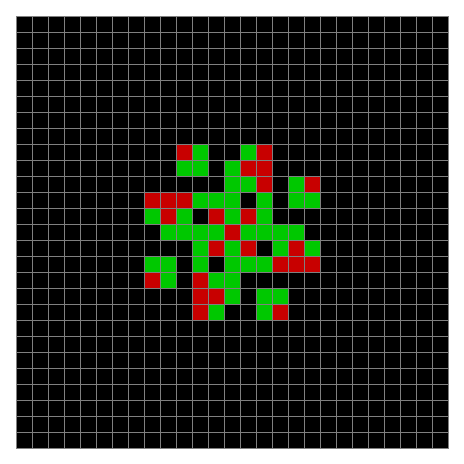
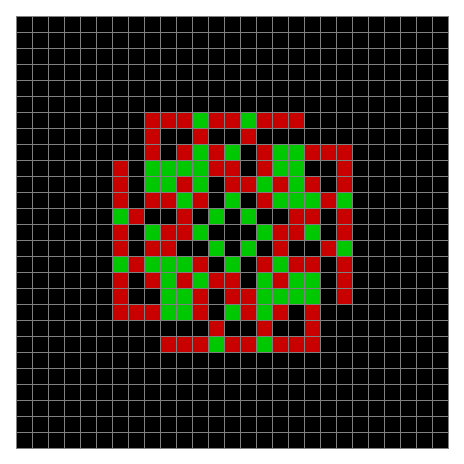
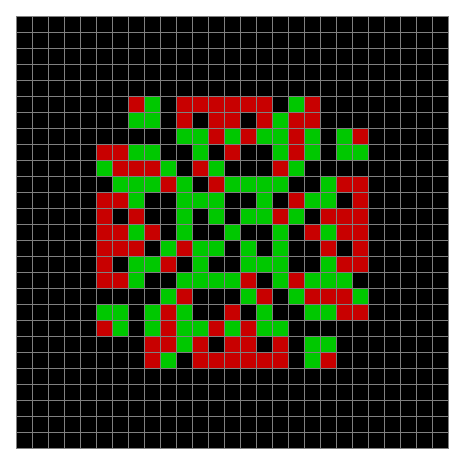
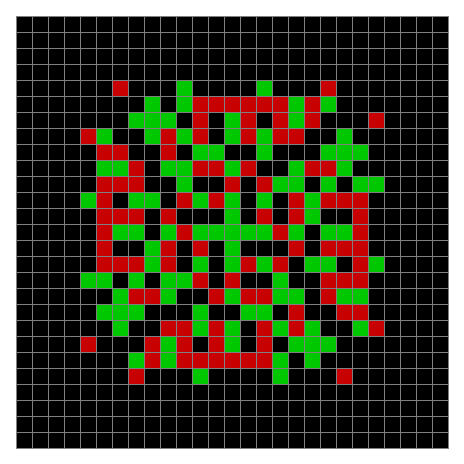
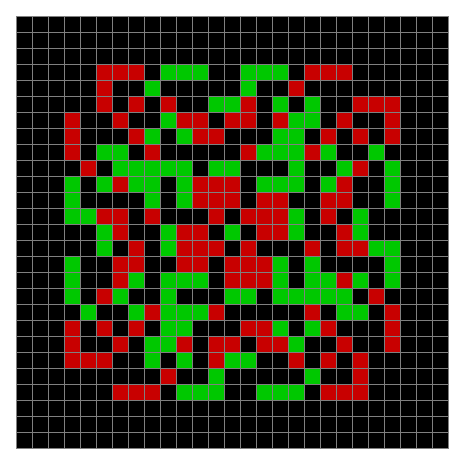
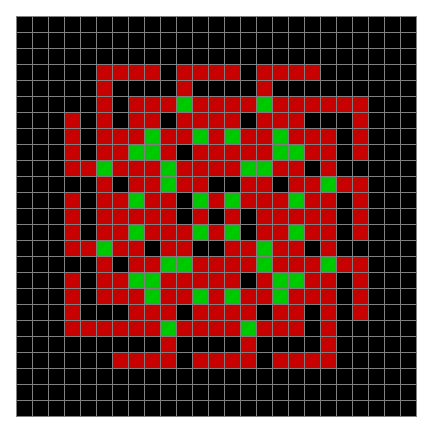
Now try the same pattern using modulo 3, where 0s are represented in black, 1s are represented in red and 2s in green. The pattern returns with different colors, i.e. with different underlying digits:
Spiral mod 3 on 27×27 square #1
Spiral mod 3 #2
Spiral mod 3 #3
Spiral mod 3 #4
Spiral mod 3 #5
Spiral mod 3 #6
Spiral mod 3 #7
Spiral mod 3 #8
Spiral mod 3 #9
Spiral mod 3 #10
Spiral mod 3 #11
⇓
[…]
Spiral mod 3 #19
⇓
[…]
Spiral mod 3 #28
⇓
[…]
Spiral mod 3 #37
⇓
[…]
Spiral mod 3 #46
Spiral mod 3 (animated)
LIFE mod 3 (animated)
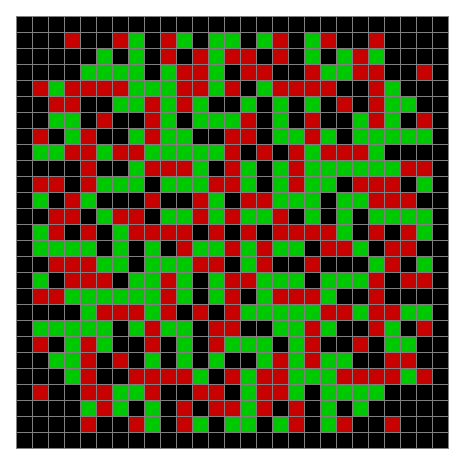
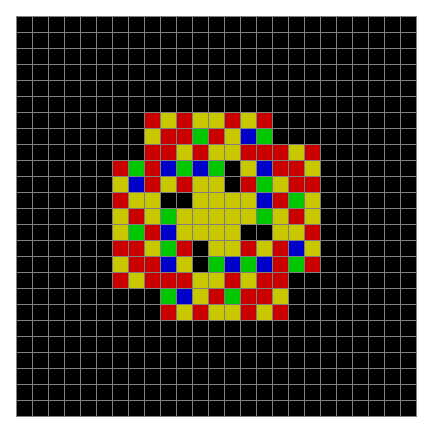
Now try n modulo 5, with 0s represented in black, 1s represented in red, 2s in green, 3s in yellow and 4s in dark blue. Again the pattern returns in different colors:
Spiral mod 5 on 25×25 square #1
Spiral mod 5 #2
Spiral mod 5 #3
Spiral mod 5 #4
Spiral mod 5 #5
Spiral mod 5 #6
⇓
[…]
Spiral mod 5 #26
⇓
[…]
Spiral mod 5 #31
⇓
[…]
Spiral mod 5 #76
⇓
[…]
Spiral mod 5 #81
Spiral mod 5 (animated)
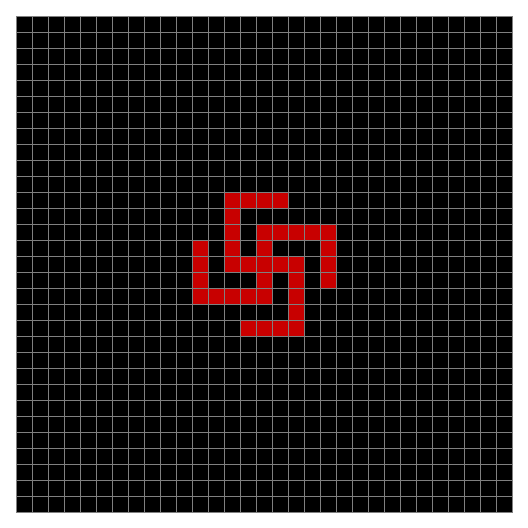
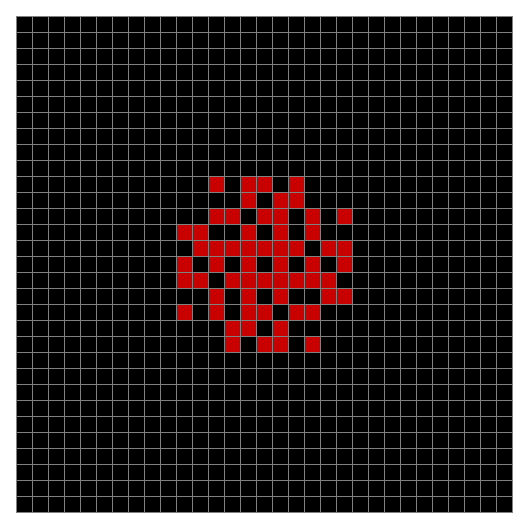
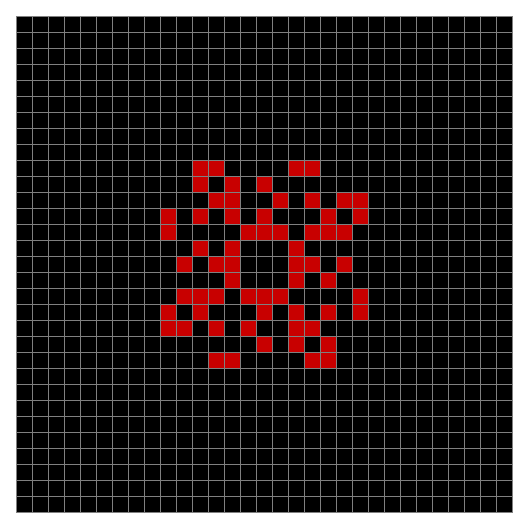
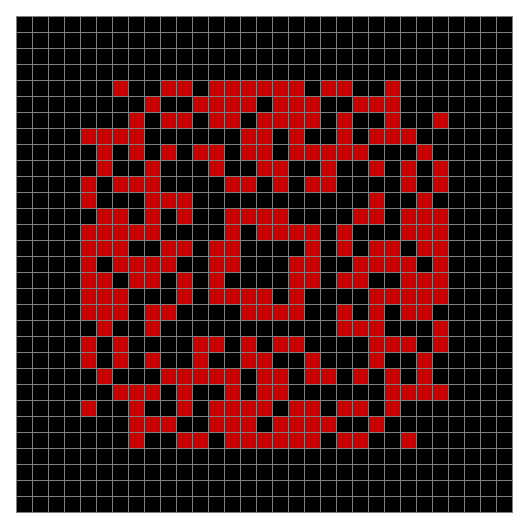
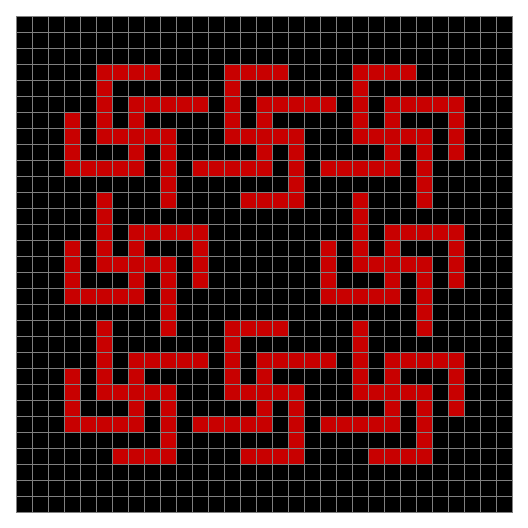
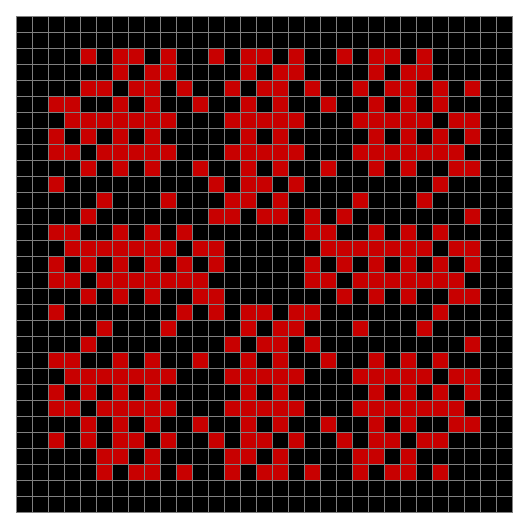
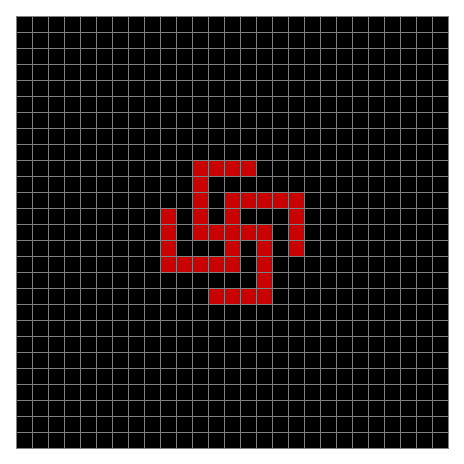
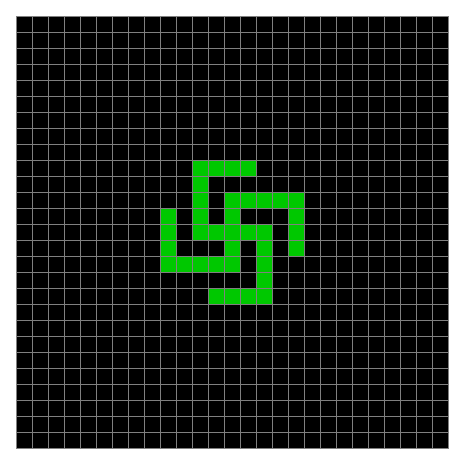
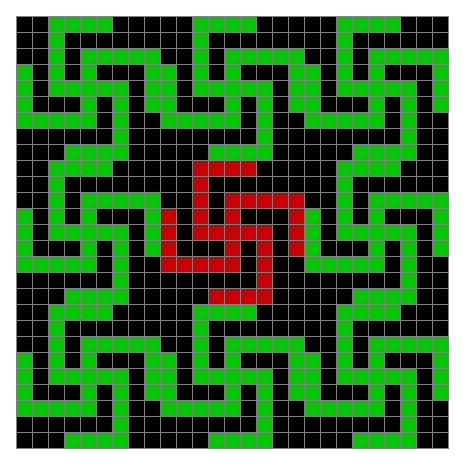
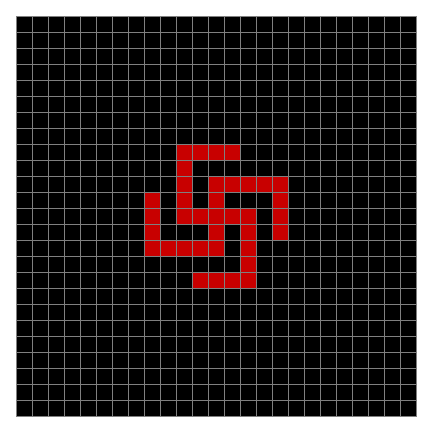
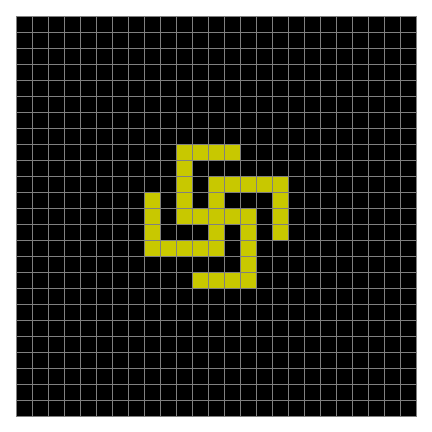
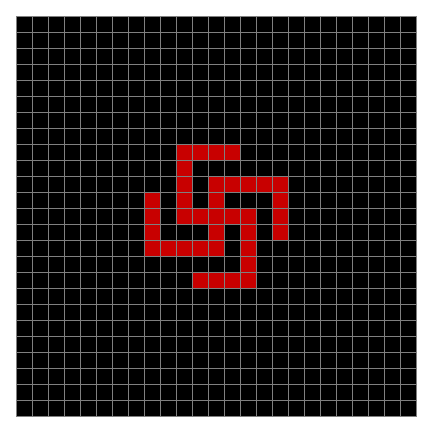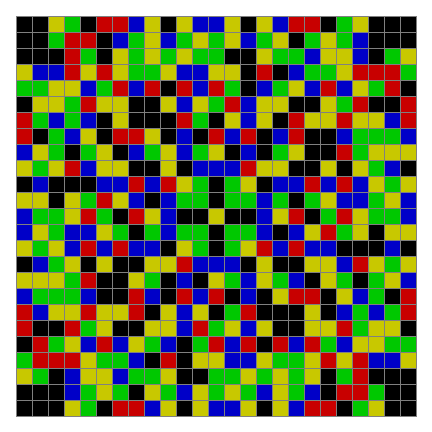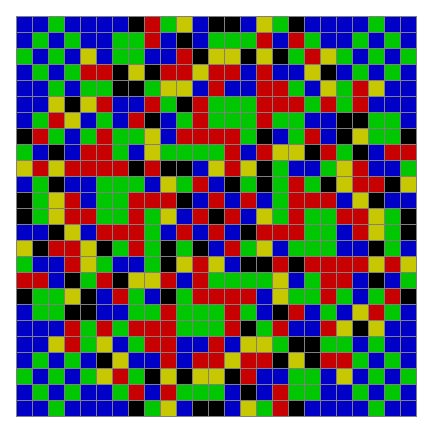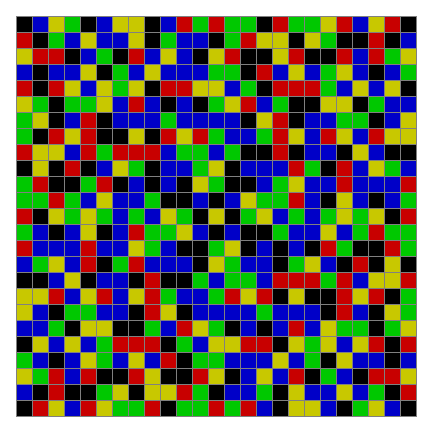
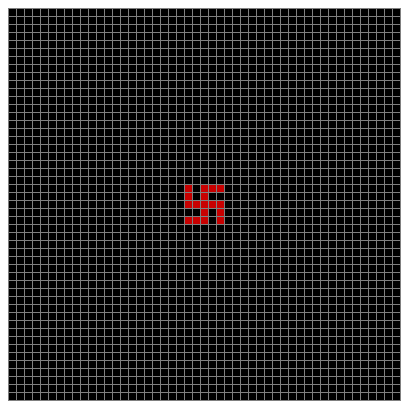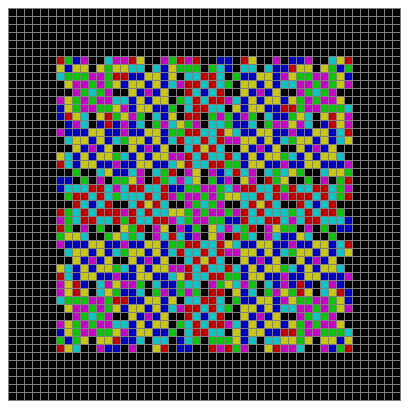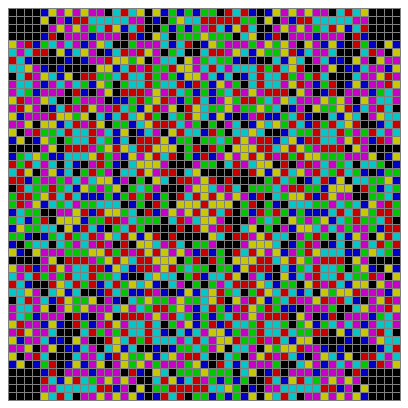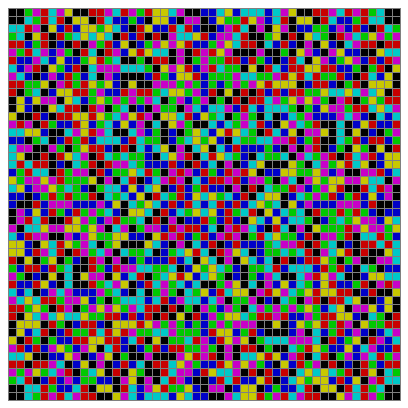
Finally, try a svastika modulo 7, with 0s represented in black, 1s represented in red, 2s in green, 3s in yellow, 4s in dark blue, 5s in purple and 6s in light blue:
Svastika mod 7 on 49×49 square #1
Svastika mod 7 #2
Svastika mod 7 #3
Svastika mod 7 #4
Svastika mod 7 #5
Svastika mod 7 #6
Svastika mod 7 #7
Svastika mod 7 #8
⇓
[…]
Svastika mod 7 #15
⇓
[…]
Svastika mod 7 #22
⇓
[…]
Svastika mod 7 #29
⇓
[…]
Svastika mod 7 #36
⇓
[…]
Svastika mod 7 #43
Svastika mod 7 (animated)
Previously Pre-Posted…
• Eternal LIFE — a first look at the Game of Life